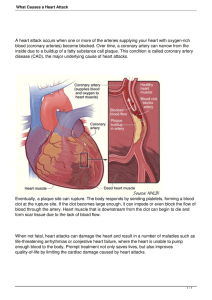
Myocardial infarction, commonly referred to as heart attack, is the sudden death of part of the heart due to the loss of blood flow. This occurs when one of the coronary artery – the arteries that supply blood to the heart – is blocked The blockage is commonly due the atherosclerosis – cholesterol plaques/ fat deposit on the wall of blood vessels. As the plaques builds up, the vessels become narrow, restricting blood flow. Under stress, the plaque may rupture. This triggers formation of blood clot on top of the plaque, leading to complete blockage of blood flow When this happens to a coronary artery, the downstream patch of the myocardium dies from lack of oxygen. Weaken heart muscle may disrupt electrical activity of the heart and subsequently cause cardiac arrest. Coronary angioplasty is a non-surgical procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It can also be performed as an emergency treatment for myocardial infarction The first part of the procedure is to localize the site of the blockage. This part is called cardiac catheterization. A guiding catheter is inserted through the femoral artery at the groin and threaded all the way to the aorta The tip of the catheter is placed at the beginning of the coronary artery to be investigated. A radio-opaque dye is injected through the catheter into the coronary artery. This enables real-time visualization of the artery using X-ray imaging A narrow part of an artery would appear as a bottle neck on an X-ray image. After the location of narrowed artery is identified, angioplasty can begin A guide wire with a deflated balloon is inserted and pushed to the location of blockage. The balloon is inflated to crush the plaque. At the end of the procedure, the balloon is again deflated and removed together will all catheter and guidewire. In some cases, a stent is inserted together with the balloon, inflated and left in place of the plaque to keep the artery open permanently. Angioplasty: tạo hình mạch/nong mạch Coronary artery: động mạch vành Atherosclerosis: xơ vữa Plaque: mảng Rupture: gián đoạn Blood clot: máu đông Myocardium: cơ tim Cardiac arrest: ngưng tim Catheterization: đặt ống thông radio-opaque dye: nhuộm cản tia X femoral artery: động mạch đùi