Water Cycle Explained: Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation
advertisement

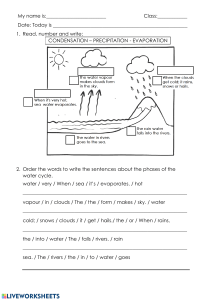
Water cycle: The water cycle is also known as the hydrological cycle. It is called a cycle because water continuously moves around the system. Rivers are part of this cycle. Water goes through three different stages in the water cycle It can be a liquid (water), a gas (water vapour) or a soild (ice) These three states are interchangeable, as water can freeze into ice or evaporate into water vapour, water vapour can condense as water, and ice can melt into water How does the water cycle work? Energy from the Sun heats the surface of the Earth. Water is evaporated from oceans, rivers, lakes, etc. The warm, moist air rises because it is less dense. Condensation occurs when water vapour is turned back into water droplets as it cools down. Clouds are formed. Precipitation occurs as water droplets get bigger and heavier they begin to fall as rain, snow and sleet, etc. When the precipitation reaches the surface, some falls directly into the sea but other water falls on land: Some water is intercepted by vegetation. Some water may then slowly reach the ground. Some will evaporate from the surface of leaves or be taken up by the plant roots, and some of this water will eventually return to the air as vapour through the process of transpiration. This slows down or prevents some water flowing back to the river. Some water flows across the surface of the ground - surface run-off. This happens when the surface doesn't allow water to penetrate. Surface run-off is more likely to occur if the ground is saturated with water or when the rock is impermeable. This water moves quickly to the river. Some water infiltrates into the soil. This through flow moves more slowly back to the river than surface run-off. Some water percolates deeper into the ground and is slowly transferred back to the river or sea. The water cycle process is driven by sun Evaporation: Evaporation is the process of liquid water’s (ocean, lakes, or rivers) surface changing to a gas (becomes water vapour) In shortly - Water is heated by the sun and turns into water vapour Condensation: It is the process when gas is changing into a liquid In water cycle, water vapour in the atmosphere condenses and becomes liquid Clouds form as water vapour condenses or becomes more concentrated (dense) Then, water vapour condenses around tiny particles called as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) CCN can be flecks of dust, salt, or pollutants Precipitation: Water returning to the ground as rain, sleet or snow Precipitation reaches the river by infiltration – seeps down through spaces in the soil, reaches permeable rock and flow or passes through gaps or pores within the rock In some areas precipitation reaches the river more quickly because, Down valley side slope speeding up surface runoff Less surface resistance of flow over the agriculture land especially where the field is ploughed down the slope In some areas precipitation reaches the river more slowly because, Large area of woodland at the top of slope to intercept rain Interception reduces runoff because of deforestation Permeable rock under the soil so that some can penetrate underground Surface run-off: It is where water flows downhill across the surface Surface run-off helps move elements(C, N, P, S) from terrestrial, land-based to aquatic ecosystems If trees were cleared and tourist resort built, the run-off would increase or no interception by leaves or stem (trees), therefore no absorption by roots concrete or surface not absorb Transpiration: It is the process by which plants lose water out of their leaves It is important in the water cycle because plants absorb the moisture from the soil and release it into the atmosphere as water vapour Interception Water is stoped from reaching the ground by trees and plants. It will propably be reduced after deforestation, because thre will be less vegetation to trap or intercept the rainwater Infilteration: It refers to water sinking into to the soil It is the downward movement of water from the land surface into the soil or porous rock Percolation: Rainfall seeps underground through a process called percolation, where water travels downwards through the tiny spaces between rocks and soil particles due to the force of gravity The water eventually saturates the underlying rock much like water fills the tiny holes of sponge. This helps to replenish aquifers under the ground