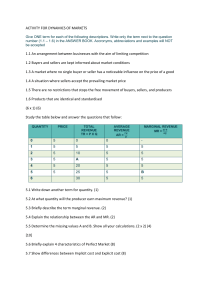
MARKET STRUCTURE What is a Market? • Place where there are many buyers and sellers actively engaged in buying and selling acts. Contact through different means of communication like internet, telephone etc. • Thus, It does not mean a particular place but the entire area where buyers and sellers of a commodity are in close contact and they have one price of same commodity. WHAT IS MARKET STRUCTURE? It is therefore understood as those characteristics of a market that influence the behavior and results of the firms working in that market. According to J.C. Edwards, “ A market is that mechanism by which buyers and sellers are bought together. It is not place.” necessarily a fixed • Perfect Competition • Monopoly • Monopolistic Competition • Oligopoly • It is such a market structure where there are large numbers of sellers and buyer producing Homogeneous product at the price of the product which is the determined by industry. • One price prevails in the market and all the firms sell the product at the prevailing price (which means price is fixed). • Fixed Price for a single seller Very Large number of sellers • Homogeneous product • No barriers to entry • Perfect knowledge of the market • Profit Maximization objective • Example: Agriculture Market • It is a market structure in which there is only a single seller of the product . • One firm has full control over the supply and price of the product . • Example : WAPDA • Monopolist is price maker • Unique Product • No close substitutes • Sole supplier of the product • Large number of buyers • One firm industry • Blocked entry • It is a mid-way between perfect competition and monopoly . • A type of market where large number of small sellers are selling differentiated products with some control over price. • Large number of small firms • Product differentiation • Freedom of entry and exit • Non price competition • Availability of Close substitutes • Some Control over price • Example: All type of Retailors (Like Boutiques , Shoe Market etc) • • It is a market structure in which there are few sellers of a product selling identical or differentiated products with price decision on collusion basis. • If they are selling identical products, it’s a case of Pure Oligopoly. • If they are selling differentiated products, it’s a case of Differentiated Oligopoly . • Relatively small number of Large sellers • Interdependence of the firms • Price rigidity and price war • Difficulty in entry and exit • Collective price decision of all sellers • Examples: Pakistan Telecommunication Authority • OPEC (Oil Petroleum Exporting Countries ) etc. MONOPSONY A monopsony is a market condition in which there is only one buyer. Because there is only one buyer for a good or service, the buyer sets the demand, and therefore, controls the price. DUOPOLY A situation in which exactly two suppliers dominate the market for a commodity or service. ??????????? Question