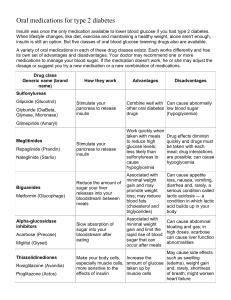
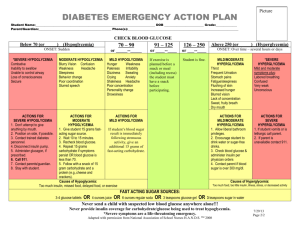
HYPOGLYCEMIA IN DIABETIC PATIENT PRESENTED BY : االء عبدهللا محمد علي فاطمة محمد يوسف الساقزلي مبروكة نصر الوقاع رتاج احسين اوحيدة ايناس OUR GOALS : ➢ Presenting the Case Scenario ➢ Answer the possible questions ➢ Introduction of hypoglycemia ➢ management ➢ prevention THE CASE Dania. 7yrs old, known case of type I DM for 3yrs, she is on Novo rapid pre meal and 14 fU Lantus once at morning she presented to the casualty last night because of abnormal movement. At afternoon Dania visited her grandma, when she came back to home she started to complain from headache, she became pale, sweaty then developed tonic convulsion involved LT upper limb associated with rolling up of her eyes and bluish discoloration of lips, mam gave her some honey and convulsion stopped, mam did not record blood sugar at that time, this event lasted for about 2 min followed by lethargy and sleep. No history of fever, no vomiting or diarrhea, No palpitation or blurred vision, no previous history of head trauma. Mam explained this attack by heavy exercise. . QUESTION : Q.1 Q.2 Q.3 Q.4 What are the information’s should be taken in the history ? What could be D/D her condition ? How to manage hypoglycemic attacks in diabetic patients ? Mention one of emergency treatment could be used in this situation ? . Q.1 WHAT ARE THE INFORMATION’S SHOULD BE TAKEN IN THE HISTORY ? ● last time eat or take insulin before the attack ? ● blood sugar measurements before and after attack? ● When she went to her grand mother • take extra dose insulin • who gave the routine dose ? •Adjustment of the does to exercise and playing • change diet or missed meal ? • Matching with food? • measure the blood suger after attack in afternoon? ● change in diet or medication regimen recently? ● change in exercise routine recently? ● experience any symptoms before and attack such as .. Sweating ,shaking, dizziness, pallor? ( to exclude Hypoglycemia symptoms ) ● other symptoms such as Polyuria Polydipsia, Vomiting ,Abdominal pain ,Cozumel breathing ( to exclude DkA symptoms) ● other symptoms such as Generalized or localized abnormal movement, unrolling eye, forty secretion from mouth • headache ,photophobia , projectile Vomiting ( to exclude cns symptoms) . Q.1 WHAT ARE THE INFORMATION’S SHOULD BE TAKEN IN THE HISTORY ? PAST MEDICAL : ●Dm (H\o Admitions \ ICU ) • Drug names • doses • Route • change site of administration • given by who? • eating after • regular meals and snaks, healty diet ● S\E • Episodes of low blood sugar in the past ? if yes what’s the trigger? • H\o DKA ● Adjustment of the insulin to heavy exercises and illness ● Educated on how to recognize and treat hypoglycmia ● Regular monitering of blood sugar ● How to use glucometer ● Regular follow up ● Psychological impact of DM in patient and parents ● school preference ● outcome of parents ● other medical conditions ● family history of chronic disease Q.2 WHAT COULD BE D/D OF HER CONDITION? ❑ Hypoglycemia (most likely) ❑ epilepsy ❑ meningitis ❑ stroke ❑ Brain tumor ❑ cerebral edema Q.3 Q.3 ? How to manage hypoglycemic attacks in diabetic patients How to manage hypoglycemic attacks in diabetic Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, adipiscing elit patients ? ➢ WHAT'S HYPOGLYCEMIA ? Hypoglycemia is a condition that occurs when the blood glucose level in a diabetic patient drops below normal levels (CHILD less than 70 mg/dL) , neonate according to age and sex (less than 40mg/dl) This can happen due to various reasons such as 1-taking too much insulin or other diabetes medications, skipping meals, exercising excessively. 2- Growth hormone deficiency 3-hypothyroidism 4-insulimoma 5-addison disease Symptoms of hypoglycemia include sweating, shaking, dizziness, confusion, irritability, pallor, abnormal behavior and weakness. If left untreated, severe hypoglycemia can lead to seizures, loss of consciousness or even death Note: Diabetic patients are advised to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly and take appropriate measures to prevent hypoglycemia . ●Diagnosis: ✓ Clinically( presence of symptoms ) ✓ Investigation : 1-blood glucose montring (Gluometer,laboratory) 2-hormone: insulin, growth hormone ,sex hormones (androgen,estrogen,progesterone), TFT,cortisol 3- c-peptides level 4-urine anylsis 5-serum for ketone body and FFA 6- Imaging tests: In some cases, MRI or CT scans may be used to investigate if there is an underlying condition such as a tumor or pancreatic disease causing hypoglycemia. MANAGEMENT DEPEND ON : Conscious level severity Q.3 How to manage hypoglycemic attacks in diabetic patients ? ❑ IN CONSCIOUS PATIENT (MILD TO MODERATE ) ➢ ROLE OF 15 WE NEED APPROXIMATELY 15 GRAMS OF GLUCOSE TO CORRECT HYPOGLYCEMIA ➢ TAKE AT LEAST ½ CUP FRUIT JUICE , 3 SPOONS OF SUGAR IN GLASS OF WATER OR SPOON OF HONEY. ➢ 3 GLUCOSE TABLETS ➢ AFTER 15 MINUTES, CHECK YOUR BLOOD SUGAR AGAIN AND REPEAT A DOSE OF FAST-ACTING CARBOHYDRATES 2 OR 3 UNTIL BLOOD GLUCOSE INCRESASE TO >70MG/DL ➢ ONCE BLOOD GLUCOSE IS NORMALIZED ,CONSUME SNAK AND MEAL CONTANING COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES AND PROTEIN IN ORDER TO AVOID RECURRENCE OF HYPOGLYCEMIA Q.3 How to manage hypoglycemic attacks in diabetic patients ? ❑ IN UNCONSCIOUS PATIENT (SEVER) (EMERGNCY) ●ADMISSION ●CALL FOR HELP ●AIRWAY ●BREATHING ●CIRCULATION ➢ IF INTRAVENOUS ROUTE IS OPEN ▪ *ADMINISTER OF 10% DEXTROSE IV OVER 1-3 MINUTES IN INFANT , 25% DEXTROSE IV IN CHILD *REPEAT THE BLOOD GLUCOSE TEST AFTER 5MINUTES ▪ *IF BLOOD GLUCOSE IS STILL 70 MG/DL, RE- ADMINISTER THE DOSE AND CHECK SUGAR USING FINGERTIP WITHIN 5 MINUTES *REPEAT THE PROCEDURE UNTIL THE GLUCOSE LEVEL >70 •MG/DL ➢ NO INTRAVENOUS ACCESS ▪ ADMINISTER 1 MG OF GLUCAGON SUBCUTANEOUSLY OR INTRAMUSCULARLY ▪ REPEAT THE BLOOD GLUCOSE TEST AFTER 15MINUTES ❖ IF BLOOD GLUCOSE IS STILL 70 MG/D, RE-ADMINISTER THE DOSE, AND CHECK GLUCOSE USING FINGERTIP WITHIN 15 MINUTES, REPEAT PROCESS UNTIL GLUCOSE LEVEL >70 MG/DL. ❖ PREVENTION ➢ monitor blood sugar levels regularly and keep them within the target range ➢ inform family and friends about hypoglycemia and what symptoms to look for so they can alert you to early symptoms ➢ Great effort must be invested in patient education on hypoglycemia prevention and management ➢ Education about adjustment of the insulin doses before heavy exercise THANK YOU