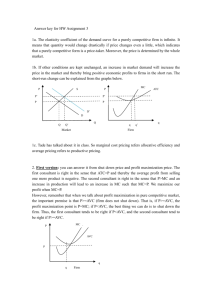
Quiz 3 1. List the characteristics of the four different types of market structures discussed in class and give an example of each. Answer: Perfect Competition The characteristics of Perfect Competition are as follows• Many Buyers and Sellers in the Market • Products sold are identical • Easy to Enter the Market Example: Staple foods, daily goods, etc. Monopoly Competition The characteristics of Monopoly Competition are as follows• One firm operating in the market • Products sold are differentiated • Difficult to enter the market Example: WASA, Titas Gas, DESCO, etc. Monopolistic Competition The characteristics of Monopolistic Competition are as follows• Many Buyers and Sellers in the Market • Products sold are differentiated • Easy to Enter the Market Example: Restaurants, hair salons, beauty industry, clothing store, etc. Oligopoly Competition The characteristics of Oligopoly Competition are as follows• Few firms operating in the market • Products sold may be are differentiated • Difficult to enter the market Example: Telecommunication, aviation, gold suppliers, etc. 2. Suppose you start a business of manufacturing computer software. Assume that this computer software company is a perfectly competitive firm. Your fixed cost per month is Tk. 40,000 and total cost is Tk. 120,000. You sell 100 software per month and average revenue is Tk. 80, what should be your shortrun decision regarding shut down and long-run decision regarding exit? Answer: Given, Total Cost, TC = Tk. 120000 Fixed Cost, FC = Tk. 40000 Quantity, Q = 100 Price (P) = Average Revenue (AR) = Tk. 80 Now, Average Total Cost, ATC = Tk. (120000/100) = Tk. 1200 Average Fixed Cost, AFC = Tk. (40000/100) = Tk. 400 Average Variable Cost, AVC = Tk. (1200 - 400) = Tk. 800 As, AVC > P, the firm will shut down in short-run decision. And, Average Total Cost, ATC = TC/Q = Tk. (120000/100) = Tk. 1200 As, ATC > P, the firm will exit in the long-run decision. 2nd Method: Total Revenue, TR = P x Q = Tk. (80 x 100) = Tk. 8000 Variable Cost, VC = TC – FC = Tk. (140000 – 40000) = Tk. 80000 As, TR < VC, the firm will shut down in short-run decision. And, Total Revenue, TR = P x Q = Tk. (80 x 100) = Tk. 8000 As, TR < VC, the firm will exit in the long-run decision. 3. On x and y axes, draw ATC, AVC, and MC curves and four alternative demand curves that the Perfectly Competitive Firm might face. a) Draw D1 such that the firm makes a profit. Answer: b) Draw D2 such that the firm breaks even (profit = 0). Answer: c) Draw D3 such that the firm is at its shut down point. Answer: d) Draw D4 such that the firm would shut down rather than produce. Answer: