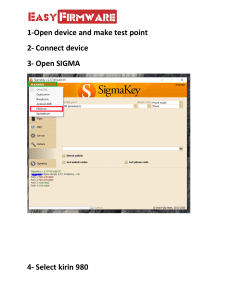
LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis The transmit filter is not ideal, and therefore the transmitter out-of-band leakage, harmonic emission, parasitic emission, intermodulation products, and frequency conversion products fall into the band of another system. Consequently, the noise floor of other systems increases, causing sensitivity deterioration. Spurious interference is generated by a transmitter and includes the thermal noise generated and amplified by the power amplifier (PA). Spurious interference is intermodulation products generated during multi-carrier operating, and spurious signals are generated by frequency mixer. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis The receive filter is not ideal, and therefore it does not completely suppress out-of-band signals but receives out-of-band signals with certain strength. If the strength of the out-ofband signals is strong enough, these signals will be received by the receive filter, causing interference. Blocking interference is generated mainly because of component non-linearity, which causes multi-order intermodulation and crossmodulation products. In addition, blocking interference is caused by the limited dynamic range of the receiver. If blocking interference persists for a long time, the receiver performance may deteriorate permanently. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis ACLR refers to the ratio of transmit signals' power on the local channel to the power of leak signals on the adjacent channel. A small frequency spacing causes certain power leakage to the adjacent frequency. Therefore, interference occurs. This type of interference is similar to spurious interference, but its frequency spacing is much smaller. Receive interference: Total power of interfering signals – ACLR Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis ACS is a counter used to measure the receive filter and represents the ratio of the receiver filter suppression on the local channel to that on adjacent channels. ACS indicates the capability of the receive filter receiving signals from effective channels. Due to a small frequency spacing, some local channels receive power from some adjacent channels, causing interference. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Interference is one of the key factors that affect network quality. The most direct impact is sensitivity deterioration, thereby causing a decrease in the coverage radius and throughput rate. The impact of sensitivity deterioration on the capacity can be obtained based on simulation. The theoretical analysis can provide only assessment at fixed points, and the impact on the throughput rate depends on the actual scenarios. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Commonly inter-eNodeB interference: Spurious interference Blocking interference Intermodulation interference Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Interference between an eNodeB and a UE (same-band adjacent-channel interference) cannot be accurately calculated based on the theoretical analysis method due to the following causes: unfixed UE locations, diversified services and UEs, and scheduling factors. During analysis on interference between an eNodeB and a UE, theoretical analysis functions only as a supplementary method (single point analysis), for example, check whether coverage holes exist and whether the service rate of cell edge users is normal, and know coverage changes in co-site scenarios. Simulation analysis is a type of systematic analysis method and can be used to simulate different UE behaviors. Therefore, the calculation result is close to the actual situation. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis The figure in this slide shows the main factors that cause LTE network interference. The words in red apply only to LTE TDD networks, and other words apply to both LTE FDD and LTE TDD networks. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis LTE TDD networks use the time duplex mode, and therefore have strict requirements on system clock synchronization. If the clock of eNodeB A is not synchronized with that of adjacent eNodeBs, downlinks signals of eNodeB A will be received by adjacent eNodeBs, causing interference to uplink signal receiving of adjacent eNodeBs. In most cases, out-of-frame is caused by clock system faults, such as GPS out-of-lock. Interference caused by GPS out-of-synchronization has a severe impact in a large scale. eNodeB with GPS out-of-synchronization may cause interference to multiple eNodeBs surrounding it. If this happens, UEs served by these eNodeBs cannot perform services. In severe cases, UEs cannot access the network under these eNodeBs even if the RSRP is good. In this case, the uplink RSSI of these eNodeBs may be 10 dB to 20 dB (or much higher) higher than the normal value. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis The guard period in the special subframe specifies the minimum distance that downlink signals cannot cause interference to uplink signals. The GP lengths listed in the following table can be used to calculate the protection distance, which ranges from 21.4 km to 214.3 km. If the radio propagation environment between eNodeBs is good and the GP for the special subframe is small, TDD super-distance interference occurs. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Measurement point for counters in the table above: Within each TTI, the system measures the total power of noise floor and neighboring cell interference on each PRB, and the measured value is used as a sample result. For SFN cells, the interference power of each PRB in all physical cells must be measured. The maximum sampling result in a measurement period is used as the maximum PRB-level interference noise detected on uplink PRBs. The average value of the sampling results is used as the average PRB-level interference noise detected on uplink PRBs. The minimum sampling result is used as the minimum PRB-level interference noise detected on uplink PRBs. Measurement point for the counter in the table below: The system detects the total power of UpPTS interference and noise that are received by specified RRUs in every 2 seconds and then average the detection results. The averaged power of interference noise for each PRB is used as a sampling result. The average value of sampling results in a measurement period is the value of this counter. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis You can check whether the uplink interference exists according to the RSSI. When using this method to determine uplink interference, ensure that no UE accessing the network exists in the sector to be detected. If the sector receives UE signals, the RSSI will be high. In this case, check the difference between main and diversity RSSIs to determine interference. Generally, the difference within 5 dB is considered normal. Receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) indicates the in-band total signal strength. Theoretically, RSSI can be calculated using the following formula: RSSI = –174 dBm/Hz + 10 x log10(BW) + NF + AD quantitative error Read the RSSI when the sector does not serve any UEs or in off-peak hours by disconnecting all UEs. In multiple receive channel mode, frequency scanning can be simultaneously performed on all receive channels. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Generally, the TDD eNodeB has a greater noise factor than that of the FDD eNodeB. Therefore, the RSSI in LTE TDD networks is higher than that in LTE FDD networks. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Generally, OOF interference is caused by GPS problems or incorrect parameter configuration (such as: TDDFRAMEOFFSET). Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis The RSSI can be detected on the gateway, as shown in the following figure. Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission LTE Network Interference Analysis Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without Permission