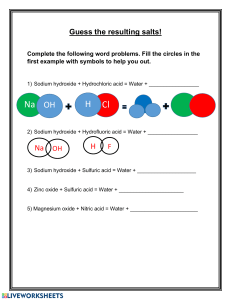
Grade 11 Chemistry Review: The Mole, Chemical Reactions, and Chemical Reaction Calculations 1. Write balanced chemical equations for the following chemical reactions: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Potassium metal reacts with chlorine gas to produce solid potassium chloride. Heated copper metal reacts with chlorine gas to produce copper (II) chloride. magnesium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid = magnesium chloride + water Solid lithium oxide reacts with water to give a solution of lithium hydroxide. Solid barium oxide reacts with water to give a solution of barium hydroxide. When calcium hydroxide is heated, calcium oxide and water vapour are produced. Aqueous calcium hydroxide reacts with aqueous magnesium chloride to produce a precipitate of magnesium hydroxide and a solution of calcium chloride. 2. Balance the following equations. What type of reaction is each? a) b) c) d) e) f) K + F2 KF Ca + H 20 Ca(0H)2 + H2 NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 NH3 + ZnO + HCl ZnCl2 + H20 CuSO4 + Fe Fe2(S04)3 + Cu Cu2S + 02 Cu2O + 502 H20 + CaCl2 3. Balance these equations and classify the reactions as exothermic or endothermic. What type of reaction are they? a) C12(aq) b) Mg(s) c) energy + d) C8H18(l) + + KI(aq) 02(g) NaClO3(s) + 02(g) KCl(aq) + MgO(s) NaCl(s) + C02(g) I2(aq) + + energy 02(g) + H20(g) energy + 4. Predict the products and write the balanced equation for each of these reactions. Synthesis/ Combination: a) Sr(s) + 02(g) b) Na(s) + 02(g) c) d) Decomposition: a) MgBr2(l) b) AlCl3(l) c) H20(l) d) KI(l) Single replacement: a) Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) b) C12(g) + KI(aq) e) Zn(s) + Ni(N03)2(aq) c) Ni(s) + MgSO4(aq) d) Br2(aq) + CaCl2(aq) f) Zn(s) + MgSO4(aq) Double replacement: a) FeCl2(aq) + K2S(aq) b) AlCl3(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) e) KCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) Ca(s) + F2(g) K(s) + C12(g) c) ZnSO4(aq) + SrCl2(aq) d) (NH4)2S04(aq) + BaCl2(aq) energy Percentage composition, Empirical formula, and Molecular formula: 1. The following chemicals are used as colourants for ceramic glazes. Find the percentage composition of each. a) cobalt (II) carbonate, which produces a blue glaze colour b) barium chromate, which produce colours in the yellow to light green range c) iron (III) chloride hexahydrate, which produces an iridescent gold colour 2. Determine the empirical formula that corresponds to each of the following percentage compositions. a) 7.2% phosphorous, 92.8% bromine b) 19.0% tin, 81.0% iodine c) 36.5% sodium, 25.4% sulfur, 38.1% oxygen 3. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) has a molar mass of 180 g/mol. And contains 60.02% carbon, 4.44% hydrogen, and 35.54% oxygen by mass. Find the molecular formula of this substance. 4. When 7.59g of an oxide of manganese is heated, 3.76h of manganese metal is obtained. What is the empirical formula of this compound? 5. A compound containing only carbon and hydrogen was burned and the water produced was condensed and collected. From a 0.436g sample of the compound, 0.478g of water was obtained, together with an undetermined amount of carbon dioxide. What is the empirical formula of the compound? If the molar mass of the compound is 82.1 g/mol, what is its molecular formula? Mole calculations: 6. Calculate the number of grams of sodium oxide that will be produced when 5 moles of sodium react with oxygen gas. (155g) 7. For this reaction, answer the questions that follow: Cu(s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag(s) a) How many grams of copper are required to displace 9.35g of silver from the solution of silver nitrate? (2.75g) b) If 5.50g of silver are produced in the above reaction, how many moles of copper were reacted? (0.0255 mol) 8. Calculate the number of grams of solid sodium oxide that will be produced when 115g of solid sodium react with oxygen gas. (155 g) 9. If 1.21 moles of solid zinc are added to 2.65 moles of hydrochloric acid, then zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are formed. Determine which reactant is in excess and by what amount, and calculate the number of moles of each product. (2.43 mole hydrochloric acid required, 1.21 mol of hydrogen gas and 1.21 mole of zinc chloride)