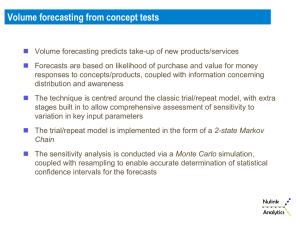
Planning & Forecasting Advanced Organizer Managing Engineering and Technology Management Functions Planning Decision Making Organizing Leading Controlling Managing Technology Personal Technology Research Time Management Design Ethics Production Career Quality Marketing Project Management Advanced Organizer Managing Engineering and Technology Management Functions Planning Decision Making Organizing Leading Controlling Managing Technology Personal Technology Research Time Management Design Ethics Production Career Quality Marketing Project Management Chapter Objectives • • • • • • • • Explain the importance of planning Identify missions and vision Explain the roles of goals and objectives Identify strategies a planning Define the different types of forecasting Define different approaches to forecasts Solve forecasting problems Discuss some strategies for managing technology Importance of Planning • Provides method for identifying objectives • Designs sequence of programs and activities to achieve objectives Effective Planning • Plan to plan • People implementing plan should be involved in preparing plan Nature of Planning Deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who is to do it. --Amos & Sarchet Planning/ Decision-Making Process 1. Recognize Problem / Opportunity 2. Define Goals/Objectives Overall Mission / Objectives 3. Assemble Relevant Data 5. Select the Criterion 4. Identify Feasible Alts 6. Construct a Model 7. Predict Alts’ Outcomes 9. Audit the Results 8. Choose the Best Alt. The Foundation for Planning • Mission/Vision • Goals and Objectives • Strategies All Customer Driven Planning: Mission Statement • First step in planning process • The mission statement answers the following questions: Who we are? Who are the customers? What we do? and How we do it? • This statement is usually one paragraph or less in length, is easy to understand, and describes the function of the organization. Mission – Pal’s To deliver excellence in food service while providing a menu focused on exceptional quality. Mission Example The mission of Southwest Airlines is dedication to the highest quality of Customer Service delivered with a sense of warmth, friendliness, individual pride, and Company Spirit. http://www.southwest.com 9/9/05 Mission Example At Microsoft, our mission and value are to help people and businesses throughout the world realize their full potential. http://www.microsoft.com/about/default.mspx#values Mission Example Florida International University is an urban, multicampus, research university serving South Florida, the state, the nation and the international community. It fulfills its mission by imparting knowledge through excellent teaching, promoting public service, discovering new knowledge, solving problems through research, and fostering creativity. http://www.fiu.edu/docs/fiumission_statement.htm Vision • A vision statement describes in graphic terms where the goal-setters want to position themselves in the future. • A statement of how someone wants the future to be or believes it will be; it is used to set direction for an organization. --“Information Systems Management in Practice” by B.C. McNurlin Vision Example “To Be the World's Preferred Chemical Company” -- Eastman Chemical Company "A personal computer on every desk, and every computer running Microsoft software." --Microsoft (1980’s) Vision Example We will be the preferred provider of safe, reliable, and cost-effective products and services that satisfy the electric-related needs of all customer segments. -- Florida Power & Light Co. Top Urban Public Research University. -- Florida International University Mission/Vision Example Our Mission • Sustainable Growth: The creation of shareholder and societal value while we reduce our environmental footprint along the value chains in which we operate. Our Vision • To be the world's most dynamic science company, creating sustainable solutions essential to a better, safer, healthier life for people everywhere. Our Core Values • Safety and Health • Environmental Stewardship • Highest Ethical Behavior • Respect for People Planning: Goal and Objectives • • • • • Gives purpose and direction More detailed goal statement How do we go about it? To (action verb) Consistent with Mission/Vision Planning: Develop Objectives • • • • • Specific Measurable Attainable Realistic Time-limited Characteristics of Objectives • • • • Outcome - what is to be accomplished Time Frame - expected completion date Measure - metrics for success Action - how the objective will be met Goals and Objectives • Drucker’s Objectives for Organizational Survival – – – – – – – – Market Share Innovation Productivity Physical and Financial Resources Manager Performance and Development Worker Performance and Attitude Profitability Social Responsibility Management by Objectives • Commonly Referred to as MBO • Corollary MBWA (Management by Walking Around) Management by Objectives (MBO) Translates broad organizational goals into specific individual objectives. 1. Common understanding of overall organization and group goals. 2. Mutual agreement on the subordinate’s attention and superior’s support. 3. Execution 4. Review and evaluation Strategic Planning Strategies: • Grand plans to attain longer-range objectives Strategic Planning: • Identify where the organization is • Identify where does it want to be in the future • Define a strategy to get there Strategic Planning Vision/Mission SWOT Analysis Gap Analysis Goals Objectives Strategies Strategic Planning Mission Goal 1 Objective 1 Goal 2 Objective 2 Strategy 1 Strategy 2 Goal 3 Strategic Planning • Suggests ways (strategies) to identify and to move toward desired future states • Consists of the process of developing and implementing plans to reach goals and objectives • Not a business plan • Not an operational plan Strategic Planning Vision/Mission Vision/Mission Aligned towards meeting customer expectations and within framework Of organizations philosophy ’ SWOT Analysis SWOT Analysis Gap Analysis Gap Analysis Forecasting Strategic Issues Ongoing Strategic Planning, Goals Goals, Objectives Objectives, Strategies SWOT Analysis • Internal – Strengths – Weaknesses • External – Opportunities – Threats Some Planning Concepts Responsibility for planning • Planning is a continuing responsibility of every manager. • Higher the manger, more time and further into future. Planning Premises (assumptions) • The anticipated environment in which plans are expected to operate, including assumptions and known conditions. • Contingency plan Some Planning Concepts Planning Horizon Logical planning encompasses a future period of time necessary to fulfill the commitment involved in decisions made today ($ and time). – Commitment principle. Some Planning Concepts Policies: Guides for decision making that permit implementation of upper management objectives, with room for interpretation and discretion by subordinates. Procedure: A prescribed sequence of activities to accomplish a desired purpose. Strategic Planning: Forecasting Vision Vision/Mission /Mission Aligned towards meeting customer expectations and within framework Of organization s philosophy ’ SWOT Analysis SWOT Analysis Gap Analysis Gap Analysis Forecasting Strategic Issues Ongoing Strategic Planning , Goals Goals , Objectives Objectives , Strategies Forecasting • Essential preliminary to effective planning • Engineering manager must be concerned with both future markets and future technology Forecasting • Sales (Market) Estimates • Technological Forecasting Why Forecasting? • New facility planning • Production planning • Work force scheduling Long Range Forecasts • Design new products • Determine capacity for new facility • Long range supply of materials Short Range Forecasts • Amount of inventory for next month • Amount of product to produce next week • How much raw material delivered next week • Workers schedule next week Forecasting: Qualitative Methods Judgment Methods: • Jury of executive opinion • Sales force composite • Users’ expectation • Delphi method Counting Methods: • Market Testing • Market Survey Delphi Method • • • • • • • • Delphi coordinator develops objective of forecast Determine number of participants Select and contact participants Develop first questionnaire (opinions & forecasts) and submit Coordinator analyzes responses Develop second questionnaire based on results of first Analyze responses Rounds continue until consensus reached or experts’ opinions cease to change Delphi Method • Eliminates effects of interactions between members • Experts do not need to know who other experts are • Reaches consensus Forecasting: Quantitative Methods Time Series Methods • Moving Average • Weighted Moving Average • Exponential Smoothing Association or Causal Method • Simple Regression • Multiple Regression Simple Moving Average Fn1 n 1 n A t 1 t Weighted Moving Average n Fn1 w t A t t 1 n where w t 1 t 1 Exponential Smoothing Fn1 Fn ( An Fn ) An (1 )Fn A n (1 )A n1 (1 ) A n2 2 (1 )3 A n3 Excel: Tools: Data Analysis Damping Factor = 1 - Exponential Smoothing Advantages: • Simple in concept • Powerful because of its weighting process. Disadvantages: • Exponential smoothing will lag as the trend increases or decreases over time. • Exponential smoothing will fail to account for the dynamic changes. Simple Regression Model D a bI ni1(IiDi ) (i1Ii )( i1Di ) n b n n n (I ) (i1Ii ) n 2 i1 i n 2 1 n b n a i1Di ( i1Ii ) n n Excel: FORECAST (X, known_y’s, known_x’s) SLOPE (known_y’s, known_x’s) INTERCEPT (known_y’s, known_x’s) ` Multiple Regression Model 1 2 D c 0 c1I1 c 2 c 3I3 I2 http://www2.chass.ncsu.edu/garson/pa765/regress.htm http://www.statsoft.com/textbook/stmulreg.html http://www.minitab.com/resources/whitepapers/burril2.aspx Technological Forecasting Prediction that certain technical development can occur within a specified time period with a given level of resource allocation • Normative technological forecasting: After a desired future goal is selected, a process is developed backward, from future to present, to achieve a goal. • Exploratory technological forecasting: It begins with the present state of technology and extrapolates into the future assuming some expected rate of technical progress. Technology S-curve Natural Limits Technology Performance Parameter New Invention Period Technology Improvement Period Mature Technology Period Strategies for Managing Technology • Doing new and better things – Invention – Innovation • Doing things in new and better ways – Quality – Productivity Entrepreneurship • Entrepreneurship – A person who organizes and manages a business undertaking, assuming the risk for the sake of profit. • Intrapreneurship – Continuing entrepreneurial activities to create new products and new business. Managing Technological Changes • Internet – Marketing (B2C) – Purchasing, Supply Chain Management (B2B) – Design, Manufacturing – Customer Service • Information Age Government Regulation • Environment concerns • Safety