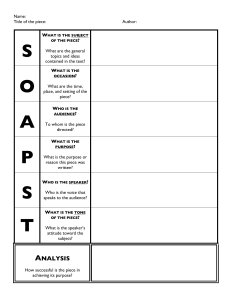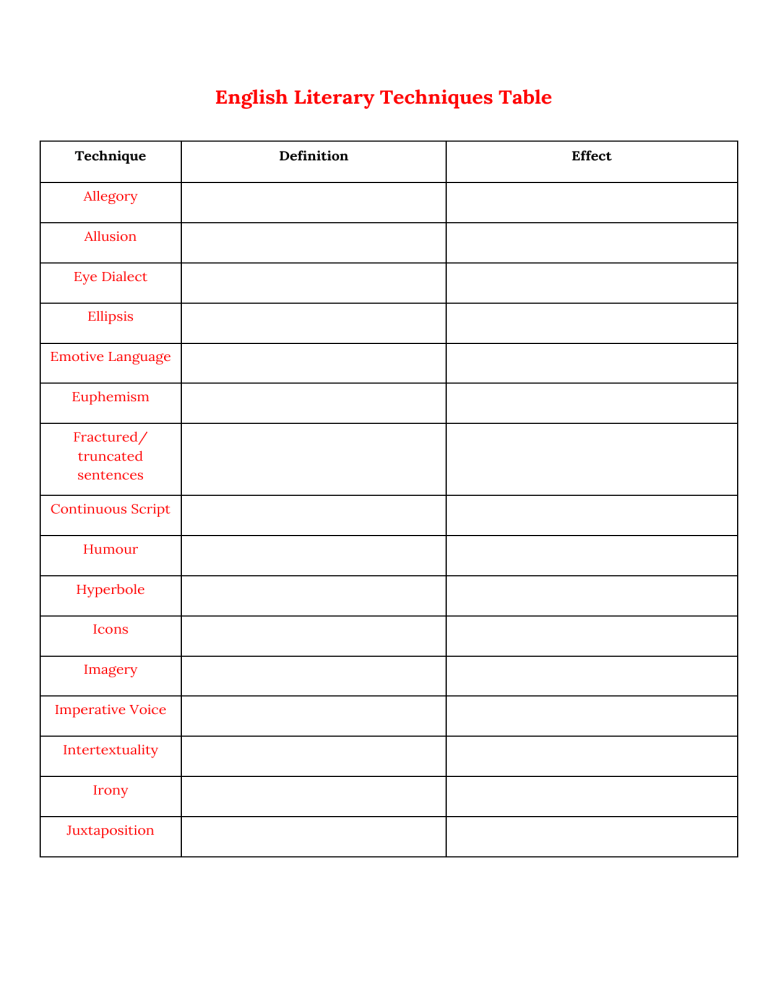
English Literary Techniques Table Technique Allegory Allusion Eye Dialect Ellipsis Emotive Language Euphemism Fractured/ truncated sentences Continuous Script Humour Hyperbole Icons Imagery Imperative Voice Intertextuality Irony Juxtaposition Definition Effect Level of usage of language Slang, colloquial, informal or formal. Linear/ non-linear Metaphor Modality Onomatopoeia Person Personification Repetition Satire Simile Theme First, second, or third. First person refers to the speaker himself or a group that includes the speaker (I, me, we, and us). Second person refers to the speaker’s audience (you). Third person refers to everybody else (he, him, she, her, it, they, James, mice).