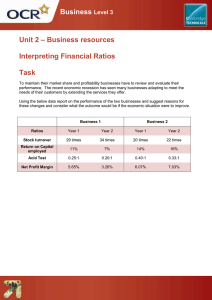
Chapter 12 Financial Analysis: Improving Your Decision Making Benchmarking • Provides comparisons with the best practices of other organizations • Firms do not have to be in the same industry; however traditionally comparisons based within specific industries Common Size Balance Sheets • One number is selected and then divided into all other numbers in the statement • Total assets are used as baseline figure • Gross revenue or net revenue is used as basis for income statement • Presents trends over time • Factors that may influence calculation – Amortization – Forward purchase contract – Put option Common Size Income Statements • Calculated in the same matter as common size balance sheets • Converts information into common basis to detect trends in operations Financial Ratio Analysis • Liquidity ratios – Current ratio – Quick or acid-test ratio • Activity ratios – Accounts receivable collection period Accounts receivable ÷ Average daily revenue – Inventory turnover Cost of goods sold ÷ Inventory OR Revenue from inventory Financial Ratio Analysis—cont’d • Leverage ratios – Debt ratio – Long-term debt to total capitalization – Debt to equity • Profitability ratios – Operating profit margin • Net trade cycle Not-for-Profit Comparisons • Profitability ratios may not be calculated in the same manner • Balance sheets have unrestricted and temporarily restricted fund balances – Unrestricted fund balances are provided to others to support the mission – Temporarily restricted fund balances are used for projects having a specific purpose Not-for-Profit Comparisons— cont’d • Lack of standardization in terminology and formats make comparison difficult • Information is not as readily available • Consolidated balance sheet and statement of activity – Current Ratios – Activity Ratios – Leverage Ratios – Profitability Ratios Cash on Hand The amount of cash necessary to meet actual daily cash operating expenses Days of cash on hand = __________Cash + Marketable securities__________ (Operating expenses – Bad debts – Depreciation)/365 Cash Flow Coverage Measures how well able to cover required payments Cash from operations + Interest + Rent Interest + Rent + Debt payments Program Service Ratio • Designed to determine what proportion of a firm’s expenditures goes directly into its program services • Unique to not-for-profit organizations Program service ratio= Program services expenses Total expenses Additional Financial Ratios • Ratios computed for either for-profit or notfor-profit entities – Revenue per Employee: Net Revenue ÷ Number of Employees – Net income per Employee: Net Income ÷ Number of Employees – Price earnings ratio: Market price of stock ÷ Earning per common share – Growth Rate of Revenue: Percentage Change in Revenue from Previous Time Period Additional Financial Ratios— cont’d • Ratios more applicable for not-for-profit entities – Percentage of deductibles: Deductibles ÷ Gross patient service revenue – Reported income index: Net income ÷ Changes in fund balance – Long-term debt to fund balance: Long-term debt ÷ Fund balance