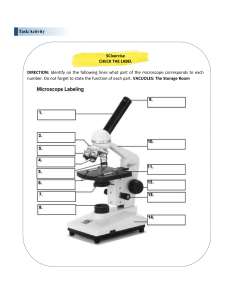
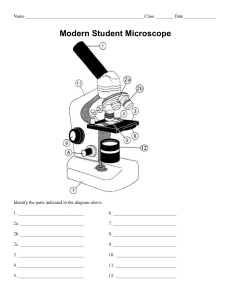
Laboratory Report Microscopy Group number: ___________ Group members: ______________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Section:______________ Date Submitted: _____________ Activity 1: Parts of the Microscope and Characteristics of the Objectives 1. Identify the part of the microscope that is being described (1 pt each): a) These are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. b) Brings the object into approximate focus. c) Collects and focuses the light from the illuminator into the specimen. d) Controls the amount of light that reaches the specimen. e) Carries the optical parts in the upper part of the microscope. 2. Complete the table below. (0.25 pts each) Characteristics of the Objectives Low power objective High power objective Oil immersion objective Focal length (mm) Linear magnification (x) Numerical aperture (N.A.) Working distance (mm) 3. How does the compound microscope magnify an object? (Answer in not more than 5 sentences) (2pts) 4. Can you observe the SARS-CoV-2 virion (causative agent of CoViD-19) using a compound light microscope? (Answer in not more than 5 sentences) (2 pts) Activity 2: Care of the Microscope Modified True or False: Write True if the statement is correct and provide an explanation if otherwise. 1. Lift the microscope using only one hand. (1pt) 2. Clean the lenses using paper towel. (1 pt) 3. Make sure to clean the body of the microscope using a paper towel. (1 pt) Activity 3: Calibration of the Microscope 1. Consider the following image: Ocular Stage Under the 4mm Compute the calibration factor (CF). Show your calculations and box your final answer. (3 pts) 2. Based on your computed CF in number 1, determine the size of the specimen of the image below. Show your calculations here and box your final answer. (2 pts) 3. Calculate the area of the field of vision from the image below. Show your calculations and complete the table below. Objective 4mm Show your calculations here. (2 pts) Page 3 Number of SM divisions Subtended by the Area of field of vision Diameter mm cm Radius mm cm Area mm2 cm2 Guide Questions 1. Why contrast is also important in microscopy? 2. How can contrast be achieved in using the microscope? 3. What is the relationship of wavelength and numerical aperture in getting a good resolving power? 4. How does oil increases resolution? Explain your answer.