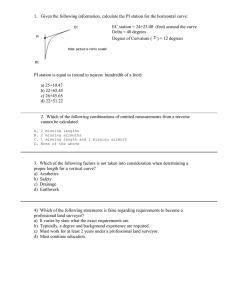
WORKSHOP ON CIVIL ENGINEERING DESIGN AND PRACTICE Ir. Dr. Abdul Naser Abdul Ghani, P.Eng, MIEM, MASCE, MACEM Associate Professor School of Housing, Building and Planning, USM Consulting Engineer ABADINI INTEGRAS ENGINEERS SDN BHD PERUNDING PINANG SDN BHD USAINS HOLDING SDN BHD Earthwork and ESCP Design Practice Ir. Dr. Abdul Naser Abdul Ghani, P.Eng, MIEM, MASCE, MACEM Associate Professor School of Housing, Building and Planning, USM Consulting Engineer ABADINI INTEGRAS ENGINEERS SDN BHD PERUNDING PINANG SDN BHD USAINS HOLDING SDN BHD EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION DRAWINGS EXISTING LAND SURVEY /DTM EW LAYOUT PLAN Drawings X-SECTION DRAWINGS DETAIL DRAWINGS EARTHWORK CONSTRUCTION DRAWINGS Land survey plan indicates existing ground level and details such as existing stream and structures. Depending on whether there is significant variation in ground level, contour lines indicating major and minor interval will be shown in this drawing. The land survey drawing will also show or indicate the location of bench mark (BM) or temporary benchmark (TBM). Reference to a BM is important during earthwork operation activities to ensure correct design and construction of platform level. LAND SURVEY PLAN Graphic courtesy of : Perunding Pinang SB DTM Graphic courtesy of: ABADINI Integras Engineers SB EARTHWORK LAYOUT DRAWINGS The earthwork layout plan will show and describe the earthwork components within a project. Information such as cut and fill area, temporary works, cross section alignment, various earth retaining structures and earthwork operation notes will be shown in this drawing. EARTHWORK LAYOUT EARTHWORK X-SECTION DRAWINGS Cross section drawing is usually drawn to an exaggerated scale especially the vertical scale. Usually the vertical scale is 10 times the horizontal scale. This will give clear indication of changes in level or level variation along the section. Cross section drawing can also be used estimate volume of earthworks. EARTHWORK DETAIL DRAWINGS Detail drawing for earthwork is the type of drawing that is prepared or made to ensure all the details can be seen clearly. The number of detail drawings depends on the components shown in the earthwork layout. An example could be the detail of a sedimentation pond, silt trap, silt fence, temporary earth drain, and the various earth retaining structures. EARTHWORK CALCULATIONS In the absence of a pre-computed earthwork volume by design engineers, a contractor or a builder will need to carry out the computation to ensure the earthwork operation can be carefully planned and executed. This demands basic knowledge of plan reading including using scales, calculation of area on plan, determination of cut and fill area and finally earthwork volume computation using suitable methods. EARTHWORK AREA CALCULATION Area for cut and fill or for other construction component such as open space, pond or slope can be calculated using several techniques. Other reasons why there will be the needs to determine area are: · To check the acreage or area within your boundary, project or property To determine the area of sections of interest, for example Open space lakes or water pond watersheds / catchment area Pavement / parking space To estimate materials for: area to be paved area to be seeded area to be resurfaced AREA CALCULATIONS There are three common methods that can be used to determined or calculate an area. They are : 1) Division of the area into simple figures (triangles, rectangles, and trapezoids), 2) Triangulation, and 3) Rectangular coordinates. AREA CALCULATIONS Using simple division as shown , the area of each triangle can be calculate by using simple trigonometric equation such as: Where: C is the angle between ‘a’ and ‘b’ In the case of when lengths of all the three sides are known, the following formula can be used to calculate the area within the triangle: Where, AREA – COORDINATE METHOD the area concerned is plotted into a coordinate systems with which each corner of the site is identified with reference coordinate based on suitable X and Y axis. COORDINATE METHOD The steps to calculate the shaded area shown is as follows: •List X and Y coordinate in two columns. •Repeat coordinates of starting point at the end •Sum the products designated by the arrows as shown in Figure xx •Difference between the two sums = twice the area PRACTICAL APPLICATION PRACTICAL APPLICATION Example 1: The site plan shows several existing boundary marker in circles. The rectangular grid shown in the plan is actually 200 meter x 200 meter on site. 1) Identify the scale of this plan and: 2) Determine the distance between marker “D” and marker “17” 3) Calculate the area in between “16-13-14-D-17-16” PRACTICAL APPLICATION - SOLUTION Step 1: Use suitable ruler or scale to measure the rectangular 200 m x 200 m grid on the plan. Step 2: Find the ratio between measurement on the plan (in cm or mm) to the 200 meter ( use similar unit e.g. cm) Step 3: Measure the distance between “D” and “17” in cm or mm, and use the scale found in step 2 to determine actual distance on site between the two points. (Answer: 177 meter) In order to calculate the area within “16-13-14-D-17-16” using triangulation, the boundary length and diagonal distances between the marks may be needed. Alternatively, plot suitable X, Y axis and determine the coordinate at each corner then use coordinate method to find the area. In both situations, use the scale found in solution 1 to measure the distance for the boundaries and the coordinates. (Answer: 31307 m2) EARTHWORK OPERATION AREA – CUT/FIL Earthwork plan prepared by the engineers usually indicates the layout of the cut and fill area. However, in the absence of such information, it is the responsibility of the builder to correctly identify the boundary. Laws regarding the boundary of earthworks especially when there will be deep cut or fill must be referred before the start of work. Platform level for the proposed building or structure will usually determine the extent of cut and fill required. Existing survey plan showing the present ground level will help one decide a suitable platform level for the building site. Once the platform level is decided, the cut and fill area and boundary can be determined. This will also identify the needs for any retaining structure to contain the slope within certain perimeter. For example, retaining wall is required to prevent cut or fill slope encroaching into neighboring land. EW Bylaw OK ????? TROUBLE EARTH FILL TROUBLE EARTHWORK VOLUME COMPUTATION Earthworks involve cutting down of hills and filling in of valleys to create building platform or road sub-grade. Other related earthworks include excavation for drains and channels. Average end area or sometimes called double end areas method is usually used for calculating the earthwork quantities along a road, drain or channel projects. This method calculates the average end areas of cross sections times the distances between the cross sections. The volumes are then added together along the route to yield the total volume. Another method called grid method is more suitable for site development although the average end area is also suitable in most situations including site development. Therefore, two primary methods usually used in earthwork volume computations are: 1) Average end area of cross sections 2) Average cut/fill depth using grid EARTHWORK –AVE. END AREA Average end area from cross section method, as discussed earlier is particularly more suitable for road, highways, drain, irrigation canal and other linear structures. For site specific project such as housing development, school and building platform, this method will give quick estimation of earthwork volumes required within the site. VOLUME – AVE END AREA VOLUME – SHRINKAGE FACTOR VOLUME – X-SECTION INFO VOLUME – BASED ON X-SECTION AND ‘AEM’ VOLUME – GRID METHOD Grid method of earthwork volume computation utilizes imaginary gridline spread onto the site. Existing and propose elevation at grid intersections are abstracted and used to calculate average elevation for the known grid area. Smaller grid space will require more data abstraction but will improve the accuracy of calculation. VOLUME – GRID METHOD VOLUME – GRID