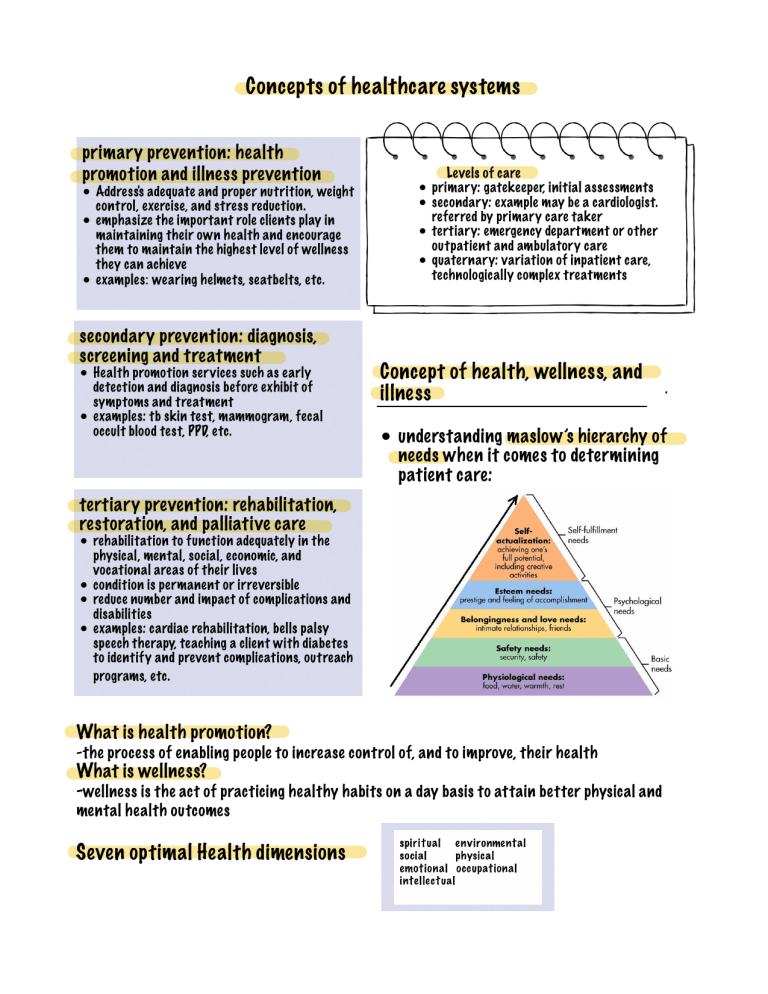
Concepts of healthcare systems primary prevention: health promotion and illness prevention • Address's adequate and proper nutrition, weight control, exercise, and stress reduction. • emphasize the important role clients play in maintaining their own health and encourage them to maintain the highest level of wellness they can achieve • examples: wearing helmets, seatbelts, etc. secondary prevention: diagnosis, screening and treatment • Health promotion ser vices such as early detection and diagnosis before exhibit of symptoms and treatment • examples: tb skin test, mammogram, fecal occult blood test, PPD, etc. Levels of care • primary: gatekeeper, initial assessments • secondary: example may be a cardiologist. referred by primary care taker • tertiary: emergency department or other outpatient and ambulatory care • quaternary: variation of inpatient care, technologically complex treatments Concept of health, wellness, and illness • understanding maslow’s hierarchy of needs when it comes to determining patient care: tertiary prevention: rehabilitation, restoration, and palliative care • rehabilitation to function adequately in the physical, mental, social, economic, and vocational areas of their lives • condition is permanent or irreversible • reduce number and impact of complications and disabilities • examples: cardiac rehabilitation, bells palsy speech therapy, teaching a client with diabetes to identify and prevent complications, outreach programs, etc. What is health promotion? -the process of enabling people to increase control of, and to improve, their health What is wellness? -wellness is the act of practicing healthy habits on a day basis to attain better physical and mental health outcomes Seven optimal Health dimensions . What is illness? -a disease or period of sickness affecting the body or mind Acute illness? -acute illnesses generally develop suddenly and last only a short amount of time. an example of an acute illness would be strep throat Chronic illness? -chronic illnesses are diseases or conditions that are persistent or other wise long lasting in it’s effects. chronic illnesses can also be diseases that come with time. examples of chronic illnesses are high blood pressure, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease Illness behaviors? -illness behaviors are best described as a belief that one is threatened by illness or in need of protective action, including medical attention/care Illness-wellness continuum factors in uencing health: internal variables • biologic dimension • psychological dimension • cognitive dimension external variables • environment • standards of living • family and cultural belief • social support net works



