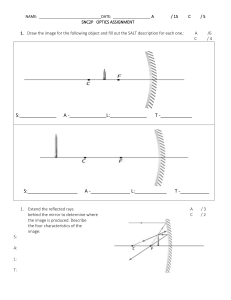
Back Print Name Class Date Assessment Chapter Test A Light and Reflection MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. ______ 1. Which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is used in a television? a. infrared waves c. radio waves b. X rays d. gamma waves ______ 2. Which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is used in a microscope? a. infrared waves c. visible light b. gamma rays d. ultraviolet light ______ 3. Which portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is used to identify fluorescent minerals? a. ultraviolet light c. infrared waves b. X rays d. gamma rays ______ 4. In a vacuum, electromagnetic radiation of short wavelengths a. travels as fast as radiation of long wavelengths. b. travels slower than radiation of long wavelengths. c. travels faster than radiation of long wavelengths. d. can travel both faster and slower than radiation of long wavelengths. ______ 5. If you know the wavelength of any form of electromagnetic radiation, you can determine its frequency because a. all wavelengths travel at the same speed. b. the speed of light varies for each form. c. wavelength and frequency are equal. d. the speed of light increases as wavelength increases. ______ 6. The farther light is from a source, a. the more spread out light becomes. b. the more condensed light becomes. c. the more bright light becomes. d. the more light is available per unit area. ______ 7. A highly polished finish on a new car provides a surface for reflection. a. rough, diffused c. rough, regular b. specular, diffused d. smooth, specular Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Physics 97 Chapter Test Back Print Name Class Date Chapter Test A continued ______ 8. When a straight line is drawn perpendicular to a flat mirror at the point where an incoming ray strikes the mirror's surface, the angles of incidence and reflection are measured from the normal and a. the angles of incidence and reflection are equal. b. the angle of incidence is greater than the angle of reflection. c. the angle of incidence is less than the angle of reflection. d. the angle of incidence can be greater than or less than the angle of reflection. ______ 9. The image of an object in a flat mirror is always a. larger than the object. b. smaller than the object. c. independent of the size of the object. d. the same size as the object. ______10. Which of the following best describes the image produced by a flat mirror? a. virtual, inverted, and magnification greater than one b. real, inverted, and magnification less than one c. virtual, upright, and magnification equal to one d. real, upright, and magnification equal to one ______11. When the reflection of an object is seen in a flat mirror, the distance from the mirror to the image depends on a. the wavelength of light used for viewing. b. the distance from the object to the mirror. c. the distance of both the observer and the object to the mirror. d. the size of the object. ______12. What type of mirror is used whenever a magnified image of an object is needed? a. flat mirror c. convex mirror b. concave mirror d. two-way mirror ______13. The mirror equation and ray diagrams are valid concepts only for what type of rays? a. parallel rays c. intersecting rays b. perpendicular rays d. paraxial rays ______14. Object distance, image distance, and radius of curvature are for curved mirrors. a. interdependent c. directly related b. independent d. unrelated Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Physics 98 Chapter Test Back Print Name Class Date Chapter Test A continued ______15. For a spherical mirror, the focal length is equal to radius of curvature of the mirror. a. one-fourth c. one-half b. one-third d. the square of the ______16. A parabolic mirror, instead of a spherical mirror, can be used to reduce the occurrence of which effect? a. spherical aberration c. chromatic aberration b. mirages d. light scattering ______ 17. When red light and green light shine on the same place on a piece of white paper, the spot appears to be a. yellow. c. white. b. brown. d. black. ______18. Which of the following is not an additive primary color? a. yellow c. red b. blue d. green ______19. Which of the following is not a primary subtractive color? a. yellow c. magenta b. cyan d. blue A C B D ______20. Which pair of glasses shown above is best suited for automobile drivers? The transmission axes are shown by straight lines on the lenses. (Hint: The light reflects off the hood of the car.) a. A c. C b. B d. D Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Physics 99 Chapter Test Back Print Name Class Date Chapter Test A continued SHORT ANSWER 21. What type of reflection is illustrated in the figure shown above? 22. A line parallel to the principal axis is drawn from the object to a spherical mirror. How should the reflected ray be drawn? 23. What type of image do flat mirrors always form? 24. What percentage of light passes through a polarizing filter when the transmission axis is perpendicular to the plane of polarization for light? PROBLEM 25. Yellow-green light has a wavelength of 560 nm. What is its frequency? Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Physics 100 Chapter Test Back Print PAGE TEACHER RESOURCE 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Solution P Intensity 4pr2 0.30 W Intensity 4p(1.6 m)2 9.3 103 W/m2 23. 0.350 m Given v 577 m/s f1 825 Hz Solution v f1 2L v 577 m/s L 0.350 m 2f1 2(825 Hz) 24. The resonant length must be shortened by 2.5 cm to 25.0 cm. Given v 348 m/s f1 349 Hz Linitial 27.5 cm Solution Rearrange the wave speed equation, c fl, to isolate f, and calculate. (3.00 108 m/s) c f (5.6 107 m) l 5.4 1014 s1 5.4 1014 Hz Light and Reflection CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. c Given f 3.0 109 Hz 3.0 109 s1 c 3.00 108 m/s Solution v f1 4L v 348 m/s L 0.250 m 4f1 4(349 Hz) 25.0 cm Change in length Linitial L Solution Rearrange the wave speed equation, c fl, to isolate l, and calculate. (3.00 108 m/s) c l 0.10 m (3.0 109 s1) f 2. b Given l 1.0 105 m c 3.00 108 m/s 27.5 cm 25.0 cm 2.5 cm 25. 565 Hz or 577 Hz Given freference 571 Hz beats 6/s Solution f freference beats 571 Hz diffuse through the focal point (F) virtual 0% 5.4 1014 Hz Given l 560 nm 560 109 m 5.6 107 m c 3.00 108 m/s Solution Rearrange the wave speed equation, c fl, to isolate f, and calculate. (3.00 108 m/s) c f (1.0 105 m) l 6 Hz f 577 Hz or 565 Hz 3.0 103 s1 Light and Reflection 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. c c a a a a d a d c 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. b c d a c a a a d c 3.0 103 Hz c b b d d a a Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Physics 200 Chapter Test