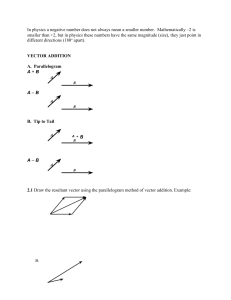
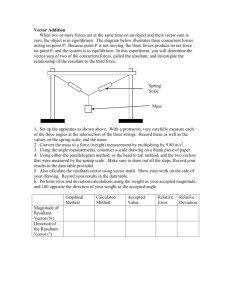
PRELIMS: PHYSICS FOR ENGR. LAB MATRIZ, RAINIE STEFANIE | BSCE-1C | 2ND SEMESTER | 2022-2023 ACT. 1 FAMILIARIZATION OF LABORATORY MATERIALS/EQUIPMENTS ● VECTOR- can be specified by magnitude and direction. - Ex. spatial displacement, force and velocity ● RESULTANT FORCE- single force that represents the effects of all the other forces acting on an object. EQUIPMENTS/MATERIALS 1. FORCE TABLE (PASCO) ● ● Tool used a to determine the equilibrium and measure the effects of vector quantities. Tool for demonstrating Newton’s First Law of Motion 2. TENSION PROTRACTOR (PASCO) ● It is a tool that combines a protractor with a spring scale. The rotary dial reads the angle where the string crosses the degree scale on the outer ring, making it ideal for studies involving static equilibrium and string tension. 3. ATWOOD MACHINE ● Device used for illustrating fundamental dynamics and acceleration laws. It consists of string, pulley and a system of masses. Ex. temperature, mass, volume and time intervals. THREE PROCESS ON HOW TO GET THE RESULTANT VECTOR Graphical Process- polygon method. Drawing process according to the measured scale of vectors. Analytical Process- process of adding vectors using trigonometry to express each vector in terms of its component projected on the axes of a rectangular coordinate system. Experimental Process- process of getting a resultant vector using the device called the force table. In which, the force table provides a force from the gravitational attraction on masses attached to a ring by a string passing over a pulley. EXPERIMENT 2: FIRST CONDITION OF EQUILIBRIUM USING TENSION PROTRACTORS EXPERIMENT 1: FORCE TABLE AND VECTOR ADDITION OF FORCES ● ● SCALAR- physical quantity that can be specified by magnitude only. The first condition in which an object remains at equilibrium states that the net external force acting on the object must be zero. PRELIMS: PHYSICS FOR ENGR. LAB MATRIZ, RAINIE STEFANIE | BSCE-1C | 2ND SEMESTER | 2022-2023 ● Any object hangs at rest if it weight is counteracted by other forces, so that the vector sum of all occurrences along the vertical and horizontal directions is zero. LAW OF MECHANICS ⅀Fn= 0 ● For components: ⅀Fx= 0 ⅀Fy= 0 EXPERIMENT 4: NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION ON THE ATWOOD MACHINE ⅀Fz= 0 SECOND LAW OF MOTIONwhen there is net force acting on a body, the body would accelerate in the same direction as the net force. 𝑎 = 𝑭𝑛𝑒𝑡/ 𝒎 or 𝑎 = ⅀𝑭/ 𝒎 2 EXPERIMENT 3: UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION USING TICKER TAPE TIMER ● ● ● VELOCITY- speed with specific direction ACCELERATED MOTION- motion in which the velocity change ACCELERATION- the state of an object in which the object experiences a change in its state of motion; rate of change of velocity AVERAGE ACCELERATION= change in velocity/change in time 𝑎 = 𝝙𝐯⁄𝝙𝙩 UNIFORM ACCELERATED MOTIONmotion of an object where the acceleration is constant; speed changes by a constant amount without change in the direction. 𝑎 = 2𝑥/𝑡 𝑎 = (𝑚1 − 𝑚2/𝑚1 + 𝑚2)𝒈