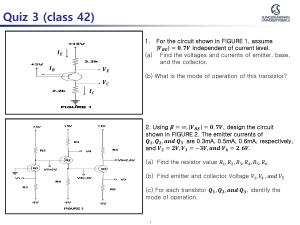
KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY School of Engineering Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BASIC ELECTRONICS [EEEG 204 ] – Assignment I To be submitted till 7 July 2022 Reference: Principle of Electronics VK Mehta, Rohit Mehta th 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 1 (i), find: (i) the output voltage (ii) the voltage drop across series resistance (iii) the current through zener diode. Figure 1 2. Determine the current I in the circuit shown in Figure 2 (i). Assume the diodes to be of silicon and forward resistance of diodes to be zero. Figure 2 3. An a.c. supply of 230 V is applied to a half-wave rectifier circuit through a transformer of turn ratio 10 : 1. Find (i) the output d.c. voltage and (ii) the peak inverse voltage. Assume the diode to be ideal. Figure 3 4. A crystal diode having internal resistance rf = 20Ω is used for half-wave rectification. If the applied voltage v = 50 sin ω t and load resistance RL= 800 Ω, find : (i) Im, Idc, Irms (ii) a.c. power input and d.c. power output (iii) d.c. output voltage (iv) efficiency of rectification. 5. A full-wave rectifier uses two diodes, the internal resistance of each diode may be assumed constant at 20 Ω. The transformer r.m.s. secondary voltage from center tap to each end of secondary is 50 V and load resistance is 980 Ω. Find: (i) the mean load current (ii) the r.m.s. value of load current. 6. Derive relation for calculating efficiency of half wave rectifier using diode. 7. Explain working of full wave center tapped and bridge rectifier. (In detail) 8. Explain working of Zener Diode as voltage regulator with its characteristics. 9. Explain types of semiconductors. 10. Briefly with symbol write on LED and Photodiode with their respective application. 11. Explain VI characteristics of PN junction diode. EEEG 204 KATHMANDU School of Engineering UNIVERSITY Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BASIC ELECTRONICS [EEEG 204] –Assignment II To be submitted till 29th July 2022 Reference: Principle of Electronics VK Mehta, Rohit Mehta 1. A common base transistor amplifier has an input resistance of 20 Ω and output resistance of 100 kΩ. The collector load is 1 kΩ. If a signal of 500 mV is applied between emitter and base, find the voltage amplification. Assume αac to be nearly one. 2. In a common base connection, the emitter current is 1mA. If the emitter circuit is open, the collector current is 50 μA. Find the total collector current. Given that α = 0.92. 3. For the common base circuit shown in Fig, determine IC and VCB. Assume the transistor to be of silicon. 4. Find the value of β if (i) α = 0.9 (ii) α = 0.98 (iii) α = 0.99. 5. Find the α rating of the transistor shown in Fig. 4. Hence determine the value of IC using both α and β rating of the transistor. 1 EEEG 204 6. A transistor is connected in common emitter (CE) configuration in which collector supply is 8 V and the voltage drop across resistance RC connected in the collector circuit is 0.5 V. The value of RC = 800 Ω. If α = 0.96, determine: (i) collector-emitter voltage (ii) base current. 7. An n-p-n transistor at room temperature has its emitter disconnected. A voltage of 5 V is applied between collector and base. With collector positive, a current of 0.2 μA flows. When the base is disconnected and the same voltage is applied between collector and emitter, the current is found to be 20 μA. Find α, IE and IB when collector current is 1 mA. 8. Figures shows the open circuit failures in a transistor. What will be the circuit behavior in each case? 9. For the circuit shown in Fig, draw the d.c. load line. 2 EEEG 204 10. Is the transistor in Fig operating in saturated state? 11. Determine the state of the transistor in Fig. for the following values of collector resistor : (i) RC = 2 kΩ (ii) RC = 4 kΩ (iii) RC = 8 kΩ. 12. Determine the Q point of the transistor circuit shown in figure. Also draw the d.c. load line. Given β = 100 and VBE = 0.7V. 3 EEEG 204 13. Explain working of npn and pnp transistor. 14. How can BJT be used as switch? Explain. 15. Explain common base and common collector configuration. 16. Derive relation between alpha and beta. 17. Explain load line and Q-point in transistor. 4 KATHMANDU School of Engineering UNIVERSITY Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BASIC ELECTRONICS [EEEG 204] –Assignment III Submission Date: 7 August 2022 Answer the following questions 1. Mention the characteristics of ideal Op-Amp. 2. Write in brief on Op-Amp and explain inverting and non-inverting amplifiers. Explain with figures and numerical derivations (if any). 3. What is unity gate buffer? Mention its applications. 4. With brief explanations, diagrams and numerical derivations, write on: a. Differential Amplifier b. Summing Amplifier 5. Design a summing amplifier with necessary numerical values for gaining output -10V. Take three input voltages. 6. How does High and low pass Op-Amp work? Explain on High pass OpAmp (Even Roll Numbers) and Low pass Op-Amp (Odd Roll Numbers). 7. Write merits of Instrumentation Amplifiers and draw its circuit diagram. 8. Draw a block diagram of interfacing with analog signals. Explain in brief. 9. Explain working of binary weight DAC. Show with diagram how the issue of large difference in resistors values between the LSB and MSB is solved. 10. Explain Ramp ADC. ** THE END ** 1 KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY School of Engineering Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BASIC ELECTRONICS [EEEG 204] –Assignment IV Answer the following questions 1. Mention the types of logic gates (Basic and Universal). Draw its symbol, Waveform behavior, write its Boolean equation and tabulate its truth table. 2. Write few key points on logic gates and note down its applications. 3. Write few key points on Boolean algebra and note down its applications. 4. Explain logic function implementation using switches for AND, OR, NOT and NAND gate. 5. Draw logic diagram and tabulate truth table for following logic equations: a. F = X+YZ b. D= A.B + A'C + B'C' c. Z = (X’+X). (Y+X) d. W= A.B.C + A’.B.C + A.C + A.B (also write dual of W) 6. Explain gate delay. 7. Writing the min term expression: F = A’ B’ C + A B’ C’ + ABC’ + AB’C + ABC. Also, draw logic diagram. 8. Identify what type of logic function is represented by this gate circuit (AND, OR, inverter, etc.). Also, trace the directions of all currents in this circuit. 1 KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY School of Engineering Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering BASIC ELECTRONICS [EEEG 204] –Assignment V Submission Deadline: 10 September 2022 Answer the following questions 1. Mention and explain in brief about measuring instruments. 2. Explain Permanent Magnet Moving Coil (PMMC) Instrument with merits and demerits. 3. In brief show the working of multirange ammeter and multirange voltmeter. 4. Show construction of power meter and explain in brief. 5. Mention properties of sensors with dynamic and static characteristics explanation. 6. Show different modes of optical proximity sensors. 7. Explain working of pressure sensors with any one example. 8. How are flow rate sensors different from pressure sensors? Write in brief about Coriolis sensor with its working principle. 9. What is see-back effect? How it can be utilized in temperature sensors? 10. Explain use of Bimetallic strips as switch. 11. What are discrete level and continuous level detectors? Mention few of them. 12. Explain DAQ and data logger with block diagrams. 13. Mention some applications of DAQ and data logger. THE END 1