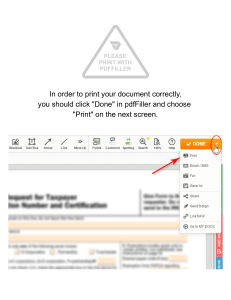
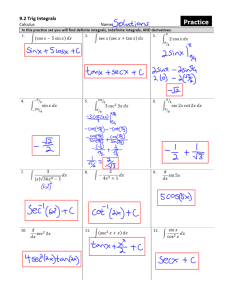
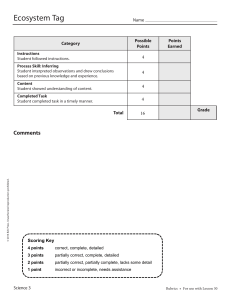
Unit 1 – Section 1 Quiz – Scoring Guidelines Front Page (4 graded parts) Question 1: Solution a. Sample – The first 100 students who entered the cafeteria on a certain day. Population – All students who entered the cafeteria on a certain day. b. Sample – All Sugar Maples located in the 25 randomly selected plots of land in a large forest. Population – All Sugar Maples located in a large forest. Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student correctly identifies the sample and population for both part (a) and part (b). Partially correct (P) if the student currently identifies the sample and population for either part (a) OR part (b) Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Question 2: Solution a. Convenience sample b. Cluster sample Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student correctly identifies the sampling design for both part (a) and part (b). Partially correct (P) if the student currently identifies the sampling design for either part (a) OR part (b) Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Question 3(a): Solution A potential drawback of a convenience sample is that maybe the students who enter the cafeteria most quickly are more likely to be satisfied with the food in the cafeteria (and will be among those who are surveyed). This will cause the average satisfaction rating obtained from the sample to overestimate the true average satisfaction rating of the population. Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student gives a reasonable justification of why convenience sampling would lead to bias AND gives a direction of the bias (over- or under-estimate) consistent with their justification. Partially correct (P) if the student gives a reasonable justification of why convenience sampling would lead to bias but does not give a direction of the bias consistent with their justification. Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Question 3(b): Solution A pro is that a cluster sample saves time and money. A potential flaw could be the chance selection of plots that are similar (homogeneous) in some way, causing the trees to be larger (or smaller) than the others in the unselected plots. Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student gives a reasonable pro AND con of the sampling method. Partially correct (P) if the student gives either a reasonable pro OR con of the sampling method, but not both. Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Note: The pro should be directly related to the benefits of cluster sampling (saves time/money), the con should be related to the main potential problem of location-based sampling (too homogenous/similar, not diverse/representative enough). Final Score • • • • Each (E) is worth 1 point. Each (P) is worth 0.5 points. Each (I) is worth 0 points. Add all (4) graded components together to get a score between 0 and 4. o Round half-scores DOWN. Back Page (3 graded parts) Question 4(a): Solution Label: Number the 975 students from 001 to 975 alphabetically. Randomize: Go to the random number table and pick a starting point. Moving left to right, record three-digit numbers, skipping any that are not between 001 and 975 and any repeated numbers, until you have 50 different numbers between 001 and 975. Select: Select the 50 students corresponding to these numbers Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student meets the following components: • • • Correctly labels from 001 to 975 (or equivalent) Correctly describes the random selection processes using a random digit table Correctly describes how to select using the random numbers. Partially correct (P) if the student satisfies 2 of the 3 components for an (E). Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Notes: • • Labeling from 1 – 975 does not satisfy Component 1. To satisfy Component 2, the student must: o describe selecting 3-digit numbers o describe that the numbers selected should be in the range of 001 to 975 / ignored if they’re not in the range o state that repeated values should be ignored OR state that only unique numbers should be selected o state that 50 numbers should be generated Question 4(b): Solution The 10 selected students are underlined below. Note that 658 (in bold) is skipped because it is a repeat. 120 354/76 5/597/0 39/421 658/50 0/426/6 58/435 43742 11937 The selected students are numbered 354, 765, 597, 039, 421, 658, 500, 426, 435, and 437. Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student correctly selects 10 students with supporting work. Partially correct (P) if the student correctly selects 10 students with no supporting work OR has supporting work but incorrectly selects 10 students. Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Question 4(c): Solution Stratify by year in school, because students who are farther along might earn more money in the summer than students who are recent high school graduates. Scoring Essentially correct (E) if the student gives an appropriate variable to stratify by with justification. Partially correct (P) if the student gives an appropriate variable to stratify by but has no justification. Incorrect (I) if the response does not meet the criteria for (E) or (P). Final Score 4 EEE 3 EEP 2 EEI EPP PPP 1 EII PPI PII 0 III EPI Order of E, P, and I do not matter.