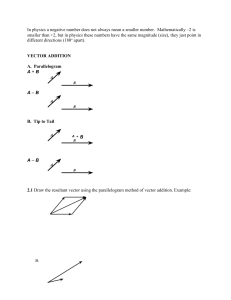
Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 1 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 2 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 3 Scalar Vs Vector Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 4 Scalar Vs Vector Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 5 Addition of planar forces Line of action 10lb A Fixed axis 1. Point of application 2. Magnitude 3. Direction : • Line of action • sense 30° Line of action 10lb A 30° Fixed axis Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 6 Line of action F Angle A Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Line of reference Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 7 P A Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith R=P+Q P Q A Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering Q 8 Joining tip to tail Q R=Q+P P P A Q Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith P R=P+Q Q A Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering A 9 P ‐P Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 10 Production of a Scalar and a Vector P P P P P 2P P P 3P ……….. P n P We define the production kP of a scalar k and a vector P as a vector having the same direction as P if k is positive or a direction opposite of P if k is negative and the magnitude equal to the product of P and the absolute value of k. Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith P Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 2P ‐2P 11 Associative addition S P Q S P P Q Q S P Commutative addition Q S P Q S S P Q This expression shows that the order of addition is immaterial Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 12 Since a particle A acted by several coplanar forces, since all forces pass through A, we said the forces are CONCURRENT. P S WE CAN ADD ALL THE VECTORS USING THE POLYGON RULE joining tip to tail of all vectors R has the same effect as the given forces. As we saw before the order of adding all forces is immaterial Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Q A S P Q Q P S A Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering R A R 13 Two forces are applied as shown to a bracket support. Determine the magnitude and direction of their resultant using: 1. The parallelogram Law 2. The triangle Law. Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 14 PROBLEM 2.6 A telephone cable is clamped at A to the pole AB. Knowing that the tension in the left-hand portion of the cable is T1 = 800 N, determine by trigonometry (a) the required tension T2 in the right-hand portion if the resultant R of the forces exerted by the cable at A is to be vertical, (b) the corresponding magnitude of R. Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 15 We have seen that we can add 2 or more forces acting on a particles and obtain the RESULTANT that has the same effect on this particle # The single forces acting on a particle may be replaced by two or more forces that, together, have the same effect on this particle, This forces are called COMPONENTS F P Of the original forces A Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering Q 16 y F 𝐹 𝐹 and 𝐹 called rectangular components Rectangular components of F, axes rotated from horizontal and vertical. O x 𝐹 y F x 𝐹 𝐹 O Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 17 𝐹 𝐹 cos 𝛼 y 𝐹 𝐹 sin 𝛼 tan 𝛼 𝐹 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith 𝐹 F 𝐹 𝐹𝑦 𝐹 O 𝐹 x 𝐹 Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 18 Y Doing projection of each force to both axis X and Y, we obtain 𝑅 Py P Sy 𝐹 S Px Sx 𝑅 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Qy 𝐹 Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering X Qx Q 19 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 20 PROBLEM 2.25 Member BC exerts on member AC a force P directed along line BC. Knowing that P must have a 325-N horizontal component, determine (a) the magnitude of the force P, (b) its vertical component. Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 21 Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 22 Problems 2.1 and 2.36 Please see problem statement in next slide Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 23 PROBLEM 2.1 Two forces are applied as shown to a hook. Determine graphically the magnitude and direction of their resultant using (a) The parallelogram law, (b) the triangle rule. Dr. Hamadi M. Belghith Natural & Applied Science Division ‐ Engineering 24