pdfcoffee.com 3rd-mod-part-2-dll-3rd-qrtr-g9-pdf-free
advertisement
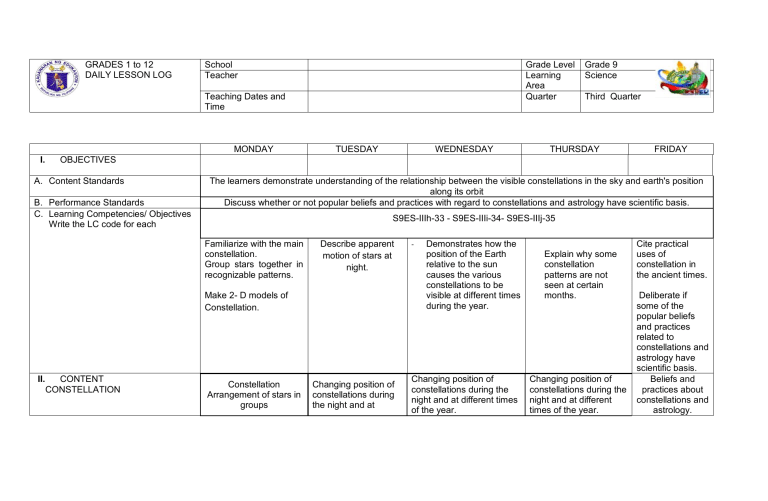
GRADES 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Teaching Dates and Time MONDAY I. TUESDAY WEDNESDAY Third Quarter THURSDAY FRIDAY OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards B. Performance Standards C. Learning Competencies/ Objectives Write the LC code for each The learners demonstrate understanding of the relationship between the visible constellations in the sky and earth's position along its orbit Discuss whether or not popular beliefs and practices with regard to constellations and astrology have scientific basis. S9ES-IIIh-33 - S9ES-IIIi-34- S9ES-IIIj-35 Familiarize with the main constellation. Group stars together in recognizable patterns. Describe apparent motion of stars at night. Make 2- D models of Constellation. II. Grade 9 Science CONTENT CONSTELLATION Constellation Arrangement of stars in groups Changing position of constellations during the night and at - Demonstrates how the position of the Earth relative to the sun causes the various constellations to be visible at different times during the year. Changing position of constellations during the night and at different times of the year. Explain why some constellation patterns are not seen at certain months. Changing position of constellations during the night and at different times of the year. Cite practical uses of constellation in the ancient times. Deliberate if some of the popular beliefs and practices related to constellations and astrology have scientific basis. Beliefs and practices about constellations and astrology. different times of the year. III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 161-162 161-162 161-162 161-162 217-220 218-225 218-225 218-225 218-225 everydayme.com.ph www.scienceteachers.com/constellati ons everydayme.com.ph www.scienceteachers.com/constell ations www.scienceteachers.com/space http://museumvictoria.com .au/scienceworks/educati on/ everydayme.com.ph www.scienceteachers.com/constellati ons www.scienceteachers.com/spac e Flash cards of different constellations. ( www.scienceteachers.com/space) Ask: What recognizable patterns have you observed? Use K-W-L approach to gather information from the students about constellations. Connect the dots. Students will connect the dots forming some patterns of constellations. Use the Logo Quiz in naming some constellations (Use pictures of animals that correspond to the name of different constellations.) 160-161 3. Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resources (LR) portal B. Other Learning Resources IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lessons or presenting the new lesson What are the characteristics of stars? How would you relate the color of the star with its temperature? B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson C. Presenting examples/ instances of the new lesson Picture Analysis. (This will lead students to describe stars forming groups.) Show a North Star (Polaris). Let them describe the star. Show pictures of constellations. Ask: Can you see them across the sky every night? Show a video capturing constellation. Ask: What did you see? What images are formed? Present a video of Ursa Minor and Ursa Major. Emphasizing the apparent motion due to Earth's rotation. Show model of constellations such as Orion and Scorpius. Note that both are located at opposite sides of the celestial sphere. https://m.youtube.com/w atch?v=hepzUgFhgis D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 Perform Activity 2: Patterns in the Sky in p. 217. Guide Questions: https://m.youtube.com /watch?v=hepzUgFhgi s Perform Activity 3 in L.M pp. 218-219 From the dots, identify two constellations and its month of appearance. Note that not all can be seen all throughout the months. Unlock term Revolution. This will lead students to the idea of the appearance of constellations at certain months and certain regions of earth. Perform Activity 1 (See attached Activity What patterns did you identify in the map? Can you name them? How are these constellations named? Give some bases how early civilizations came up with names. ( Early Greeks named Orion Perform Activity 4 in L.M pp.220-223 Using Orion and Gemini from the Logo Quiz, students associate them with stories of the ancient time. Orion signifies cold season and Gemini signifies end of planting season "Do popular beliefs and practices related to constellations and astrology have scientific basis? "Using the background information about certain constellations, students brainstorm with their core group and answer the which means hunter and prominent in the night sky all over the world during winter.) E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 F. focus question. A representative or two from each group will present their ideas through panel discussion. Make a 2-D model of constellation. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment Describe the movement of the stars in the night sky. How would you describe the position of the Earth during summer in the Southern Hemisphere? What will happen if Earth comes between the sun and Scorpius? How does the position of the Earth relative to the sun affect the appearance of constellation? Give some fun facts about constellations. Give some fun facts about constellations. 3) Ask students in how they can group stars in recognizable patterns. Students name familiar constellation. G. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living 1. A starry night would indicate good weather condition. 2. Balatik which is a local group of stars for early Filipinos can be used as trap for hunting wild pigs. Why can’t some constellation patterns be observed at certain months? Match Game for Constellations. Match the name of the constellation with the name of the animals. Cite constellations, its month of appearance and practical use. 1. Polaris which position does not change at any time of the night or year is widely used in navigation. 2. Matigsalug of Bukidnon use stars and H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson How do stars move? What images are formed in your map? How do motion of Name common stars similar to the constellation. motion of the sun? I. Evaluating learning Map constellation. J. Additional activities for application or remediation V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the Evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% Do Constellation Crossword for more basic constellation. www.scienceteachers.com/contellatio ns 1. What things did you learn most in the topic? 2. What thing or part of the lesson did you find most difficult? ( Use Reflective Evaluation) Why do we observe constellation patterns at different times during the year? Give a 5-Item formative assessment. Elicit ideas from students how constellations can be seen on different months and what are prominent during winter? Fall? Summer? Spring? 1. What things did you learn most in the topic? 2. What thing or part of the lesson did you find most difficult? ( Use Reflective Evaluation) Perform Summer and Winter Constellation in a Cup(see attached activity sheet) constellation in agriculture. Given the chart of different constellations, let students give their own beliefs with scientific basis. A summative assessment will be given to the students in pp. 226-227 of the L.M C. Did the remedial lesson works? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these works? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovations or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers?