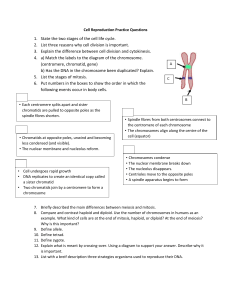
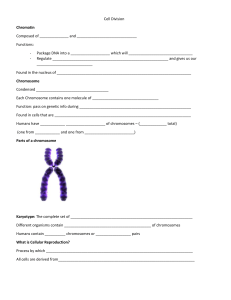
Mitosis Step by Step Mitosis Model • Each string of beads represents a chromosome • Each bead represents a gene • Red (ish) chromosomes inherited from mother • Blue (ish) chromosomes inhertited from father Mitosis Model • In this example, the cell has a chromosome complement of 4 • This is known as the DIPLOID NUMBER • What is the Diploid Number for Humans? Interphase • The Chromosomes shorten and thicken and become visible under the microscope (if stained) Nuclear Membrane Prophase • Each Chromosome replicates itself • This is where DNA replication (studied in Unit 1 comes in) • The chromosomes are made up of 2CHROMATIDS held together by a CENTROMERE (not shown) Chromosome Chromatid Chromatid Centromere Metaphase • Spindle fibres form • The Chromosomes line up, at random, along the equator of the spindle Anaphase • The spindle fibres contract pulling the chromatids apart and to opposite poles of the cell • Once separated, the chromatids are now known as chromosomes Telophase • 2 new “Daughter” cells are formed • Nuclear membrane reforms End Result Mother cell How do the cells compare • With the mother cell? • With each other? • Why is Mitosis important? Daughter cells