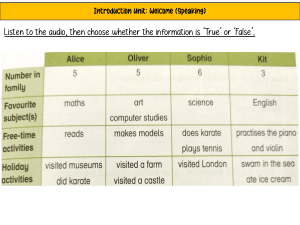
Codes, Conventions, and Language of Media Understanding the language of media is a skill that you must acquire. Remember the following terms: • Language pertains to the technical and symbolic ingredients or codes and conventions that media and information professionals may select and use in an effort to communicate ideas, information and knowledge. • Media language are the codes, conventions, formats, symbols and narrative structure that indicate the meaning of media messages to an audience. • Messages are the information sent from a source to a receiver Media codes and conventions are like the building blocks of all the media around us which generally have an agreed meaning, or connotation to their audience (Young, 2017). There are three (3) types of media codes: symbolic codes, technical codes, and written codes. 1. Symbolic codes are social in nature. Such codes exist beyond the media product themselves but can be interpreted in similar ways in the everyday life of the viewer (Young, 2017). Example: which means Christianity These also include setting, mise en scene, acting and color Setting is the time and place of the narrative. It can be the setting of the whole story or just a specific scene. This will create atmosphere or build a frame of mind (Young, 2017). Mise en scene is a French term meaning ‘everything within a frame’. Costume and props are included in the analysis in the frame (Young, 2017). Acting is how an actor portray a character that will lead to character development and tension making through facial expression, body language and vocal qualities (Young, 2017). Color is used to connect connotation to specific scenes, characters or object. Red, for instance, is typically seen as a color of passion, danger, romance, or violence. Green is connected with nature or sickness, blue with calm or depression. Purple is seen to be connected with royalty (Young, R. 2017). 2. Technical codes. According to Arniel Ping technical codes are all the ways in which equipment is used to tell a story in a media text like camera techniques, framing, lighting, etc. (Ping, 2016). Camerawork refers to how the camera is handled, positioned and moved for specific effects like a highangle camera shot to create a feeling of power in a photograph. Lighting. According to Robert Young lighting is the manipulation of natural or artificial light to selectively highlight specific elements of the scene( Young, 2017). Audio is the expressive or naturalistic use of sound. It includes dialogue, sound effects and music. According to Chris Constantine(Constantine, 2010) music often defines a scene. An example is the use of ominous music to communicate danger in films. Intellectual Property, Copyright, and Fair Use Guidelines Copyright is a legal device authorizing the creator of a literary piece, artistic work, musicals or other creative compositions the sole right to publish and sell such work. Copyright owners have the right to control the reproduction of their work, including the right to receive payment for that reproduction. An author may grant or sell those rights to others, including publishers or recording companies. Violation of such right is called infringement. Copyright law gives creators of original material the exclusive right to further use and duplicate that material for a given amount of time, at which point the copyrighted item becomes public domain. (KENTON, 2020) Plagiarism is an instance of using or closely imitating the language and thoughts of another author without authorization; the representation of that author's work as one's own, as by not crediting the original. phishing is a cybercrime in which a target or targets are contacted by email, telephone or text message by someone posing as a legitimate institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, and passwords. The information is then used to access important accounts and can result in identity theft and financial loss. The fair use of a copyrighted work for criticism, comment, news, reporting, teaching including multiple copies for classroom use, scholarship, research and similar purposes is not an infringement of copyright. Decompilation which is the reproduction of the code and translation of the forms of the computer programs to achieve the inter-operability of an independently created computer program with other programs, may also constitute fair use. To determine whether use of a work constitutes fair use, the following factors are considered: 1. The purpose and character of the use, including whether such use is of a commercial nature or is for non-profit educational purposes; 2. The nature of the copyrighted work; 3. The amount and substantiality of the portion used in relation to the copyrighted work as a whole; and 4. The effect of the use upon the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work. Republic Act No. 8293 or the Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines AN ACT PRESCRIBING THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CODE AND ESTABLISHING THE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OFFICE, PROVIDING FOR ITS POWERS AND FUNCTIONS, AND FOR OTHER PURPOSES Digital Divide, Addiction, and Bullying Digital Divide (DD) Digital divide pertains to the social and economic imbalance of the opportunities to access to, use of or knowledge of information and communication technology (ICTs). It is referring to a gap between sector in the community who can access, has the skills and has desire to the internet and those who cannot. Cyber Bullying 1. Any unwanted physical contact between the bully and the victim like punching, pushing, shoving, kicking, slapping, tickling, headlocks, inflicting school pranks, teasing, fighting and the use of available objects as weapons; 2. Any Act that causes damage to a victim’s psyche and /or emotional well-being; 3. Any slanderous statement or accusation that causes the victim undue emotional distress like directing foul language or profanity at the target, name -calling, tormenting and commenting negatively on victim’s looks, clothes and body.” (Republic Act No. 10627Anti-Bullying Act) Bullying happens in face to face (like in school) while cyber-bullying happens in a cyberspace (means in interconnected digital technology). What is cyber bullying? Cyber bullying is a type bullying done online with the use of technology like computers, laptops, and cellphone that can destroy the physical and emotional aspect of the victim (called as bullied) by the one who does the act (refers as bully). Different resources information: of media and a. People Media b. Text c. Visual d. Audio e. Motion f. Manipulatives / Interactive g. Multimedia Text Media Text – a simple and flexible format of presenting information or conveying ideas whether hand-written, printed or displayed on-screen. Design principles and elements – 1. Emphasis - refers to the importance or value given to a part of the text-based content. 2. Appropriateness - refers to how fitting or suitable the text is used for a specific audience, purpose or event. In the creation of text-based content, make sure that the selection criteria (tone, style, purpose, clarity) is followed. 3. Proximity - refers to how near or how far are the text elements from each other. When two things are closely related, we bring them close together. 4. Alignment - refers to how the text is positioned in the page. This can be left, right, center or justified. 5.Organization - refers to a conscious effort to organize the different text elements in a page. 6. Repetition- concerns consistency of elements and the unity of the entire design. Repetition encourages the use of repeating some typefaces within the page. 7. Contrast- creates visual interest to text elements. Contrast is achieved when two elements are different from each other. Visual Information and Media Discussion Visual media and information – materials, programs, applications and the like that teachers and students use to formulate new information to aid learning through the use, analysis, evaluation and production of visual images. Types of visual media – photography, video, screenshots, infographics, data visualization (charts and graphs), comic strips/cartoons, memes, visual note-taking, etc (Give examples of each type and highlight special characteristics of a given type and its application). Purpose of visual information – the primary purpose of visual information is to gain attention, create meaning, and facilitate retention. Visual design elements - the building blocks or basic units in the construction of a visual image. (Show visual media and information that incorporates most of the design elements. a. Line – describes a shape or outline. It can create texture and can be thick or thin. Lines may be actual, implied, vertical, horizontal, diagonal, or contour lines. b. Shape – usually a geometric area that stands out from the space next to or around it, or because of differences in value, color, or texture. Shape may also be organic. c. Value – the degree of light and dark in a design. It is the contrast between black and white and all the tones in between. Value can be used with color as well as black and white. Contrast is the extreme changes between values. d. Texture – the way a surface feels or is perceived to feel. Texture can be added to attract or repel interest to a visual element. Visual texture is the illusion of the surfaces peaks and valleys, resulting in a feeling of smoothness or roughness in objects. e. Color – determined by its hue (name of color), intensity (purity of the hue), and value (lightness or darkness of hue). Color and color combination can play a large role in the design. f. Form – a figure having volume and thickness. An illusion of a 3-dimensional object can be implied with the use of light and shading. Form can be viewed from many angles. Visual Design Principles are: 1. Consistency of margins, typeface, typestyle, and colors is necessary, especially in slide presentations or documents that are more than one page. 2. . Center of interest – an area that first attracts attention in a composition. This area is more important when compared to the other objects or elements in a composition. This can be by contrast of values, more colors, and placement in the format. 3. Balance – a feeling of visual equality in shape, form, value, color, etc. Balance can be symmetrical and evenly balanced, or asymmetrical and unevenly balanced. Objects, values, colors, textures, shapes, forms, etc. 4. Harmony – brings together a composition with similar units. If for example your composition was using wavy lines and organic shapes, you would stay with those types of lines and not put in just one geometric shape. (Notice how similar Harmony is to Unity - some sources list both terms). 5. Contrast – offers some change in value creating a visual discord in a composition. Contrast shows the difference between shapes and can be used as a background to bring objects out and forward in a design. It can also be used to create an area of emphasis. 6. Directional Movement – a visual flow through the composition. It can be the suggestion of motion in a design as you move from object to object by way of placement and position. 7. Rhythm – a movement in which some elements recur regularly. Like a dance, it will have a flow of objects that will seem to be like the beat of music. 8. Perspective – created through the arrangement of objects in twodimensional space to look like they appear in real life. Perspective is a learned meaning of the relationship between different objects seen in space. Audio Information and Media a. Radio broadcast - live or recorded audio sent through radio waves to reach a wide audience. b. Music - vocal and/or instrumental sounds combined in such a way as to produce beauty of form, harmony, and expression of emotion. c. Sound recording - recording of an interview, meeting, or any sound from the environment. d. Sound clips/effects - any sound, other than music or speech, artificially reproduced to create an effect in a dramatic presentation, as the sound of a storm or a creaking door. e. Audio Podcast - a digital audio or video file or recording, usually part of a themed series, that can be downloaded from a website to a media player or computer. Different ways of storing audio media: a. Tape - magnetic tape on which sound can be recorded. b. CD - a plastic-fabricated, circular medium for recording, storing, and playing back audio, video, and computer data. c. USB drive - an external flash drive, small enough to carry on a key ring, that can be used with any computer that has a USB port. d. Memory Card - (aka flash memory card or storage card) is a small storage medium used to store data such as text, pictures, audio, and video, for use on small, portable, or remote computing devices. e. Computer hard drive - secondary storage devices for storing audio files. f. Internet/Cloud - websites or file repositories for retrieving audio files, and more precisely the files are stored in some datacenter full of servers that is connected to the Internet. Different audio file formats: a. MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3) - a common format for consumer audio, as well as a standard of digital audio compression for the transfer and playback of music on most digital audio players. b. M4A/AAC (MPEG-4 Audio/Advanced Audio Coding) - an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates. c. WAV - is a Microsoft audio file format standard for storing an audio bitstream on PCs. It has become a standard file format for game sounds, among others. d. WMA (Windows Media Audio) - is an audio data compression technology developed by Microsoft and used with Windows Media Player. Sound Characteristics and Purposes a. Elements of Sound Design – the objects or things that we have to work with: • Dialogue - speech, conversation, voiceover. • Sound Effects - any sound other than music or dialogue. • Music - vocal or instrumental sounds (or both) combined in such a way as to produce beauty of form, harmony, and expression of emotion. • Silence - absence of audio or sound. Principles of Sound Design • Mixing - the combination, balance and control of multiple sound elements. • Pace - Time control. Editing. Order of events: linear, non-linear, or multilinear. • Transitions - How you get from one segment or element to another. Types of transitions: - Segue - one element stops, the next begins ("cut" in film). - Cross-fade - one element fades out, the next fades in, and they overlap on the way. - V-Fade - First element fades to inaudible before the second element begins. - Fade to Black - V-Fade with some silence between elements. - Waterfall - As first element fades out, the second element begins at full volume. Better for voice transitions, than for effects. • Stereo Imaging - Using left and right channel for depth. Motion Media and Information • Speed, direction and timing should depict natural laws of physics. This included trajectories, impact on objects and reactions of the environment. • Timing affects recall. Fast movement sends much information Slow movement provides emphasis and lasting recall. • Transitions are used to switch between scenes. Having a clear start and finish in your motion path or scenes Using neutral colors at the start or end of a scene is a good method for creating the right mindset. • Sound and color adds depth and meaning to movement. • Cartooning your graphic and text provides dynamic movement. This can be done by using the following movements: stretching, rotating, squashing • Blurring can be used in different ways. In animation, blurring can provide the illusion of fast movement. Manipulatives / Interactive Media . Interactive Media – a method of communication in which the program's outputs depend on the user's inputs, and the user's inputs in turn affect the program's outputs. Interactivity – the communication process that takes place between humans and computer software. Different platforms of interactive media: a. Mobile apps - a software application developed specifically for use on small, wireless computing devices such as smartphones and tablets, rather than desktop or laptop computers. b. 3D TV - a television display technology that enables a threedimensional effect, so that viewers perceive that an image has depth as well as height and width, similar to objects in the real world. c. Video games (multi-player) - a game played by electronically manipulating images produced by a computer program on a television screen or other display screen. Multiplayer games allow two or more players to play with one another or play together. d. Role-playing games (RPG) - a game in which players assume the roles of characters in a fictional setting. e. Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Game (MMORPG) - any storydriven online video game in which a player, taking on the persona of a character in a virtual or fantasy world, interacts with a large number of other players. f. Interactive websites (pools, surveys, exams, exercises) g. Virtual reality and immersive environments - the computer-generated simulation of a threedimensional image or environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by a person using special electronic equipment, such as a helmet with a screen inside or gloves fitted with sensors. h. Social media - websites or online services where users (actual people) are the creators and consumers of the content, and where social interactions (commenting, liking, posting, talking) are the main features of content.