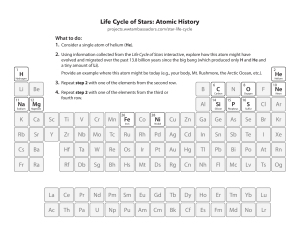
Was the Big Bang Actually an Explosion? • The “big bang” wasn’t a “bang” at all, at least not in the common definition. It didn’t explode in a scene of shrapnel and fire, and there was definitely no mushroom cloud. https://www.britannica.com/story/was-the-big-bang-actually-an-explosion • The big-bang theory of the universe is derived from Albert Einstein’s general theory of relativity and the idea that the universe expanded from a miniscule dense collection of energy called a singularity. • There was no bang, just a vast expansion of extremely condensed material. https://www.britannica.com/story/was-the-big-bang-actually-an-explosion The Big Bang and the Elements Elements and the ‘Big Bang’ theory • During the formation of the universe some 14 billion years ago in the so-called ‘Big Bang’, only the lightest elements were formed – hydrogen and helium along with trace amounts of lithium and beryllium. • As the cloud of cosmic dust and gases from the Big Bang cooled, stars formed, and these then grouped together to form galaxies. Elements and the ‘Big Bang’ theory • The other 86 elements found in nature were created in nuclear reactions in these stars and in huge stellar explosions known as “Supernova”. Elements and the ‘Big Bang’ theory Elements and the ‘Big Bang’ theory Elements and our Sun • For most of their lives, stars fuse elemental hydrogen into helium in their cores. • Two atoms of hydrogen are combined in a series of steps to create helium-4. • These reactions account for 85% of the Sun’s energy. The remaining 15% comes from reactions that produce the elements beryllium and lithium. The Sun At this stage of our Sun’s life cycle, hydrogen atoms are fused to form helium atoms. This nuclear reaction produces very large amounts of energy. FORMATION OF THE ELEMENTS DURING THE BIG BANG AND DURING STELLAR EVOLUTION ELEMENTS WERE FORMED DURING THE BIG BANG • In the beginning, or at least following the Big Bang more than 14 billion years ago, there was hydrogen, some helium and a little bit of lithium FORMATION OF THE ELEMENTS DURING STELLAR EVOLUTION • Incredibly massive stars continue fusion from helium until they create iron (Fe) in their core. • In this fusion process, these massive stars create neon (Ne), magnesium (Mg), oxygen (O), sulfur (S), silicon (Si) and finally iron (Fe). Big Bang Nucleosynthesis • Light elements (namely deuterium, helium, and lithium) were produced in the first few minutes of the Big Bang, • Heavier elements than helium are thought to have their origins in the interiors of stars which formed much later in the history of the Universe. Big Bang Nucleosynthesis • Nucleosynthesis • occurs when Proton & Neutron combine Stellar Formation And Evolution • Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. • Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. DYING STAR • When a star’s core runs out of hydrogen, the star begins to die out. DYING STAR • The dying star expands into a red giant, and this now begins to manufacture carbon atoms by fusing helium atoms. DYING STAR • More massive stars begin a further series of nuclear burning or reaction stages. The elements formed in these stages range from oxygen through to iron. DYING STAR • During a supernova, the star releases very large amounts of energy as well as neutrons, which allows elements heavier than iron, such as uranium and gold, to be produced. • In the supernova explosion, all of these elements are expelled out into space. Atomic Number Symbol Element Name Mass Number Proton = Atomic Number Electron =Proton Neutron = mass # - proton SYMBOL C ____ He ____ ____ ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER 6 8 ____ 10 ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 5 ____ 8 2 10 6 ____ 8 2 10 ____ ATOMIC MASS 12 ____ 4 ____ ____ Nucleosynthesis occurs when Proton & Neutron combine 1 1 H 1 2 H 1 3 H •FORMATION OF LIGHT ELEMENTS •FORMATION OF HEAVIER ELEMENTS End End End SYMBOL ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER C 6 1.___ 4.___ 8 5.___ He 7.___ 8.___ 9.___ 10 11.__ B 13.__ 5 2.___ 8 2 10 6 3.___ 8 2 10 14.__ ATOMIC MASS 12 6.__ 4 12.__ 15.__ SYMBOL C O He Ne B ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER 6 8 2 10 5 6 8 2 10 5 6 8 2 10 6 6 8 2 10 5 ATOMIC MASS 12 16 4 20 11