Uploaded by
June Dalumpines
Heredity & Variation Lesson Plan: Genetics for High School
advertisement
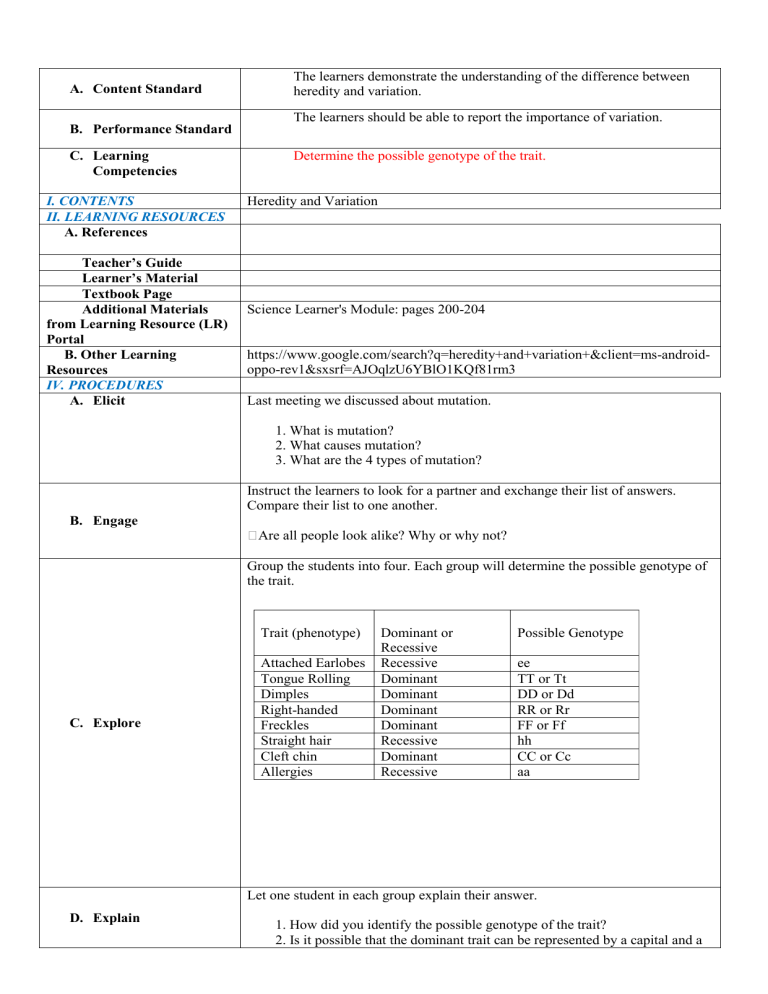
A. Content Standard The learners demonstrate the understanding of the difference between heredity and variation. The learners should be able to report the importance of variation. B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competencies I. CONTENTS II. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References Teacher’s Guide Learner’s Material Textbook Page Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) Portal B. Other Learning Resources IV. PROCEDURES A. Elicit Determine the possible genotype of the trait. Heredity and Variation Science Learner's Module: pages 200-204 https://www.google.com/search?q=heredity+and+variation+&client=ms-androidoppo-rev1&sxsrf=AJOqlzU6YBlO1KQf81rm3 Last meeting we discussed about mutation. 1. What is mutation? 2. What causes mutation? 3. What are the 4 types of mutation? Instruct the learners to look for a partner and exchange their list of answers. Compare their list to one another. B. Engage �Are all people look alike? Why or why not? Group the students into four. Each group will determine the possible genotype of the trait. Trait (phenotype) C. Explore Attached Earlobes Tongue Rolling Dimples Right-handed Freckles Straight hair Cleft chin Allergies Dominant or Recessive Recessive Dominant Dominant Dominant Dominant Recessive Dominant Recessive Possible Genotype ee TT or Tt DD or Dd RR or Rr FF or Ff hh CC or Cc aa Let one student in each group explain their answer. D. Explain 1. How did you identify the possible genotype of the trait? 2. Is it possible that the dominant trait can be represented by a capital and a small letter? 3. What do you call that trait if its genotype are both small letters? Let the student understand heredity and variation. To understand better, ask the student the following questions: E. Elaborate 1. What is heredity? 2. What is genetic variation? 3. Differentiate heredity and variation. 4. Why do different people have different trait? 5. How allele affect variation? Let the learners answer the following questions. 1. It is the transmission of genetic characters from parents to offspring. 2. Any of the alternative forms of gene in a genotype and represents by a letter? 3. Refers to the difference between individual. 4. An observable characteristics of an organism. 5. It is weak, unexpressed trait of pair that has no effect in the phenotype. Determine whether the trait is dominant or recessive. F. Evaluate 6. Curly hair - CC 7. Dimples - Dd 8. Left handed - ff 9. Green eyes - Gg 10. Pointed nose - nn Answer key: 1. Heredity 2. Alleles 3. Variation 4. Phenotype 5. Recessive traits 6. Dominant 7. Dominant 8. Recessive 9. Dominant 10. Recessive G. Extend V. REMARKS/REFLECTION Research about Mendelian Genetics.