Higher Nationals
Internal verification of assessment decisions – BTEC (RQF)
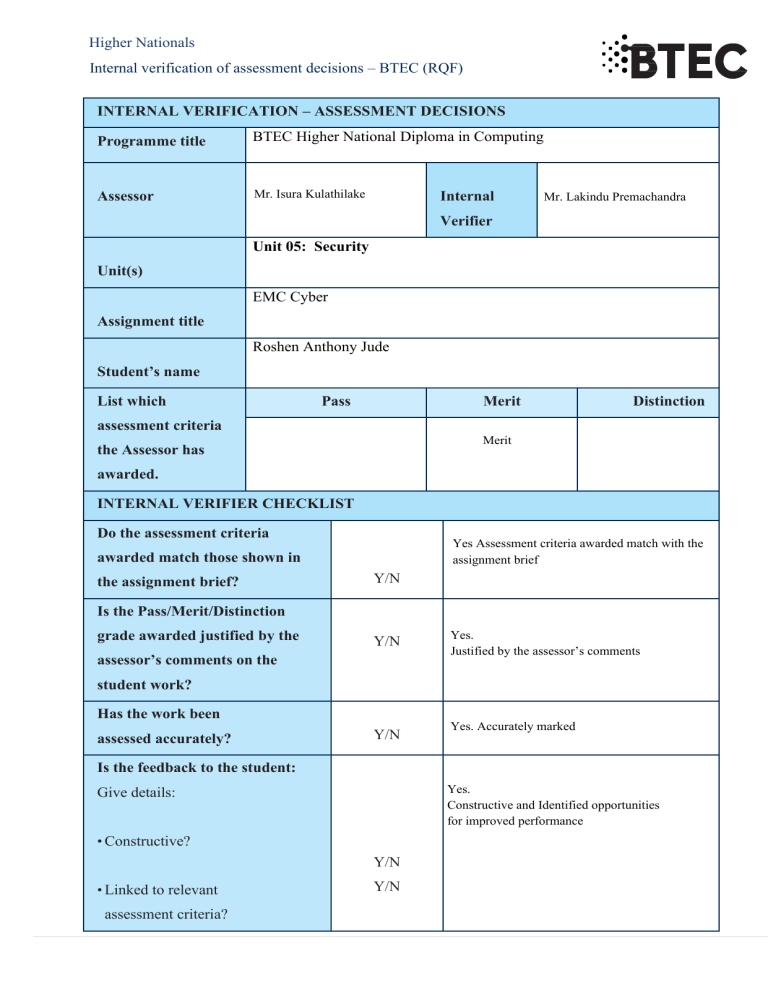
INTERNAL VERIFICATION – ASSESSMENT DECISIONS
Programme title
BTEC Higher National Diploma in Computing
Assessor
Mr. Isura Kulathilake
Internal
Mr. Lakindu Premachandra
Verifier
Unit 05: Security
Unit(s)
EMC Cyber
Assignment title
Roshen Anthony Jude
Student’s name
List which
Pass
Merit
Distinction
assessment criteria
Merit
the Assessor has
awarded.
INTERNAL VERIFIER CHECKLIST
Do the assessment criteria
Yes Assessment criteria awarded match with the
assignment brief
awarded match those shown in
the assignment brief?
Y/N
Is the Pass/Merit/Distinction
grade awarded justified by the
Y/N
assessor’s comments on the
Yes.
Justified by the assessor’s comments
student work?
Has the work been
assessed accurately?
Y/N
Yes. Accurately marked
Is the feedback to the student:
Yes.
Constructive and Identified opportunities
for improved performance
Give details:
• Constructive?
Y/N
• Linked to relevant
assessment criteria?
Y/N
• Identifying opportunities
for improved
Y/N
Y/N
performance?
• Agreeing actions?
Does the assessment decision
need amending?
Assessor signature
Y/N
isuranilupul@gmail.com
Date
lakinducp@gmail.com
Internal Verifier signature
Date
Programme Leader
signature (if required)
Date
18.19.2021
18.09.2021
Confirm action completed
Remedial action taken
Give details:
Assessor signature
Date
Internal Verifier
signature
Date
Programme Leader
signature (if required)
Date
Higher Nationals - Summative Assignment Feedback Form
Student Name/ID
Roshen Anthony
Unit Title
Unit 05: Security
Assignment
1
Assessor
Mr. Isura Kulathilake
Number
Date Received
Submission Date
16.05.2021
16.05.2021
1st
submission
Date Received 2nd
Re-submission Date
submission
Assessor Feedback:
LO1. Assess risks to IT security
Pass, Merit &
P1
P2
M1
D1
P4
M2
D1
Distinction Descripts
LO2. Describe IT security solutions.
Pass, Merit &
P3
Distinction Descripts
LO3. Review mechanisms to control organisational IT security.
Pass, Merit &
P5
P6
M3
M4
M5
D3
Distinction Descripts
LO4. Manage organisational security.
Pass, Merit &
Distinction Descripts
P7
P8
D2
Grade: Merit
Assessor Signature: isuranilupul@gmail.com
Date: 18.09.2021
Resubmission Feedback:
Grade:
Assessor Signature:
Date:
Internal Verifier’s Comments:
The learner has gained more theoretical knowledge about network security. And also, the learner has done D3, D2 criteria but missed D1. Therefore, the learner needs to study how to secure network by adding more software
and hardware security configurations and tools. Furthermore, needs to explain how the IT solution be the "Trusted Network" with those configurations. The grading criteria have been clearly identified and completed but need
more potential when completing D criteria to achieve D grade. And the first marking assessor did an excellent job marking the work and agreeing with the grade.
Signature & Date: lakinducp@gmail.com
18.09.2021
* Please note that grade decisions are provisional. They are only confirmed once
internal and external moderation has taken place and grades deci
General Guidelines
1. A Cover page or title page – You should always attach a title page to your
assignment. Use previous page as your cover sheet and make sure all the details
are accurately filled.
2.
Attach this brief as the first section of your assignment.
3. All the assignments should be prepared using a word processing software.
4. All the assignments should be printed on A4 sized papers. Use single side
printing.
5. Allow 1” for top, bottom , right margins and 1.25” for the left margin of each
page.
Word Processing Rules
1. The font size should be 12 point, and should be in the style of Time New
Roman.
2. Use 1.5 line spacing. Left justify all paragraphs.
3. Ensure that all the headings are consistent in terms of the font size and font
style.
4. Use footer function in the word processor to insert Your Name, Subject,
Assignment No, and Page Number on each page. This is useful if individual
sheets become detached for any reason.
5. Use word processing application spell check and grammar check function to
help editing your assignment.
Important Points:
1. It is strictly prohibited to use textboxes to add texts in the assignments, except
for the compulsory information. eg: Figures, tables of comparison etc. Adding
text boxes in the body except for the before mentioned compulsory information
will result in rejection of your work.
2. Carefully check the hand in date and the instructions given in the assignment.
Late submissions will not be accepted.
3. Ensure that you give yourself enough time to complete the assignment by the
due date.
4. Excuses of any nature will not be accepted for failure to hand in the work on
time.
5. You must take responsibility for managing your own time effectively.
6. If you are unable to hand in your assignment on time and have valid reasons
such as illness, you may apply (in writing) for an extension.
7. Failure to achieve at least PASS criteria will result in a REFERRAL grade .
8. Non-submission of work without valid reasons will lead to an automatic RE
FERRAL. You will then be asked to complete an alternative assignment.
9. If you use other people’s work or ideas in your assignment, reference them
properly using HARVARD referencing system to avoid plagiarism. You have
to provide both in-text citation and a reference list.
10. If you are proven to be guilty of plagiarism or any academic misconduct, your
grade could be reduced to A REFERRAL or at worst you could be expelled
from the course
Student Declaration
I hereby, declare that I know what plagiarism entails, namely to use another’s work and
to present it as my own without attributing the sources in the correct way. I further
understand what it means to copy another’s work.
1. I know that plagiarism is a punishable offence because it constitutes theft.
2. I understand the plagiarism and copying policy of the Edexcel UK.
3. I know what the consequences will be if I plagiarize or copy another’s work in
any of the assignments for this programme.
.
4. I declare therefore that all work presented by me for every aspects of my
programme, will be of my own, and where I have made use of another’s work,
I will attribute the source in the correct way.
5. I acknowledge that the attachment of this document, signed or not, constitutes
a binding agreement between myself and Pearson UK.
6. I understand that my assignment will not be considered as submitted if this
document is not attached to the main submission.
roshen.anthony@gmail.com
Student’s Signature:
(Provide E-mail ID)
16.09.2021
2021/11/01
Date:
(Provide Submission Date)
Assignment Brief
Student Name /ID Number
Roshen Anthony
Unit Number and Title
Unit 5- Security
Academic Year
2020/2021
Unit Tutor
Mr. Isura Kulathilake
Assignment Title
EMC Cyber
Issue Date
Submission Date
IV Name & Date
10.02.2021
16.05.2021
Mr. Lakindu Premachandra
18.09.2021
Submission Format:
The submission should be in the form of an individual written report written in a concise, formal business
style using single spacing and font size 12. You are required to make use of headings, paragraphs and
subsections as appropriate, and all work must be supported with research and referenced using Harvard
referencing system. Please provide in- text citation and an end list of references using Harvard
referencing system.
Section 4.2 of the assignment required to do a 15 minutes presentation to illustrate the answers.
Unit Learning Outcomes:
LO1 Assess risks to IT security.
LO2 Describe IT security solutions.
LO3 Review mechanisms to control organisational IT security.
LO4 Manage organisational security.
Assignment Brief and Guidance:
Scenario
‘EMC Cyber’ is a reputed cyber security company based in Colombo Sri Lanka that is delivering security
products and services across the entire information technology infrastructure. The company has a
number of clients both in Sri Lanka and abroad, which includes some of the top-level companies of the
world serving in multitude of industries. The company develops cyber security software including
firewalls, anti-virus, intrusion detection and protection, and endpoint security. EMC Cyber is tasked with
protecting companies’ networks, clouds, web applications and emails. They also offer advanced threat
protection, secure unified access, and endpoint security. Further they also play the role of consulting
clients on security threats and how to solve them. Additionally the company follows different risk
management standards depending on the company, with the ISO 31000 being the most prominent.
One of the clients of EMC Cyber, Lockhead Aerospace manufacturing which is a reputed aircraft
manufacturer based in the US, has tasked the company to investigate the security implications of
developing IOT based automation applications in their manufacturing process. The client has requested
EMC to further audit security risks of implementing web based IOT applications in their manufacturing
process and to propose solutions. Further, Lockhead uses ISO standards and has instructed EMC to use
the ISO risk management standards when proposing the solution.
The director of the company understands such a system would be the target for cyber-attacks. As you
are following a BTEC course which includes a unit in security, the director has asked you to investigate
and report on potential cyber security threats to their web site, applications and infrastructure. After the
investigation you need to plan a solution and how to implement it according standard software
engineering principles.
Activity 01
Assuming the role of External Security Analyst, you need to compile a report focusing on following
elements to the board of EMC Cyber’;
1.1 Identify the CIA Triad concept and evaluate why and how the CIA Triad could be utilize to EMC
Cyber in order to improve the organization’s security.
1.2 Identify types of security risks EMC Cyber is subject to its present setup and the impact that they
would make on the business itself. Evaluate at least three physical and virtual security risks identified
and suggest the security measures that can be implemented in order to improve the organization’s
security.
1.3 Develop and describe security procedures for EMC Cyber to minimize the impact of issues
discussed in section (1.1) by assessing and rectifying the risks.
Activity 02
2.1 Identify how EMC Cyber and its clients will be impacted by improper/ incorrect configurations
that are applicable to firewalls and VPN solutions. IT security can include a network monitoring
system. Discuss how EMC cyber can benefit by implementing a network monitoring system with
supporting reasons.
2.2 Explain how the following technologies would benefit EMC Cyber and its Clients by facilitating a
‘trusted network’. (Support your answer with suitable examples).
i) DMZ
ii) Static IP
iii)NAT
2.3 Identify and evaluate the tools that can be utilized by EMC cyber to improve the network and
security performance without compromising each other. Evaluate at least three virtual and physical
security measures that can be implemented by EMC to uphold the integrity of organization’s IT policy.
Activity 03
3.1 Discuss suitable risk assessment integrated enterprise risk management procedures for EMC Cyber
solutions and the impact an IT security audit will have on safeguarding organization and its clients.
Furthermore, your discussion should include how IT security can be aligned with an organizational IT
policy and how misalignment of such a policy can impact on organization’s security.
(This can include one or more of the following: network change management, audit control, business
continuance/disaster recovery plans, potential loss of data/business, intellectual property, Data
Protection Act; Computer Misuse Act; ISO 31000 standards.)
3.2 Explain the mandatory data protection laws and procedures which will be applied to data storage
solutions provided by EMC Cyber. You should also summarize ISO 31000 risk management
methodology.
Activity 04
4.1 Design an organizational security policy for EMC Cyber to minimize exploitations and misuses
while evaluating the suitability of the tools used in an organizational policy.
4.2 Develop and present a disaster recovery plan for EMC Cyber according to the ISO/IEC
17799:2005 or similar standard which should include the main components of an organizational
disaster recovery plan with justifications. Discuss how critical the roles of the stakeholders in the
organization to successfully implement the security policy and the disaster recovery plan you
recommended as a part of the security audit.
(Students should produce a 15 minutes PowerPoint presentation which illustrates the answer for
this section including justifications and reason for decisions and options used).
Pearson
Higher Nationals in
Computing
Unit 5: Security
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
1|Page
Contents
1
Acknowledgement ................................................................................................ 6
2
Risks in IT Security .............................................................................................. 7
2.1
2.1.1
Confidentiality ........................................................................................ 7
2.1.2
Information Integrity ............................................................................... 7
2.1.3
Availability ............................................................................................. 7
2.2
Types of Security risks to EMC Cyber .......................................................... 8
2.2.1
Passive attacks ........................................................................................ 8
2.2.2
Active attacks .......................................................................................... 9
2.3
3
CIA Triad Concept ......................................................................................... 7
Security measures for EMC Cyber............................................................... 11
2.3.1
Virtual security measures ...................................................................... 11
2.3.2
Physical security measures ................................................................... 13
2.4
Security procedures for EMC Cyber ............................................................ 15
2.5
Security procedures for EMC Cyber to minimize the impact of issues ....... 18
IT Security solutions ........................................................................................... 21
3.1
The impact of improper configurations that are applicable to firewall and
VPN solutions to EMC Cyber................................................................................. 21
3.1.1
Firewall ................................................................................................. 21
3.1.2
VPN....................................................................................................... 23
3.2
Implementing a DMZ, static IP and NAT in a network can improve network
security .................................................................................................................... 24
3.2.1
DMZ ...................................................................................................... 24
3.2.2
IP Address (Internet protocol address) ................................................. 25
3.3
The benefits of implementing network monitoring systems ........................ 28
3.3.1
4
Benefits of using different network monitoring tools ........................... 30
Mechanisms to control EMC Cyber IT security ................................................. 32
4.1
Risk assessment procedures for EMC Cyber ............................................... 32
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
2|Page
4.2
Data protection process and regulations as applicable to EMC Cyber ........ 35
4.2.1
Data protection act of 1998 ................................................................... 35
4.2.2
Steps of data protection process for EMC Cyber.................................. 36
4.3
Summarizing the ISO 31000 risk management methodology and its
application in IT security ........................................................................................ 39
4.3.1
ISO 31000 risk management methodology........................................... 39
4.4
Impacts to Organizational security resulting from IT security audit ........... 40
4.5
The impact of IT security aligns with organizational policy and the safety
consequences of any misalignment ......................................................................... 43
5
Managing Organizational security ...................................................................... 44
5.1
Designing and implementing a security policy for EMC Cyber .................. 44
5.2
The main components of an organisational disaster recovery plan, justifying
the reasons for inclusion. ........................................................................................ 48
5.3
Disaster recovery plan for EMC Cyber ........................................................ 53
5.4
The roles of stakeholders in the organisation to implement security audit
recommendations. ................................................................................................... 60
5.5
The suitability of the tools used in an organisational policy ........................ 63
5.5.1
Evaluation of the tools used in an organisational policy ...................... 64
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
3|Page
List of Tables
Table 1 Security Procedures for EMC cyber to minimize the impact of issues ......... 20
Table 2 Comparison between dynamic IP .................................................................. 26
Table 3 benefits of using different network monitoring tools .................................... 31
Table 4 Risk Assessment for EMC Cyber .................................................................. 34
Table 5 steps for Data protection process for EMC Cyber ......................................... 38
Table 6 Common IT Security audit standards ............................................................ 42
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
4|Page
List of figures
Figure 1 Example for DMZ ........................................................................................ 24
Figure 2 Disaster recovery plan slide 1....................................................................... 53
Figure 3 Disaster recovery plan slide 2....................................................................... 53
Figure 4 Disaster recovery plan slide 3....................................................................... 54
Figure 5 Disaster recovery plan slide 4....................................................................... 54
Figure 6 Disaster recovery plan slide 5....................................................................... 55
Figure 7 Disaster recovery plan slide 6....................................................................... 55
Figure 8 Disaster recovery plan slide 7....................................................................... 56
Figure 9 Disaster recovery plan slide 8....................................................................... 56
Figure 10 Disaster recovery plan slide 9..................................................................... 57
Figure 11 Disaster recovery plan slide 10................................................................... 57
Figure 12 Disaster recovery plan slide 11................................................................... 58
Figure 13 Disaster recovery plan slide 12................................................................... 58
Figure 14 Disaster recovery plan slide 13................................................................... 59
Figure 15 Disaster recovery plan slide 14................................................................... 59
Figure 16 Gantt Chart ................................................................................................. 67
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
5|Page
1
Acknowledgement
Many people have contributed to the success of this Report. Although a single sentence
hardly suffices, the author would like to thank Almighty God for blessing him with his
grace.
The author is profoundly indebted to his class guide, Mr. Isura Kulathilaka, for
innumerable acts of timely advice; encouragement and the author sincerely express his
gratitude to her. Her guidance made the author to successfully complete the report. The
author extends his sincere and heartfelt thanks to Mr. Isura Kulathilaka, for providing
him the right ambiance for carrying out this work.
The author expresses his immense pleasure and thankfulness to all the teachers and
staff for the cooperation and support. In addition, a huge thank to the google and other
sources that the author have used in this report.
Last but not the least, he thanks all others, and especially his classmates who in one
way or another helped him in the successful completion of this work.
The author hopes contributors will recognize that he has done his best to reflect the
variety of views and the wealth of information, which were so generously provided, to
him. The author takes full and sole responsibility for the content of the report and for
any errors or misrepresentations of fact or opinion it may contain.
Regards,
The Author,
Roshen Anthony
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
6|Page
2
Risks in IT Security
Information security refers to the safeguarding of data, particularly as it is being
processed. IT security aims to keep unauthorized third parties from tampering with data
and systems. This means that socio-technical systems within firms / organizations, i.e.,
people and technology, as well as their data, are safeguarded from harm and dangers.
This includes not only data and information, but also physical data centers and cloud
services.
2.1
CIA Triad Concept
Over the last few years, information has grown increasingly precious. As a result, it is
much more critical to safeguard it. The three IT protection goals of availability,
integrity, and secrecy characterize information security. These three parts are known
as CIA Triad Concept.
2.1.1 Confidentiality
IT Security confidentiality means that data is only available to authorized individuals.
Only a limited number of people, for example, have access to the information it
contains. To put it another way, access control must be defined. This necessitates the
assignment of access rights.
The conveyance of data is another crucial aspect of information secrecy. This should
be encrypted at all times, whether symmetrically or asymmetrically. Unauthorized
individuals will be unable to access the information.
2.1.2 Information Integrity
The information's integrity should be seen, with the contents and data being complete
and correct at all times. As a result, the systems must cooperate for their mutual
advantage. Data must not be modified as a result of a sales or processing transaction in
order to be used. As a result, it's also worth noting that the authoritative Third party
will never get access to (even a portion of) the data. Because it is only conceivable to
make a mistake, it must be demonstrated that this art of manipulation can be avoided,
enhanced in terms of safety, and applied.
2.1.3 Availability
Having the appropriate information available ensures that data processing within the
systems goes smoothly. The data must be retrievable in a timely and accurate manner.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
7|Page
This necessitates the protection of computer systems against failure. This is why load
testing is used to check the limitations, ensuring that company operations are not
disrupted.
Use of CIA Triad Concept for Cyber
The CIA trio provides a high-level checklist for evaluating your security procedures
and equipment that is both easy and thorough. All three components of an effective
system are met: secrecy, integrity, and availability. It is insufficient to have an
information security system that is lacking in one of the three parts of the CIA trinity.
After a negative occurrence, the CIA security triangle is also useful in determining what
went wrong—and what worked. For example, if availability was harmed as a result of
a ransomware assault, but the mechanisms in place were still able to protect the
confidentiality of sensitive data. This information can be utilized to correct flaws and
replicate effective policies and procedures in EMC Cyber.
2.2
Types of Security risks to EMC Cyber
When considering the Security Attacks, these can be categorized as Passive and Active.
2.2.1 Passive attacks
A passive attack occurs when the attacker does not attempt to modify or affect the target
system's resources. Instead, the attacker is attempting to obtain or learn information
from that system.
Eavesdropping and monitoring of networks and communications are examples of
passive attacks. Listening in on communications and transmissions is referred to as
eavesdropping. For example, we could use a network monitoring tool to examine the
data transmitted by a Wi-Fi router. It would be an example of passive attack if we were
to listen in on and record a phone conversation (and possibly release the recording to
the public).
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
8|Page
2.2.2 Active attacks
An active attack occurs when the attacker attempts to alter the system (for example, by
changing data or settings) or to interfere with the system's operation. Masquerading,
replaying, modification, and denial of service are examples of active attacks.
Masquerading is the act of pretending to be someone or something else in order to fool
the system into thinking we are someone else. This could come in handy if we want to
trick the system into granting us access, or if we want to leave a false trail of evidence
that points to someone else.
EMC cyber is reputed and reliable IT security service provider based in the Colombo
Sri lanka. The EMC cyber has both abroad and Sri Lankan clients. So, EMC should
have the best secured data centres but there are some vulnerabilities which are
identified by the author. Those are,
•
Failure of the server
•
DDoS assaults are a type of distributed denial of service attack.
•
Inadequate data backups and data loss
•
The vulnerabilities of cloud service providers
•
Cloud-based phishing
•
Attacks on the virtual machine level
•
Attacks based on social engineering
•
Vulnerabilities in the system
•
Unauthorized access Malicious code
•
Natural calamity
Organizational Risks,
•
Reputation risk
•
Financial risk
•
Operational risk
•
Legal risk
•
Strategic Risk
•
Technology risk
•
People/culture risk
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
9|Page
•
Fraud risk
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
10 | P a g e
2.3
Security measures for EMC Cyber
Keeping the EMC Cyber data is very important. Since there are several threats security
measures are very important. Security measures can be categorized as two main parts.
•
Virtual Security measures
•
Physical security measures
2.3.1 Virtual security measures
Backup/ restoration of data
A backup is a copy of your data that you make for safekeeping. The backup should then
be stored somewhere secure so that it can be safely retrieved if needed.
Some people get the terms backup and archive mixed up. A backup is a duplicate copy
of your data that you keep for safekeeping. An archive is your primary data that you
simply move to another location because you don't need it right now but may need it in
the future.
There are various types of backup methods from which to choose.
Full backup
This is the most basic type and is a full backup of all of your data. The benefit is that
your entire backup is available in one location or medium. The disadvantage is that if
you have a large amount of data to backup, it will take a long time to complete the
backup.
Incremental backup
Here, you first start by taking a full backup. Then, your backup only what has changed
since your last backup. The benefit is that your backup process will take less time and
space, but there is the disadvantage that you have to maintain multiple volumes.
Differential back up
This is very similar to an incremental backup, except that your subsequent backup
includes everything from your last full backup onward.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
11 | P a g e
Audits
Auditing is the on-site verification of a process or quality system, such as inspection or
examination, to ensure compliance with requirements. A security audit for IT systems
would be a manual or systematic assessment to ensure that the proper procedures and
policies are in place, and that people are properly trained on how to respond to specific
situations that may compromise a system's security.
As part of an audit, we may verify that all systems are functioning as expected, that
proper backups and precautions are taken, that disaster recovery procedures are in
place, that people are properly trained, and that policies are properly understood and
implemented.
Testing procedures
There are several methods for testing networks. Some of the options available to you
are as follows:
Testing the Network, WAN, Intranet etc.
•
Vulnerability Scanning: This is performed using automated software to scan a
system for known vulnerability signatures.
•
Security Scanning: This involves identifying network and system flaws and
then providing solutions to mitigate these risks. This scanning can be done both
manually and automatically.
•
External Penetration Testing: The goal of this testing is to determine whether
someone outside your organization can access your critical information assets
from the internet by exploiting weaknesses in your perimeter. This is
considered ethical hacking.
•
Internal Penetration Testing: The goal is to determine whether internal staff or
someone with physical access to your premises can access information assets
that they do not have access to. This is a type of ethical hacking.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
12 | P a g e
Testing systems
•
Security auditing: Security auditing is an internal check for security flaws in
applications and operating systems. Line-by-line code inspection can also be
used for auditing.
•
Security scanning: This involves identifying network and system flaws and then
providing solutions to mitigate these risks. This scanning can be done both
manually and automatically.
•
Penetration testing: The goal of this testing is to determine whether someone
outside your organization can access your cjritical information assets from the
internet by exploiting weaknesses in your perimeter. This is considered ethical
hacking
•
Web application Security assessment: The goal of this exercise is to assess and
identify vulnerabilities that can be exploited via web applications and services
made available to clients, employees, and others... Such flaws may enable an
attacker to exploit the application and extract its data, as well as further elevate
their privileges. This is an instance of ethical hacking.
2.3.2 Physical security measures
Locking server room
You should double-check that the server room door is securely locked even before you
shut down servers, and even until you first turn them in. Of course, the best lock in the
world won't help you if you don't use it, so policies requiring that those doors be closed
whenever the room is unattended, as well as who has the key or keycode to go in, will
be necessary. The server room is the heart of your network, and it can cause massive
damage if it gets compromised. To prevent this, make sure that everyone has physical
access to all of the devices that are connected to it
Setup surveillance
Getting people to enter and out of the server room is a good start, but it can be
dangerous if someone has unauthorized access. A good way to prevent this is by
implementing an electronic access system or a log book. This method works by creating
a record that identifies each person who enters the room.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
13 | P a g e
Motion Detection Cameras can monitor continuously or they can use technology to
detect when someone is moving around. They can also send e-mails or text message
notifications if they detect motion.
Keep most vulnerable devices in a lock room
Remember, it's not only the servers about which you have to worry. A hacker can
connect a laptop to a hub and use sniffer software to capture network-wide data. Ensure
you have as many of your network devices as possible in the locked room or in the
locked closet elsewhere in the facility if they have to be in a different area.
Protect portable devices
Special physical security risks arise from laptops and handheld computers. The entire
computer can be easily robbed from a thief, including any recorded data and passwords
to the network connection. If employees use their desks on laptops, when leaving or
secure a permanent fixture with a cable lock, they should take them with them.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
14 | P a g e
2.4
Security procedures for EMC Cyber
A security procedure is a set of steps that must be followed in order to complete a
certain security duty or function. Procedures are typically developed as a set of actions
to be performed in a consistent and repeatable manner to achieve a specific goal.
Security procedures, once developed, give a set of established steps for performing the
organization's security affairs, making training, process auditing, and process
improvement easier. Procedures serve as a starting point for establishing the uniformity
required to reduce variation in security procedures, hence improving security control
inside the business. In the security sector, reducing variance is also an excellent method
to reduce waste, improve quality, and boost performance.
The following rules and procedures are required by the organizational security
program.
Physical security procedures for EMC Cyber.
Physical security measures are intended to keep buildings safe and secure while also
protecting the equipment inside. In a nutshell, they keep undesired people out while
allowing authorized individuals in. While network and cybersecurity are crucial,
physical security breaches and threats must be avoided in order to keep your technology
and data safe, as well as any staff or faculty members who have access to the facility.
Your workplace or facility will be vulnerable to criminal activity if you don't have
physical security policies in place. Physical security concerns include theft, vandalism,
fraud, and even accidents.
The EMC cloud is based on a single structure with a large number of physical
components. Then there's the issue of physical security. Physical security, like logical
security, is critical. Physical security is a type of security technology that protects
people, hardware, networks, and data from physical threats. Multiple levels of
interdependent systems were utilized for physical security.
The physical security plan should also focus on keeping all employees safe, preventing
unwanted access to the network, and keeping hardware components secure.
According to a physical security expert, the physical entrance of a structure or
environment is the first worry. EMC Cyber is based in Colombo and houses all of its
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
15 | P a g e
functions in one location. This is Sri Lanka's busiest and most commercial city. As a
result, EMC may experience certain physical difficulties. Protesters' attacks, for
example, natural disasters. There are several methods that EMC cyber use in Physical
security. Those are,
•
Lock up the server room
•
Set up surveillance
•
Keep most vulnerable devices in a locked room
•
Protect the portable devices
•
Looks
•
Disable drivers in unwanted devices
•
Security lighting
•
Alarm system and sensors
Access Control list (ACL)
Lists of Controlled Access Network traffic filters known as "ACLs" can regulate
incoming and outgoing traffic. ACLs are a set of rules that describe how a packet should
be forwarded or blocked at the router's interface. An ACL is similar to a Stateless
Firewall in that it just restricts, blocks, or allows packets to pass from one source to
another. When you define an ACL for a specific interface on a routing device, all traffic
going through that interface is compared to the ACL statement, which will either block
or allow it. The source, destination, a specific protocol, or other information could be
used to define the ACL rules. ACLs are commonly found in routers and firewalls, but
they can also be configured in any network device, including hosts, network devices,
servers, and so on.
According to investigation that given by the Director of the company, the EMC is
mainly vulnerable in Hardware and Software security. As an investigator the author
suggests below steps to increase the security of EMC cyber.
Hardware Area
•
Replace obsolete computers, laptops, and notebooks with newer models.
•
Remove the old EMC router from the network.
•
Drivers and encryption mechanisms should be updated.
•
Use biometric authentication for access
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
16 | P a g e
Software Area
•
Operating systems that have been patched or updated.
•
Updated or patched productivity software, as well as patched web browsers.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
17 | P a g e
2.5
Security procedures for EMC Cyber to minimize the impact of issues
Organizational Risk
Data loss
Data Quality
Preventing procedure
•
Always Backup Data
•
Diversify EMC backups
•
Encrypt EMC sensitive data
•
Address data security
•
Use antivirus and email security
•
Extensive data profiling and
control of incoming data are
required.
•
It is necessary to perform
extensive data profiling and
management of incoming data.
•
Accurate gathering of data
requirements.
•
Enforcement of data integrity.
•
Integration of data lineage
traceability into the data
pipelines.
•
Automated regression testing as
part of change management.
Infrastructure Risk
Operational Risk
•
Secure remote access
•
Create inventory of assets
•
Identify and patch vulnerabilities
•
Monitor for anomalies
•
Integrate OT and IT networks
•
Implement precise change
management processes
•
Restrict access to network
devices
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
18 | P a g e
•
Give your employees the
minimum access
•
Implement dual control.
•
Automate tasks to reduce the
need for human intervention
•
Incident response and disaster
recovery planning
Strategy risk
•
Examine the current system of
internal controls.
•
Working with an internal control
specialist is a good idea.
•
Maintain a high level of safety at
all times.
•
Obtain insurance coverage.
•
Keep your commitments to a
minimum.
Natural Risk
•
Data from the company should
be backed up and stored in a
secure location.
•
To safeguard against fire, use
fire-resistant building materials.
•
Every floor should have a fire
extinguisher.
•
To guard against strong forces,
reinforce doors and windows.
•
Having a first-aid kit, nonperishable food, water, and a
flashlight on hand in case of an
emergency.
Cyber threats
•
Keep software and system fully
updated
•
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
Use a firewall
19 | P a g e
•
WIFI security
•
Give employees to personal
accounts
Table 1 Security Procedures for EMC cyber to minimize the impact of issues
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
20 | P a g e
3
IT Security solutions
3.1
The impact of improper configurations that are applicable to firewall and VPN
solutions to EMC Cyber
3.1.1 Firewall
A firewall is a network security device that analyzes incoming and outgoing network
traffic and determines whether specific traffic should be allowed or blocked based on
a set of security rules.
For more than 25 years, firewalls have served as the first line of defense in network
security. They create a barrier between secure, controlled internal networks that can be
trusted and untrustworthy external networks like the Internet.
A firewall might be hardware, software, or a combination of the two.
There are several types of Firewalls. Those are,
•
Proxy Firewall
•
Stateful inspection firewall
•
Unified threat management firewall
•
Next-generation firewall
•
Threat-focused Next-generation firewall
•
Virtual firewall
A firewall serves as a link between two LAN networks; however, it is unable to deal
with the risks listed below.
Malicious employees
Actually, firewalls are terrible at evaluating and analyzing people's perceptions, as well
as locating data packets with "bad intent." If an employee attempts to engage in
malicious behavior or engages in misconduct, the firewall will be unable to stop them.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
21 | P a g e
Modem users
A firewall will not be able to protect connections that do not flow through it. A firewall
cannot prevent individual users with modems from calling into or out of the network,
thus circumventing the firewall.
Polices
The policies governing the usage of passwords are outside the control of the firewall,
resulting in the misuse of individual passwords and user accounts. This has to be
rigorously adhered to.
Previous attacks
Firewalls offer little protection against previously unknown assaults.
Viruses
Anti-virus protection that is normally down-and-out is provided.
There are common problems are caused by the Conventional Firewalls. Many
loopholes were discovered and discussed after reading and analyzing the standard
firewall. All four types of firewalls, including packet filters, circuit level gateways,
application-level gateways, and stateful multilayer inspection firewalls, have their own
set of wizards and deceptions. A few of them are listed below as well.
•
A packet filtering firewall that solely works at the network level of the OSI
model does not support complex rule-based frameworks.
•
Circuit level gateways operate at the OSI model's session layer, storing
information about protected networks but not straining individual messages.
•
Application-level gateways, sometimes known as proxies, are essentially
similar to circuit level gateways, with the exception that they are application
specific. They also advertise a high level of security, but they have a significant
impact on network performance.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
22 | P a g e
•
Stateful multilayer inspection firewalls include the aforementioned three
firewalls, however they are extremely expensive and, because of their
complexity, may be less secure than simpler firewalls.
3.1.2 VPN
A virtual private network, or VPN, is an encrypted link between a device and a network
via the Internet. The encrypted connection aids in the secure transmission of sensitive
data. It protects against illegal eavesdropping on traffic and allows the user to work
remotely. In corporate settings, VPN technology is commonly used.
A virtual private network (VPN) connects a corporate network to the Internet via
encrypted connections. Traffic remains private as it travels because it is encrypted
between the device and the network. An employee can work from home and still
connect to the company network safely. A VPN can be used to connect even
smartphones and tablets.
There are many security risks that cause by the VPN s. such as,
•
VPN hijacking
•
Data leaks
•
Malware infections
•
Cannot create an enforce policies that protects credentials
•
No third-party accountability
•
No proper encryption methods
•
Keep track of user’s data without permission of user
Since the EMC cyber is providing both local and international services Third-party
VPN are not suitable for the security and the growth of the company. As an investigator
the author suggests not to use third party VPNs.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
23 | P a g e
3.2
Implementing a DMZ, static IP and NAT in a network can improve network
security
3.2.1 DMZ
DMZ is stands for Demilitarized Zone which is in computer networks is a physical or
logical subnet that divide a LAN (local area network) from untrusted networks. Such
as public internet. Perimeter networks or screened subnetworks are also known as
DMZs.
Internal corporate networks are protected by DMZs, which provide a level of network
separation. These sub-networks limit remote access to internal and resource servers,
making access to the internal network difficult for attackers. This strategy is useful for
individual uses as well as large companies.
Web servers, FTP servers, email servers, DNS servers, and VoIP servers are among the
equipment accessible to internet traffic in the Demilitarized Zone. Incoming traffic
from the external network is routed through the DMZ filer.
Figure 1 Example for DMZ
The above figure represents a part of EMC cyber network. According to the DMZ
security method isolated network can be provided for public facing servers. Such as
Web servers and mail servers.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
24 | P a g e
3.2.2 IP Address (Internet protocol address)
An IP address, which is a unique address, identifies a device on the internet or on a
local network. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that govern how data is
transmitted across the internet or a local network.
IP addresses can be classified as two types,
•
Static IP address
•
Dynamic IP address
Dynamic IP
Dynamic IP addresses are those that change on a regular basis. ISPs buy a large range
of Ip addresses and automatically assign them to their customers. They re-assign them
on a regular basis, and the older IP addresses are returned to the pool for use by other
clients. The goal of this method is for the ISP to save money. They don't have to go
through any special procedures to re-establish a customer's IP address if they move
residence, for example, because IP addresses are routinely transferred. There are also
security benefits, since criminals will find it more difficult to obtain access to your
network interface if clients IP address changes.
Static IP
Unlike dynamic IP addresses, static IP addresses do not change. The network assigns
an IP address, which does not change. A static IP address isn't essential for most
individuals and enterprises, but it is for those who want to run their own server. This is
because a static IP address ensures that the websites and email addresses linked with it
have a consistent IP address, which is necessary if you want other devices to be able to
find them regularly on the internet.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
25 | P a g e
The below tables show a comparison between dynamic IP and static IP
Static IP
Dynamic IP
The Network Administrator assigned it
Assigned automatically by the DHCP
manually.
server
More hackable
More secure
The host in a network is given a
In a network, a temporary IP address is
permanent numeric address.
assigned to a host.
Used for dedicated servers such as mail
Connects a huge network to the internet
servers, FTP servers, and VPN servers.
and allows for communication.
Connects a huge network to the internet
and allows for communication.
After it is allocated to the computer, it
If the connection is reset or the DHCP
does not alter automatically.
leases expire, the value changes
automatically.
Table 2 Comparison between dynamic IP
NAT (Network Address Translation)
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technique for conserving IP addresses. It
allows private IP networks to connect to the Internet using IP addresses that have not
been registered. Before packets are forwarded to another network, NAT occurs on a
router, usually linking two networks, and turns private (non-globally unique) internal
network addresses into legal addresses.
As part of this feature, NAT can be configured to only advertise one address for the
entire network to the outside world. By effectively disguising the entire internal
network behind that address, the system's security is enhanced. Because it enables both
security and address conservation, NAT is often employed in remote-access scenarios.
When accessing resources outside of the network, such as the internet, these machines
must have a public address.
This is where NAT comes into play.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
26 | P a g e
When users connect to an outside network, such as the internet, they are all assigned
the same public address. As a result, a single public IP address can be utilized by
hundreds, if not thousands, of people. As a result, EMC's cyber service provider saves
money thanks to NAT. EMC saves money by not having to purchase a public IP address
for each computer. Furthermore, there are a number of advantages to using NAT.
Thanks to the NAT process, the EMC's security has increased. In addition, NAT is an
important part of firewall security.
There are several benefits when DMZ and NAT. The following table shows the
benefits.
DMZ
•
Organizational access control.
•
Prevent intruders from
conducting reconnaissance on
your network.
•
Anti-IP spoofing protection.
•
The DMZ serves to protect the
LAN from internet intruders.
NAT
•
NAT allows numerous devices to
connect to an external network,
such as the internet, using a
single public address.
•
NAT protects IP addresses that
are legally registered.
•
NAT aids in the prevention of
IPv4 address exhaustion.
•
By hiding the original source and
destination addresses, NAT adds
an extra degree of security.
•
Financial prudence.
•
Enhancements to security.
•
EMC compartmentalization ease
could be a network.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
27 | P a g e
3.3
The benefits of implementing network monitoring systems
Network monitoring gives network administrators the information they need to
determine whether a network is performing optimally in real time. Network monitoring
software, for example, can help administrators spot weaknesses early on, increase
productivity, and so on.
Network monitoring systems include software and hardware tools which can track
different aspects, such as traffic, bandwidth use and uptime, of a network and its
operation. These systems detect devices and other network elements and provide status
updates.
Network administrators rely on network surveillance tools to assist them spot failures
or problems like traffic bottlenecks that impede data flow fast. These systems can send
email or text alerts to administrators and generate reports using network analytics.
Continuously monitoring a network system is helps to identify problems and security
risks to the network system. The health of your network can measure with criteria such
as throughput, latency, reordering packets, and jitters.
Troubleshooting issues early, secure the business continuity and networking
monitoring benefits. Such as,
Enhanced growth and scalability
According to the researches there will be 25 billion parts of hardware will categorize
under Inter of things. This means smarter analytics, automated systems, and more will
be grow.
Therefore, EMC cyber will need advance monitoring solutions to keep up to speed. The
increasing demand for the network increases the complexity of the network. It's natural
to believe that relying solely on manual management will result in human error.
However, this is not always the case, so let's look at the numbers.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
28 | P a g e
45% of the downtime is human error. EMC Cyber have clear arguments for automating
the company monitoring together with network problems. Teaching advanced
networking will help EMC Cyber to keep pace with evolving demands. This could
essentially result in easier, better growth that enables you to compete in an everchanging world.
Enhance security
The security of the network is an enormous affair. You may be at risk for malicious
attacks and hacking attempts without a network monitoring service.
Smart network monitoring can provide instant attention to potential threats. The need
to detect and remedy faults by human efforts no longer exists. It saves time and removes
trouble. Weak links could be broken and detected by network monitoring tools. It could
also identify areas for enhancements
Moreover, uptime and security failures reports will give EMC Cyber additional impetus
for upgrading. Sometimes it can be difficult to justify upgrading the network.
Monitoring can provide EMC Cyber with the essential outlet for your revenue and
growth.
Providing Historical and Baseline Data
Network monitoring technologies can compare data continuously and automatically
when baseline data is available. You will receive an alert if performance degrades, and
you will be able to resolve the issue right away. Historical data provides a benchmark
for determining ideal network performance or identifying bad network performance. It
allows you to troubleshoot network issues from previous events.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
29 | P a g e
3.3.1 Benefits of using different network monitoring tools
Tool
PRTG Monitor
Feature
•
Monitoring and alerting you
about uptimes and downtimes or
slow servers
•
System health monitoring of your
various hardware devices
•
Network device monitoring and
bandwidth accounting
•
Application monitoring
•
Monitoring virtual servers
•
Service level agreement (SLA)
monitoring
•
System usage monitoring (for
example, CPU load, free
memory, or free disk space)
•
Database performance and table
values monitoring
•
Email server monitoring and
reviewing various backup
solutions
Nagios XI
•
Nagios XI is aimed at a wide
range of users, including
freelancers, small and medium
businesses, and major
enterprises.
•
Keep an eye on the network, the
infrastructure, and the database.
•
Easy to set up (it may take some
time to adjust to your needs at
first).
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
30 | P a g e
•
DataDog
Designed specifically for hybrid
cloud setups.
•
Monitor the network's, apps',
tools', and services' performance.
•
Extensibility is possible because
to a large number of APIs
(Application Programming
Interfaces) with extensive
documentation.
•
It's simple to set up and use, and
you'll be up and running in no
time.
•
Agents are available for a variety
of platforms, including Windows,
Mac OS, a variety of Linux
distributions, Docker, Chef,
Puppet, and others.
•
Can instantly construct bespoke
graphs, metrics, and warnings,
and the software can dynamically
alter them based on changing
conditions. (datadoghq.com)
Table 3 benefits of using different network monitoring tools
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
31 | P a g e
4
Mechanisms to control EMC Cyber IT security
4.1
Risk assessment procedures for EMC Cyber
A risk assessment is a careful review of your workplace to identify the situations,
processes, etc. that can harm people in particular. Once identified, the company or
person can analyze and assess the likelihood and the seriousness of the risk. After that,
the company or person can decide what measures should be in place to effectively
remove or control the damage.
There are several steps that can be identified in the risk assessment procedure.
•
Hazard identification: finding, listing and characterizing the hazards
•
Risk analysis: a process of identifying the level of the hazards and nature of
the hazards
•
Risk evaluation: Comparison process of an estimated risk with certain risk
criteria to determine the importance of the risk.
•
Risk control: Measures to implement decisions on risk assessment.
Advantages of risk assessment
•
In your workplace, recognize and control risks.
•
Sensitize your employees – and use them as a training tool.
•
Set standards for risk management, based on acceptable safe practices and
legal requirements.
•
Reduce occupational incidents.
•
Save costs by proactivity rather than reactivity.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
32 | P a g e
About Risk
Current
solution
Risk level
Risk
Steps for
Responsible person
increase
security
Operational
The possible
Maintain
Develop
Risk
losses because
good
a solid
of uncertain
records.
plan
Management
circumstances.
Includes
Keep low
reputational,
dept
legal and
accounts.
regulatory
Casualty
insurance.
Low
purchase
Infrastructure Potential
Create
Make a
Management,
Risk
structural and
awareness
proper
Network
basic
training for
plan
Administrator
structural
businesses.
failures.
Create a
Review the
Obtain an
Management
could be
current
insurance
exposed to the
internal
risk of failure
control
of EMC
system.
business
Review
decision.
Always
system for
resources.
Strategy Risk The EMC
practice
security
Roshen Anthony
Medium
human
Medium
managing
Unit 05 Security
33 | P a g e
Data Loss
Data loss is a
EMC Cyber
Keeps
Network
fault condition keeps
backup
administrator
that can be
backups and
daily
damaged by
encrypt
failure or
sensitive
failing to
data
store,
transmit, or
High
process the
data.
Good
centralized
Precise
Network
information
management
collection
administrator,
reduces the
and data
of data
Database
risk and
modeling of
needs.
Administrator,
makes
data assets
decision
that are
making more
frequently
confident.
examined
Natural Risk
High
and audited
Quality assure
An
Keep
Keep all
Network
unexpected
backups and
necessary
Administrator,
event that
store data in
databases
Database
happens
off-side
separately administrator
beyond
location
control
High
Data Quality
Table 4 Risk Assessment for EMC Cyber
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
34 | P a g e
4.2
Data protection process and regulations as applicable to EMC Cyber
Data protection is the process of protecting vital data against corruption, compromise
or loss and enabling them to restore the data to a functioning condition if something
makes the data inaccessible and unusable.
4.2.1 Data protection act of 1998
In order to safeguard your personal data kept on computers or in organized paper filing
systems, the Data Protection Statute 1998 is an act of Parliament. The EU Data
Protection Directive, the protection, processing and transfer of personal data
regulations of 1995 was implemented.
There are 8 fundamental principles of DPA 1998 specified that data must,
1. Fair and Lawful
2. Purposes
3. Adequacy
4. Accuracy
5. Retention
6. Rights
7. Security
8. International Transfers
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
35 | P a g e
4.2.2 Steps of data protection process for EMC Cyber
•
Develop a Culture of “Privacy by Design”
•
Appoint a data protection officer
•
Educate Your personal
•
Document Your information collection and usage practices
•
Confirm your lawful basis for collecting and processing personal Data
•
Update Consent Practices
•
Protect individual rights
•
Review and update your privacy notices
•
Review third party contracts
•
Prepare for data breaches
Steps
Develop a Culture of
Procedure
•
“Privacy by Design”
Check EMC Cyber privacy approach and how you
manage data protection.
•
Conduct impact assessments for data protection
and establish risk mitigation measures found in
the evaluation.
•
Make sure that the Company data that process are
adequately technological safeguarded. Technical
protections should include automatic identification
and classification methods for personal data,
pseudonymization and data encryption, and
technical security measures.
Appoint a data
•
protection officer
A DPO is necessary if your company regularly
and systematically monitors large-scale people, or
if you process any of the sensitive data categories
on a wide scale.
•
In all situations, a DPO is advised to guarantee
that a person with adequate expertise, institutional
backing and power is responsible for the security
of data.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
36 | P a g e
Educate Your personal
•
Make sure that all decision-makers and key
individuals who process or direct data use are
aware of their obligations.
Document Your
•
Continuous data protection training.
•
Make an inventory of data. Take all gathered and
information collection
used information into account in all your
and usage practices
organization areas.
•
Develop a documented internal policy on your
organization's actions to safeguard and enforce
personal data. Develop a documented internal
policy on your organization's actions to safeguard
and enforce personal data.
Confirm your lawful
•
GDPR requires you to have a legally binding basis
basis for collecting and
for personal data processing. The legally
processing personal
acceptable grounds for business undertakings
Data
•
Document the appropriate legal bases for each
type of personal data gathered, make sure that the
data can only be useful and retain records for the
specified purposes.
Update Consent
•
practices
If company agree to the processing of their
personal data on a legitimate basis, such
permission must be freely granted, explicit,
informed and clear.
•
If they do not satisfy GDPR standards, existing
consents will have to be renewed.
Protect Individual
•
Rights
develop mechanisms to answer individual requests
for their personal data rights
•
Although the majority (pre-GDPR) of these rights
exist in the EU, the right to data portability is new.
If applicable, the data record must be transferred
in an electronic format, typically readable at the
request of the individual.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
37 | P a g e
Review and Update
•
your Privacy notes
Make sure that the data collection and usage
methods assessed and defined in Steps 4 through 7
are correctly described in your data protection
information.
•
Company data protection notifications must
explicitly provide a legally-lawful basis for the
treatment, data retention and people' ability to
lodge complaints with the data protection
authorities of Member States.
Review third party
•
Contracts
If company process, store or otherwise manage
data on your behalf from third party sources,
company is liable for their GDPR compliance as
far as your data are concerned.
•
Review contracts and agreements with business
partners, cloud service providers and other third
parties to ensure that organizational and
technological information security safeguards are
in place for third parties.
Prepare for data
•
breaches
Confirm if internal processes are sufficient to
quickly discover and report violations in the
correct control chain.
•
Implement investigation and mitigation processes
for infringements of data.
Table 5 steps for Data protection process for EMC Cyber
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
38 | P a g e
4.3
Summarizing the ISO 31000 risk management methodology and its application
in IT security
4.3.1 ISO 31000 risk management methodology
The International Standard ISO 31000 for Risk Management provides concepts and
guidance for successful risk management. ISO 31000 offers advice on how to integrate
risk-based decision-making in EMC governance, management, planning, reporting and
policies and ISO 31000 to build a Risk Management Strategy to successfully identify
and mitigate risks, as the EMC's Cyber services provider notes.
Risk management Process
•
Identify threats and opportunities
•
Minimize losses
•
Improve operational efficiency and effectiveness
•
Encourage personnel to identify and treat risks
•
Improve risk management controls
The following key provisions are the ISO 31000 risk management
•
Principles
•
Framework
•
Process
Principles of risk management iso of 31000
•
Risk management establishes and sustains value.
•
Risk management is an integral part of all organizational
processes.
•
Risk management is part of decision making.
•
Risk management explicitly addresses uncertainty.
•
Risk management is systematic, structured, and timely.
•
Risk management is based on the best available information.
•
Risk management is tailored.
•
Risk management takes human and cultural factors into
account.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
39 | P a g e
•
Risk management is transparent and inclusive.
•
Risk management is dynamic, iterative, and responsive to
change.
•
Risk management facilitates continual improvement of the
organization.
4.4
Impacts to Organizational security resulting from IT security audit
There are 3 types of IT audit control
•
Detective
•
Prevention
•
Corrective
During the planning stage of an engagement, audit objectives are developed that are
clearly aligned with the business objectives of the area or process under review. The
majority of engagements are centered on ensuring that controls are in place to
effectively reduce risks that could prohibit the region or process from meeting its
business objectives. Auditors additionally make sure that engagement goals are in line
with the organization's goals in terms of:
1. Operational aims and objectives are met.
2. Information trustworthiness and integrity
3. Asset protection is essential.
4. Resource utilization that is both effective and efficient
5. Observance of key policies, processes, laws, and regulations
Being audited provide numerous advantages to management. Such as,
•
Assess the effectiveness of internal controls.
•
Encourage the use of best control practices.
•
Ensure that policies and regulations are followed.
•
Identify inefficiencies and waste in your operations.
•
Examine IT systems, programs, and technologies.
•
Provide unbiased information
•
Evaluate resource efficiency and stewardship.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
40 | P a g e
•
Determine where you can save money.
•
Assist management in resolving cross-functional challenges that are
complicated.
An audit is required by a number of IT security standards. While some are general to
the IT business, many are more sector-specific, relating to healthcare or financial
organizations, for example. A small selection of some of the most widely debated IT
security standards is provided below.
Audit standard
Description
ISO compliance
The
International
Standardization
Organization
(ISO)
creates
for
and
publishes a variety of standards to ensure
quality, consistency, and safety. Because
these
standards
focus
on
keeping
information assets secure, the ISO/IEC
27000 family of standards is one of the
most relevant to system administrators.
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard is wellknown for its standards for information
security management systems.
HIPAA Security rule
The HIPAA Security Rule lays out
detailed standards for how businesses
should safeguard patients' electronic
personal health information.
PCI DSS compliance
The PCI DSS compliance standard is
directly applicable to businesses that
handle any type of client payment.
Consider this standard to be the need for
ensuring the security of your credit card
information every time you perform a
purchase. PCI DSS compliance is a
difficult endeavor, and I propose that you
use software like SolarWinds® Security
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
41 | P a g e
Event Manager to assist you with the
auditing process.
SOX Compliance
The SOX Act, better known as the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which was adopted
in 2002 following the highly promoted
Enron scandal, was approved by Senator
Paul Sarbanes (D-MD) and Rep. Michael
G. Oxley (R-OOH-4). The purpose was
to protect investors by mandating all
public undertakings to make accurate,
dependable annual financial statements.
Table 6 Common IT Security audit standards
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
42 | P a g e
4.5
The impact of IT security aligns with organizational policy and the safety
consequences of any misalignment
The IT Security Policy defines rules and processes for everyone who accesses and uses
the IT resources and assets of a company. Effective IT security policy is a model of the
culture of the firm, which uses rules and procedures from the information and working
approach of its personnel. Therefore, for every organization, a good IT security policy
is a unique document, based on the views of its people on risk tolerance, how their
information is seen and appreciated and on their consequent availability.
There are Information security policies that can be used for EMC Cyber,
Classification of information and data — Good information and classification policies
assist firms to regulate the distribution of their safety assets. Poor grades may leave
organizations susceptible to attacks.
IT operation and management — the failure of departmental co-operation might result
in set-up problems. When the team works together, risk assessment and identification
may be coordinated across all departments to mitigate risks.
Privacy rules - Government imposed regulations such as the General End User Data
Protection Regulations. The company then needs to secure its users. If you don't secure
users' privacy, the organization risks losing its power and fines.
Personal and mobile devices - the company has moved into the cloud today. EMC
Cyber, for example. The organization offers access for any location to corporate
software assets. There is then a possibility that personal gadgets like laptop, cell phones
would introduce vulnerabilities. The corporation then needs to establish a policy to
safeguard its personal appliances properly, which can help prevent threats through its
assets.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
43 | P a g e
5
Managing Organizational security
5.1
Designing and implementing a security policy for EMC Cyber
Policies are rules, principles, guidelines, or frameworks that an organization adopts or
creates in order to achieve long-term objectives. These are frequently written in a
format that is simple to understand. All key decisions to be made within the
organization are directed and influenced by policies, which maintain all operations
within a set of established parameters.
Scope
That policy encompasses all of EMC Cyber Company’s duties and must be compliant
with it.
Purpose
To ensure that client information is kept secure, accessible, and that EMC Cyber stores,
processes, or transfers, exploits, or misuses are kept to a minimum.
Overview
A policy is a collection of approaches or ideas for dealing with a certain circumstance.
Policies assist EMC Cyber service provider personnel in making more effective plans
and implementing job-related guidelines. The regulations of the EMC Cyber assistance
provider are described in the guidelines, and the techniques indicate how things are
done.
Policy
Purpose of Policy
Network Policy
Network policies are a set
of
Element of policy
constraints
and
The network can
only be accessed
parameters that apply to a
by authorized
network who is allowed to
users.
join to the network is
defined
by
network
policies.
Roshen Anthony
•
Unit 05 Security
•
For any reason, the
user must not
reveal their
44 | P a g e
password with
anyone.
•
All modifications
must be recorded.
•
Operating systems
and application
software must be
kept in good
working order.
•
The user refuses to
authorize the
installation of
network
components.
Wireless Access Policy
The policy's goal is to
•
Unauthorized
provide wireless Internet
device access is
connection
not permitted.
customers
to
just
and
sales
•
people on the first floor.
Set up the logging
passwords.
•
Use a MAC
address that may
be traced and
registered.
•
All access must be
granted via a
secure access
point.
Mobile security Policy
To secure data in transit
A strong password
and corporate data on
must be set on all
mobile devices
devices.
On
the
EMC
Cyber,
protect critical data from
Roshen Anthony
•
Unit 05 Security
•
All stolen or lost
devices must be
45 | P a g e
threats
and
unwanted
reported to the
access.
user.
•
Security patches
must be installed
on the user's
computer.
•
For their devices,
users must use the
most recent
operating systems.
•
On their devices,
users must not
install cracked
software.
Software Security Policy
To
safeguard
sensitive
•
Software should
data on the EMC, Cyber
only be installed
from attacks and hackers.
and uninstalled by
the IT department.
•
EMC installs
Windows
operating systems
using WDS
(Windows
Deployment
Server).
•
For their devices,
EMC employed
proprietary
software.
•
Backup and recovery
A backup retention policy
policy
not only satisfies explorer
files should be
user expectations, but it
saved.
also
Roshen Anthony
gives
a
Encrypted backup
more
Unit 05 Security
46 | P a g e
thorough understanding of
•
Backup files
data reconstruction and
should be kept in
backup methods.
several locations,
as well as in a
secure location.
•
Set the failover
clustering method
for each backup
system.
•
Create a backup
schedule for each
process.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
47 | P a g e
5.2
The main components of an organisational disaster recovery plan, justifying the
reasons for inclusion.
A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is a documented, systematic technique that explains
how a company can quickly restart operations following an unanticipated event. A
disaster recovery plan (DRP) is an important component of a business continuity plan
(BCP). It's used to describe the components of an organization that rely on a working
IT infrastructure. A data recovery plan (DRP) tries to assist an organization in resolving
data loss and restoring system functioning so that it can continue to operate in the
aftermath of an incident, even if at a reduced level.
The following stages should be included in a DRP checklist:
1. determining the range or amount of required therapy and activity
2. assembling pertinent network infrastructure documentation
3. determining the most serious threats and vulnerabilities, as well as the most
important assets
4. examining the history of unforeseen occurrences and outages, as well as how
they were dealt with
5. determining the status of present disaster recovery plans
6. determining who will be on the incident response team
7. reviewing and approving the DRP with management
8. putting the plan to the test
9. updating the plan.
10. implementing a DRP audit
Advantages of Disaster recovery plan
•
Restoration times are drastically reduced, and RTO and RPO are significantly
reduced.
•
Limit the amount of money you lose as a result of revenue reductions or other
expenses.
•
Reduce the risk of Critical Processes being disrupted and protect corporate
operations.
•
Avoid jeopardizing the company's reputation.
•
Define simplified action plans to deal with unexpected occurrences and plan
for a controlled return to operations.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
48 | P a g e
•
Management on a small scale
•
There is no effect on performance.
•
Control and management of your disaster recovery plan
The components of an organizational disaster recovery plan (DRP)
•
Clustering
•
Backup
•
Cloud computing
•
Disaster recovery site
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
49 | P a g e
Procedure
Priority Level
Component
Clustering
Purpose
Justification
•Availability of
Set
resources has increased.
distributed file
Performance: More
•Obtain failover
system to allow
processing power is
•Support.
multiple servers
provided by multiple
•Load balancing is a
to access data.
machines.
term that refers to the
Load balancing
•Retailing the load. If
up
a
•Improved
process of balancing the should be set
•Project distribution and up.
a node fails, the task it
failover are two
an additional node or
important aspects of
node set.
project management.
•Application for
performs is directed at
Recovery. If a node
fails, the system tries
to reconnect users to
another node with
queued or processed
queries. To be
authenticated on a
new node, users must
login again.
• Enhancing the
availability of
resources: If an
intelligence server in a
cluster is not
available, it can be
intelligence servers in
the cluster. This
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
Medium
recovered by the other
50 | P a g e
prevents time and
information from
losing valuable time if
Backup
a server fails.
•Fast file access.
Installation of a
•to accelerate the
•Natural catastrophe
backup solution
process of catastrophe
protection.
based on cloud.
recovery and preserve
•Failed hard drive
your data.
security.
•If backup sites are
•Recovery if OS fails
implemented a few
miles away from the
main operation hub.
Both locations would
disintegrate under the
same threat when a
natural calamity
happens. As a security
expert, the writer
advocates setting up
backup sites and
redundant servers that
are placed within
Cloud computing
at the same time.
•Natural catastrophes
•Process data
•To ensure data access
Failure to communicate.
for disasters in
even in the event of
Terrorism.
the
the destruction of
management
infrastructure
hierarchy.
resources, because
Issuing a alert
data is backed up on
message
the cloud servers.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
Medium
reach via other paths
High
miles, but can readily
51 | P a g e
•Improving emergency
management by
delivering real-time
Disaster recovery site
information
Breakdown of
•Establish and
•Recover and re-
communication.
maintain
establish the
Malwares
internal
infrastructures and
recovery
services of the EMC
facility
an
for
disasters
Primary Data Centre.
•As the security
expert, the author
suggests setting up
disaster recovery sites
and redundant servers
that are situated a
distance, but can be
accessed easily via
different methods.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
52 | P a g e
5.3
Disaster recovery plan for EMC Cyber
Figure 2 Disaster recovery plan slide 1
Figure 3 Disaster recovery plan slide 2
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
53 | P a g e
Figure 4 Disaster recovery plan slide 3
Figure 5 Disaster recovery plan slide 4
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
54 | P a g e
Figure 6 Disaster recovery plan slide 5
Figure 7 Disaster recovery plan slide 6
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
55 | P a g e
Figure 8 Disaster recovery plan slide 7
Figure 9 Disaster recovery plan slide 8
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
56 | P a g e
Figure 10 Disaster recovery plan slide 9
Figure 11 Disaster recovery plan slide 10
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
57 | P a g e
Figure 12 Disaster recovery plan slide 11
Figure 13 Disaster recovery plan slide 12
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
58 | P a g e
Figure 14 Disaster recovery plan slide 13
Figure 15 Disaster recovery plan slide 14
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
59 | P a g e
5.4
The roles of stakeholders in the organisation to implement security audit
recommendations.
A stakeholder is a party that holds an interest in a company and can either influence or
influence the company. Investors, employed people, consumers and providers are the
main stakeholders in the standard company.
Stakeholders can be categorized as two types,
•
Internal stakeholder
•
External stakeholder
Internal stakeholder
According to Nilson (2006: p170), internal stakeholders are those in the management,
marketing experts, designers, purchasing, manufacturing, assembly and sales, while
external stakeholders are the users/customers, distributors, governments, suppliers,
communities, laws and regulations. (Karim, et al., 2007, pp.8).
Investors
Investors raise or decrease their holdings in a firm based on its financial performance.
Project manager
The project manager is in charge of ensuring that the project team finishes the project.
The project manager creates the project plan and oversees the team's execution of
project operations.
Directors
Directors participate in the business's decision-making process. When it comes to
EMC, mainly directors are involved in adopting EMC security policies. The author
outlines the duties that EMC directors must fulfil.
Shareholder
•
The company's stock is held by the company's shareholder. Highlight the roles
of the shareholders in the EMC as follows.
Provide a source of funding for the EMC.
•
Using their voting privileges, they can comment on and approve the EMC's
security policy.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
60 | P a g e
•
Assistance with the EMC's decision-making process.
Employees
An employee might be a worker or a manager for a corporation. The EMC employee
plays a critical role in implementing EMC security policies and procedures to secure
the information security of the EMC cloud.
External Stakeholders
External stakeholders are those who have no direct relationship with the company.
They are not staff members and have no direct financial interest in the company's profit
or loss. They are interested instead in how the business affects the community or a
segment of the community. External stakeholders include governmental entities in the
area in which the company operates, including municipal councils, local schools, other
companies and local inhabitants.
Government organizations
Governmental agencies for various areas of administration are established by the
government. Refer to the duties of government agencies as follows.
•
The government's responsibility.
•
Provide rules and regulations for companies
•
Contributes to understanding modern government economic trends
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
61 | P a g e
Team roles of the stakeholders in EMC during a disaster
The author made a list of roles for the EMC Cyber during a disaster.
Name
Title
Emergency
Role
number
Name_1
Head of IT
xxxxxxxxxx
Team lead
Name_2
Security admin
xxxxxxxxxx
Responsible for
security system
Name_3
Storage Admin
xxxxxxxxxx
Responsible for
data storage
system
Name_4
Backup Admin
xxxxxxxxxx
Responsible for
data backup
system
Name_5
Network specialist
xxxxxxxxxx
Responsible for
network system
Name_6
System expert
xxxxxxxxxx
Coordinator of the
recovery team
Name_7
System engineer
xxxxxxxxxx
Responsible for
server system
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
62 | P a g e
5.5
The suitability of the tools used in an organisational policy
Biometric security
Biometric measurements – or physical characteristics – are used for the identification
of individuals, for the definition of a quick biometric. Fingerprint mapping, face-toface recognition, and retinal scans, for instance, are all types of biometric technology.
Researchers have asserted to be an ear, to be able to sit and walk, to be unique in bodily
excretions, in one's hand veins and even face contortions are other unique indicators.
This defines biometrics further.
Fingerprint
Fingerprint used for identification of the individual because of the unique fingerprints.
Fingerprint scanners measure the finger's loop, whorl and arc patterns. The easy
implementation and cost-effectiveness of fingerprint scanners. In terms of access
control, fingerprint recognition is used in the industry.
Facial recognition
Facial recognition is a technology way to recognize a human face. A face recognition
system uses biometrics to map photographic or video facial features. It compares the
data with a database of familiar faces to find matches. Facial reconnaissance can help
to check the identity of a person
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
63 | P a g e
Theft prevention
Keep track of important data
Monitoring is one of the cornerstones of success. The company owner simply can't
know what works and does not work without tracking. The inefficiencies are also hard
to see, and how they can be enhanced.
Use physical lock
In order to meet company requirements, the company should use a physical lock if it is
using a laptop and mobile devices. Today, Kensington supports locks which can
prevent user steps from beginning.
5.5.1 Evaluation of the tools used in an organisational policy
Technique
Expected
Cost
Justification
Recomm
level
ended or
not
Installing
maintenance
recomme
nded?
Physical security
CCTV
camaras
• Monitor
High
Low
CCTV systems are able Yes
activities
to trac and monitor with
• Keep video
the EMC premises and
outside the premises and
records
• Crime
also
used
activities
prevention
monitor
of
the
employees
Fire exits
and alarms
• For safety
Medium Low
These
must
establish Yes
of the
because it is necessary to
employees.
check the safety of the
• To control
employees and also alarm
system is use to give
the fire
information
for
employees
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
64 | P a g e
Key card
• Reduce
Medium Low
When the door control Yes
entry
unauthorize
system in the EMC is
system
access.
implemented, the rules
• Reduce the
Avoid
windows
for access for employees
risk of
to
hardware.
precisely defined.
• Reduce
Low
Low
certain
areas
are
When double-glazed or Yes
unauthorize
crash resistant windows
access.
are used, the risk of
• Increase
unwanted
access
to
valuable information is
security
reduced and the security
of office areas increases
Permeant
•Assistance
security
in deterring
respond
staff
crimes at the
with EMC's corporate
premises of
approval to any situation.
the EMC.
However, the costs are
•Enhance the
more
perception of
approaches of physical
security.
safety.
Enhance
advises
client
areas as a Security Expert
service.
to provide this service.
•Efficient
Customer consent and
handling of
sales.
Low
High
Security
guards
will Yes
immediately
than
other
The
the
author
following
security
problems.
Biometric security
Fingerprint
•To compute
recognition
staff hours
authenticate
automaticall
identification
Low
Low
The greatest approach to Yes
one's
is
the
y.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
65 | P a g e
•Secure area
fingerprint
and systems
method.
recognition
access
control.
Facial
•To employ
recognition
real-time
individual's identity with
identification
his face is identified or
or
verified. Also used to
verification
identify persons at scenes
of
of crime.
Medium
Low
Using this procedure, an Yes
individuals,
photographs
and videos.
Signature
•to recognize
Dynamics
a person's
direction, pressure, stroke
behavioural
and form of individual
features
signature
when signing
dynamically recorded.
Medium
Low
Data
such
as
that
the Yes
were
the name
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
66 | P a g e
Gantt Chart
Figure 16 Gantt Chart
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
67 | P a g e
References
•
Imperva (2019). What is phishing | Attack techniques & scam examples |
Imperva. [online] Imperva. Available at:
https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/phishing-attack-scam/.
•
Ahola, M. (n.d.). Top 5 Physical Security Risks - And How to Protect Your
Business. [online] blog.usecure.io. Available at:
https://blog.usecure.io/physical-security-risks.
•
Lutkevich, B. (2019). What is firewall? - Definition from WhatIs.com.
[online] SearchSecurity. Available at:
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/firewall.
•
Johansen, A.G. (2020). What is a firewall and do you need one? [online]
us.norton.com. Available at: https://us.norton.com/internetsecurity-emergingthreats-what-is-firewall.html.
•
Walkowski, D. (2019). What Is The CIA Triad? [online] F5 Labs. Available
at: https://www.f5.com/labs/articles/education/what-is-the-cia-triad.
•
Buildings. (2021). 10 Strategies to Prevent Tailgating | Buildings. [online]
Available at: https://www.buildings.com/articles/31764/10-strategies-preventtailgating.
•
securityscorecard.com. (n.d.). 10 Best Practices to Prevent DDoS Attacks l
SecurityScorecard. [online] Available at:
https://securityscorecard.com/blog/best-practices-to-prevent-ddos-attacks.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
68 | P a g e
•
www.sciencedirect.com. (n.d.). Information Security Risk - an overview |
ScienceDirect Topics. [online] Available at:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/information-securityrisk.
•
Wilson, B. (2020). Why Firewall Misconfigurations Are Putting Your Clients
At Risk in 2020. [online] XaaS Journal. Available at:
https://www.xaasjournal.com/why-firewall-misconfigurations-are-puttingyour-clients-at-risk-in-2020/.
•
Wilson, B. (2020). Why Firewall Misconfigurations Are Putting Your Clients
At Risk in 2020. [online] XaaS Journal. Available at:
https://www.xaasjournal.com/why-firewall-misconfigurations-are-puttingyour-clients-at-risk-in-2020/.
•
Guru99.com. (2019). IPv4 vs IPv6: What’s the Difference? [online] Available
at: https://www.guru99.com/difference-ipv4-vs-ipv6.html.
•
Fortinet (2021). What Is a DMZ and Why Would You Use It? [online]
Fortinet. Available at:
https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/what-is-dmz.
•
help.apnic.net. (n.d.). KnowledgeBase. [online] Available at:
https://help.apnic.net/s/article/What-is-an-IP-address.
•
https://www.howstuffworks.com (2000). How Firewalls Work. [online]
HowStuffWorks. Available at:
https://computer.howstuffworks.com/firewall.htm.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
69 | P a g e
•
CactusVPN. (2019). The Top 8 VPN Security Risks (What to Look Out for).
[online] Available at: https://www.cactusvpn.com/vpn/vpn-security-risks/.
•
Mitchell, C. (2020). IP Address Definition. [online] Investopedia. Available
at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/ip-address.asp.
Roshen Anthony
Unit 05 Security
70 | P a g e
Grading Rubric
Grading Criteria
Achieved
Feedback
LO1 Assess risks to IT security
P1 Identify types of security risks to organisations.
Achieved
Identified different risks which will be faced by the organization according to CIA triad
P2 Describe organizational security procedures.
Achieved
Described security procedures to the each risks
Achieved
Proposed a methods to assess and treat IT security risks triad
Achieved
Identified the harmful impact due to incorrect configurations of firewalls and third party
VPNs
Achieved
Explained about DMZ. Static IP and NAT with how importance them to enhance the
network security
Achieved
Explain three major benefits of implement a network monitoring tool
M1 Propose a method to assess and treat IT security risks.
LO2 Describe IT security solutions
P3 Identify the potential impact to IT security of incorrect
configuration of firewall policies and thirparty VPNs.
P4 Show, using an example for each, how implementing a DMZ,
static IP and NAT in a network can improve Network Security.
M2 Discuss three benefits to implement network monitoring systems
with supporting reasons.
Never investigated how a ‘trusted network’ may be part of an IT security
D1 Evaluate a minimum of three of physical and virtual security
Not achieved
measures that can be employed to ensure the integrity of
organisational IT security.
LO3 Review mechanisms to control organisational IT
security
P5 Discuss risk assessment procedures.
Achieved
P6 Explain data protection processes and regulations as applicable to
an organisation.
Risk assessment procedures explained by a table with high medium low risk
measurements
Different data projection acts and principals are explained
Achieved
M3 Summarise the ISO 31000 risk management methodology and its
application in IT security.
Achieved
M4 Discuss possible impacts to organizational security resulting
from an IT security audit.
Discussed about the potential impact of a IT security audit
Achieved
Explained that how IT security can be aligned with organizational policy.
D2 Consider how IT security can be aligned with organisational
policy, detailing the security impact of any misalignment.
ISO 31000 summarized
Achieved
LO4 Manage organizational security
P7 Design and implement a security policy for an organisation.
Achieved
Design a proper security policy with a table
Achieved
Disaster recovery table provided with different risk measurements
P8 List the main components of an organisational disaster recovery
plan, justifying the reasons for inclusion.
M5 Discuss the roles of stakeholders in the organisation to
implement security audit recommendations.
D3 Evaluate the suitability of the tools used in an organisational
policy.
Discuss the main roles of the stakeholders in the organization
Achieved
Not achieved
Evaluated the suitable tools to enhance the security of the organization but expect the
answer more critically
