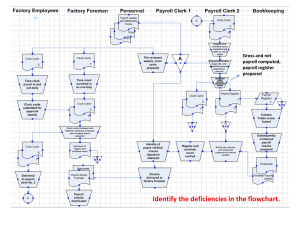
Chapter 10 Expenditure Processes and Controls Payroll and Fixed Assets Introduction to Payroll and Fixed Asset Processes Payroll processes Acquiring and maintaining human resources. Capturing and maintaining employee data. Paying employees. Recording cash and payroll liabilities and expenses. SO 1 An introduction to payroll and fixed asset processes Introduction to Payroll and Fixed Asset Processes Fixed asset processes Purchasing property. Capturing and maintaining relevant data about assets. Paying for and recording the related assets. Recording depreciation and other expenses. Accounting for gains or losses. SO 1 An introduction to payroll and fixed asset processes Introduction to Payroll and Fixed Asset Processes Various risks Recorded expenditures may not be valid. Transactions may be recorded in the wrong amount. Valid expenditure transactions may have been omitted. Transactions may have been recorded in the wrong employee or vendor account. Transactions may not have been recorded in a timely manner. Transactions may not have been accumulated or transferred to the accounting records correctly. SO 1 An introduction to payroll and fixed asset processes Payroll and Fixed Asset Processes Exhibit 10-1 Expenditure Processes within the Overall System SO 1 Payroll and fixed asset processes Payroll Processes Terminology Human resources department Organization chart Time sheet Payroll register Payroll disbursements journal SO 2 Payroll processes Payroll Processes SO 2 Payroll processes Payroll Process- Data Flow SO 2 Payroll processes Payroll Process System Flowchart SO 2 Payroll processes Risks and Controls in Payroll Processes Authorization of transactions Management carefully reviewing the payroll documents, errors and fraud prevented. Departmental supervisors must be certain that all time sheets represent actual time worked by currently active employees. The supervisors are expected to be familiar enough with their respective departments that they will recognize unusual data: fraud schemes such as overstated hours, time sheets or paychecks of former employees. Employee personnel files should contain evidence of proper authorization for pay rate adjustments, hiring, promotion, and termination (authorized by management), as well as approval for all deductions (authorized by individual employees). SO 3 Risks and controls in payroll processes Risks and Controls in Payroll Processes Segregation of duties Prevent the preparation and payment of a fraudulent or erroneous paycheck: payroll accounting functions such as authorizing, timekeeping, record keeping, and custody of the paychecks should all be separated. Human resources department, which is responsible for authorizing new employee hiring and maintaining personnel files, should be separate from the payroll time-reporting and record-keeping functions, performed primarily by the payroll, cash disbursements, and general ledger departments. Employees in each of these departments should not have check-signing authority and should not have access to the signed checks or cash account. Paymaster, should not have responsibility for any of the related payroll accounting functions and should not have custody of cash. The paymaster should also be independent of the departmental supervision responsibilities, so that a determination can be made that paychecks are being distributed to active employees. Information systems operations and programming related to the payroll processing should be separate from custody of payroll cash and record keeping for these processes SO 3 Risks and controls in payroll processes Risks and Controls in Payroll Processes Adequate records and documents Personnel files and the payroll register are the fundamental records, also numerous forms and reports that are required to be filed at designated times throughout the year. Due to the number of inputs required for accurate payroll processing and reporting, the care with which these records are prepared and maintained is crucial to the internal control environment. Security of assets and documents Payroll information must be kept confidential. Access to personnel files and payroll records should be limited to designated persons within the human resource and payroll departments. Electronic controls and physical controls should be in place to ensure the confidentiality of payroll information. Independent checks and conciliations Number of hours reported on time sheets should be reconciled to the payroll register, and time sheets may be reconciled with production reports. Payroll register should be reconciled to the general ledger on a regular basis. Someone separate from the payroll processing functions should reconcile the bank statement for the payroll cash account on a monthly basis. This bank reconciliation should follow the same procedures as required for the company’s general checking account. SO 3 Risks and controls in payroll processes Fixed Assets Processes Fixed assets may include the following: vehicles, office equipment and computers, machinery and production equipment, furniture, and real estate (such as land and buildings). SO 5 Fixed asset processes Fixed Assets Processes Fixed Asset Acquisitions Initiated by user department. Large cash outlays sometimes required. Non-routine transactions that require specific authorization. Capital budget. Fixed asset subsidiary ledger. SO 5 Fixed asset processes Fixed Assets Processes Fixed Asset Continuance Involves: Updating cost data for improvements Updating estimated figures as needed Adjusting for periodic depreciation Keeping track of physical location of assets Depreciation schedule SO 5 Fixed asset processes Fixed Assets Processes Fixed Asset Disposals Four Basis Steps: Date of disposal is noted, and depreciation computations updated through this date. Disposed assets are removed from fixed asset subsidiary ledger. Related depreciation accounts are removed. Gains or losses are computed. SO 5 Fixed asset processes Fixed Assets Processes User Department Management Sales Shipping Billing Fixed Asset Accounting General Ledger Exhibit 10-11 Fixed Asset Disposal Process Map SO 5 Fixed asset processes Risks and Controls in Fixed Assets Processes Authorization of Transactions Three Formal Steps: Investment analysis Comparison with the capital budget Review of the proposal and specific approval Exhibit 10-13 Fixed Asset Approval Levels SO 6 Risks and controls in fixed asset processes Risks and Controls in Fixed Assets Processes SEGREGATION OF DUTIES Custody of fixed assets needs to be separate from the related record keeping. Those with custody of fixed assets should not perform any duties in the purchasing, receiving, or fixed asset accounting departments. IT functions such as programming, operations, data input, and security should be segregated from each other and from the related accounting duties. ADEQUATE RECORDS AND DOCUMENTS Fixed asset subsidiary ledgers are used to control the physical custody, cost, and accumulated depreciation of the fixed assets. P, P & E purchases should be supported by a purchase requisition, purchase order, receiving report, and vendor invoice. Tags may also be used to account for the numerical sequence of items acquired. In addition, management should prepare and follow a capital budget. SECURITY OF ASSETS AND DOCUMENTS Supervisors need to make certain that the assets are being used for their intended purposes. Physical controls should also be in place to protect fixed assets from unauthorized use, and electronic controls are needed to control access to automated records. Protect its investment in fixed assets by maintaining adequate insurance coverage and conducting regular preventative maintenance procedures such as tune-ups for machinery and vehicles. INDEPENDENT CHECKS AND RECONCILIATION Fixed asset expenditures should be compared with the capital budget, and additional approval should be required if budgets are exceeded. Periodic counts of fixed assets should be made by someone not otherwise responsible for fixed-asset-related activities. Those physical counts should be reconciled with the accounting records. Performing independent verifications to match key purchasing documents and the related accounts payable reports may uncover errors or fraud within these records. SO 6 Risks and controls in fixed asset processes Ethical Issues Related to Payroll and Fixed Assets Processes Typical sources of time sheet falsifications: Exaggeration of hours worked Falsification of overtime or holiday time worked Falsification of sales in order to increase commission payouts Overstatement of job-related expenses SO 8 Ethical issues related to payroll and fixed assets processes Ethical Issues Related to Payroll and Fixed Assets Processes Ghost Employee Clues that a ghost employee may exist: Payroll register identifies paychecks without adequate tax withholdings. Personnel files contain duplicate addresses, Social Security numbers, or bank account numbers. Payroll expenses are over budget. Paychecks not claimed when paymaster distributes them. Paychecks contain dual endorsements. SO 8 Ethical issues related to payroll and fixed assets processes Ethical Issues Related to Payroll and Fixed Assets Processes Fixed asset information is more likely to be manipulated by management to unethically enhance the financial statements. Often, this occurs when management misclassifies expenses as fixed asset purchases. SO 8 Ethical issues related to payroll and fixed assets processes Corporate Governance in Payroll and Fixed Assets Processes In addition to the need for strong management oversight, internal controls, and ethical practices, corporate managers must recognize their responsibility to be good stewards of the assets underlying the payroll and fixed assets processes. SO 9 Corporate governance in payroll and fixed assets processes