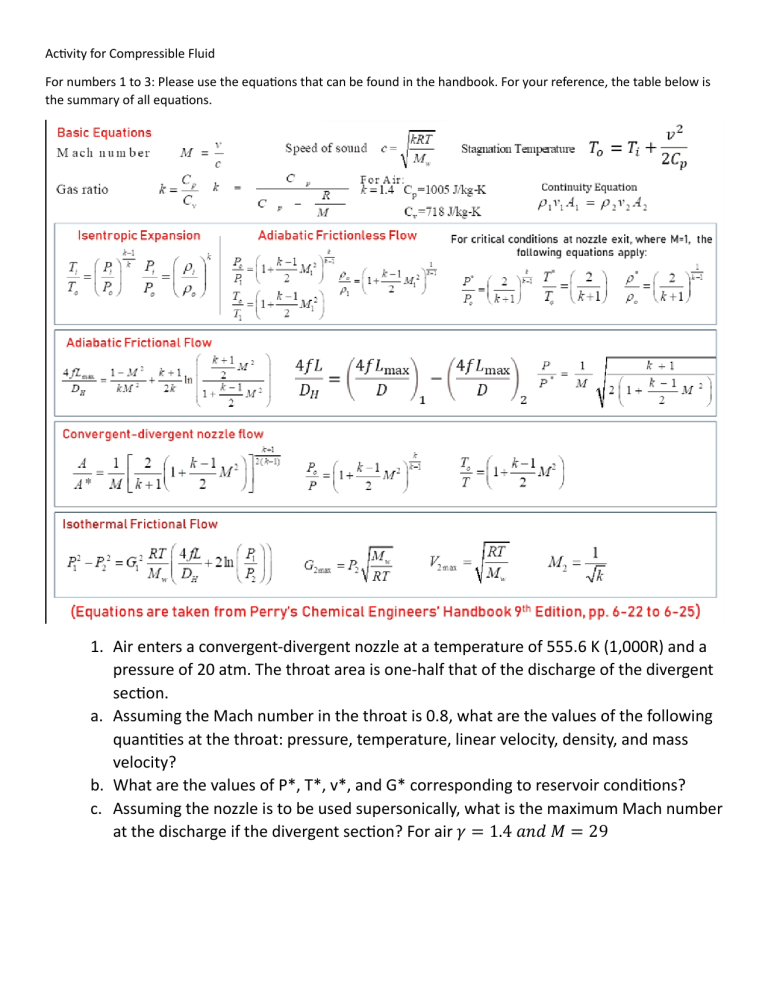
Activity for Compressible Fluid For numbers 1 to 3: Please use the equations that can be found in the handbook. For your reference, the table below is the summary of all equations. 1. Air enters a convergent-divergent nozzle at a temperature of 555.6 K (1,000R) and a pressure of 20 atm. The throat area is one-half that of the discharge of the divergent section. a. Assuming the Mach number in the throat is 0.8, what are the values of the following quantities at the throat: pressure, temperature, linear velocity, density, and mass velocity? b. What are the values of P*, T*, v*, and G* corresponding to reservoir conditions? c. Assuming the nozzle is to be used supersonically, what is the maximum Mach number at the discharge if the divergent section? For air 𝛾 = 1.4 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑀 = 29 2. Air flows from a reservoir through an isentropic nozzle into a long, straight pipe. The pressure and temperature in the reservoir are 20 atm and 1,000R (555.6K), respectively, and the Mach Number at the entrance of the pipe is 0.05. a. What is the value of 𝑓̅𝐿𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑟𝐻 ? b. What are the pressure, temperature, density, linear velocity, and mass velocity when 𝐿𝑏 = 𝐿𝑚𝑎𝑥 ? c. What is the mass velocity when 𝑓̅𝐿𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑟𝐻 = 400? 3. Natural gas, which is essentially methane, is being pumped through a 1.016m ID pipeline for a distance of 1.609 𝑥 105 𝑚 at a rate of 2.077 kmol/s. It can be assumed that the line is isothermal at 288.8K. The pressure P2 at the discharge end of the line is 170.3 𝑥 103 𝑃𝑎 𝑎𝑏𝑠. Calculate the pressure P1 at the inlet of the line. The viscosity of the methane at 288.8K is 1.04 𝑥 10−5 𝑃𝑎 𝑠. Also, calculate Vmax, Velocity at discharge and velocity at the entrance. For numbers 4, 5, and 6. You may use either the handbook’s derived formulas or you may use the formulas from our lecture (McCabe). 4. Standard 1-in. Schedule 40 horizontal steel pipe is used to conduct chlorine gas. The gas enters the pipe through a rounded entrance at a pressure of 6 atm absolute, a temperature of 120C, and a velocity of 35 m/s. (a) what is the maximum possible length of the pipe? (b) What are the pressure and stagnation temperature of the gas at the end of the pipe at maximum length? Assume adiabatic flow. For chlorine. The ratio of Cp and Cv is equivalent to 1.36 and Molecular weight is equal to 70.91. 5. Air at 30 lbf/in2 absolute and 200F flows from a reservoir into a duct. The flow is steady, adiabatic, frictionless. The flow rate is 10lbm/s. What are the cross-sectional area, temperature, pressure, and Mach number at the point in the duct where the velocity is 1,400 ft/s? 6. Nitrogen gas is flowing through a 4” sch40 steel pipe at 25 0C. The flow rate is 7.4 x10-2 kg/s and the flow is assumed isothermal. The pipe is 3000 m long and the inlet pressure is 200 kPa abs. What is the outlet pressure?




