Counting Atoms Worksheet: Chemical Formulas & Periodic Table
advertisement

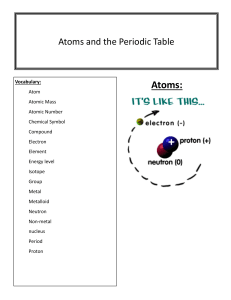
Name Period Date Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a group of atoms is called a radical. If a radical is used in a formula more than once, the radical is put in parentheses and the subscript appears outside the parentheses. When a subscript appears outside the parentheses, it indicates that all the elements inside the parentheses should be multiplied by that subscript. For example, the formula Fe (OH)3 indicates the combination of one atom of iron. Fe= three atoms of oxygen (O) and three atoms of hydrogen (H). In the following examples, list each element in the compound and the number of atoms of each element present. The first example has been done for you. You may already be familiar with some of the compounds. Name Use Formula Calcium carbonate Limestone CaCO3 Aspirin Pain reliever C9H8O4 Magnesium hydroxide Found in milk of magnesia Mg(OH)2 Paradichlorobenzene Moth crystals Acetic acid Found in vinegar Trinitrotoluene (TNT) Explosive Calcium dihydrogen phosphate Fertilizer Pyrite Fool’s gold C6H4Cl2 C2H4O2 C7H5 (NO2)3 Ca(H2PO4)2 FeS2 Sucrose Sugar Cellulose Found in wood products such as your C6H7O2(OH)3 pencil and paper C12H22O11 Atoms in Formula Ca= calcium 1 C= carbon 1 O= oxygen 3 1. What does the atomic number represent in the atom? 2. What information about the atom does the atomic mass tell us? Complete the following chart using your periodic table: Element Name Element Symbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # of Protons # of Electrons # of Neutrons Ex: Lithium Li 3 7 3 3 7-3 = 4 3. Carbon 4. Hydrogen 5. Nitrogen 6. Oxygen 7. Phosphorus 8. Sulfur 9. Magnesium 10. Argon 11. Sodium 12. Potassium 13. Calcium Color the letters based on the percentages. # of e- in energy levels