Curved Bars & Davits Test Proposal - Mechanical Engineering Lab
advertisement
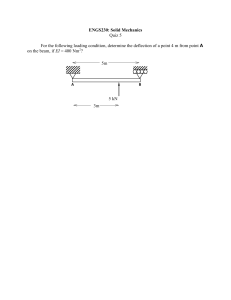
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY III BMCG 3011 PROPOSAL NAME: MUHAMMAD DANIAL HAIKAL BIN MOHD SHAHREL MATRIC NO: B042010090 CLASS SECTION: 3BMCG S2 LAB GROUP: GROUP D REPORT SUBMISSION DATE: 16 APRIL 2023 SEMESTER/SESSION: 2-2022/2023 EXPERIMENT TITLE: CURVED BARS AND DAVITS TEST LECTURER: EN. IMRAN SYAKIR BIN MOHAMMAD LECTURER REMARKS EVALUATION Objectives and Hypothesis Statement (2 Marks) Methodology (2 Marks) Expected Results & Conclusions (1 Mark) TOTAL OBJECTIVES The objective of this experiment is: 1. To determine the deformation of a structure in terms of four test structures; quarter circle, semicircle, curved davit and angled davit in horizontal and vertical deflections. 2. To compare the experimental value with the theoretical results. 3. To study the relationship between load and the deflection of curve. 4. To study the relationship between the shape of curved bar and deflection of the curved beams. HYPOTHESIS STATEMENT A beam or bar's deflection frequently needs to be restricted in order to maintain the integrity and stability of a structure or machine. In addition, code requirements frequently stipulate that these members must not shake or deflect significantly while supporting the appropriate loading in a safe manner. METHODOLOGY Procedures 1. Prepare the equipment to test the semicircle structure as the first test specimen. 2. The average width and thickness of the test structure cross section were measured and recorded. Then the second moment of area (I) of the cross section calculated. 3. The load hanger were attached to the free end of the test structure. 4. The dial indicator adjusted in positions, so it is in contact with the boss horizontally and vertically. The indicator reading was set to zero. 5. A weight of 100 g applied to the load hanger. The reading of both dial indicators were recorded. 6. The weight increased up to 500 gm in 100 gm increments, tapping the test frame each time. The reading of both dial indicators recorded. All loads and deflections reading recorded in Table 2. 7. The above procedures repeated with other structures (quarter circle, curved and angle davits). Figure 1 Test frame EXPECTED RESULT The results will be determined by observing the vertical and horizontal dial indicators for 4 different shape of specimens and loads up to 500g increments. Table 1 Theoretical formula for vertical and horizontal deflection Table 2 Expected result SHAPE a) Semi circle b) Quarter circle c) Curved Davit d) Angle Davit LOAD (g) 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 VERTICAL DEFLECTIONS (mm) 0.96 2.11 3.07 4.10 4.85 0.44 1.52 2.15 2.80 3.95 0.39 0.64 1.03 1.32 0.62 0.26 0.55 0.77 1.17 1.44 HORIZONTAL DEFLECTIONS (mm) 1.21 2.69 3.87 5.33 6.32 0.26 0.93 1.30 1.68 2.38 0.47 0.73 1.20 1.54 1.89 0.35 0.76 1.03 1.6 1.97 CONCLUSION In conclusion, the semicircle beam deflects significantly more than the structure. This is because the geometrical design of the beam gives the quarter-circle beam far greater support to bear the load applied to it.