scribd.vdownloaders.com expt-1-verification-of-superposition-theorem-for-ac-circuits
advertisement

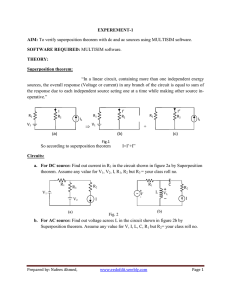
Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E. Electrical Experiment Number: 01 Title: Verification of Superposition theorem for A.C. circuits Aim: To verify Superposition theorem for A.C. circuits Apparatus: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Medium transmission line ‘T’ model AC Power Supply AC Voltmeter (0 - 150 V) AC Ammeter (0 - 1 A) Multimeter (Optional) Single Phase Autotransformer Connecting wires Diagram: 4 ohm 110 mH V1 Theory: 4 ohm 0.47 micro farad 110 mH V2 Statement of Superposition theorem: “Superposition theorem states that “In a linear network containing more than one independent source & dependent sources, the resultant current in any element is the algebraic sum of the currents that would be produced by each independent source acting alone, all the other independent sources being represented meanwhile by their respective internal resistances.” The independent voltage sources are represented by their internal resistance if given or simply with zero resistance, i.e. short circuits if internal resistances are not mentioned. The independent current sources are represented by infinite resistance, i.e. open circuit. Suppose, we have to apply Superposition theorem to following circuit then, Department of Electrical Engineering ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 Page 1 Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E. Electrical From the above circuit we have to determine the total currents due to effect of only one source at a time. Both the sources given in the above network have control variable V and I but it is to be noted that V and I does not make the source dependent on the variable of any portion of the network shown above. Steps to be followed for superposition theorem. 1. First find current through ZB by removing i.e. opening current source. This current is due to voltage source only. 𝐼′ = 𝛼. 𝑉 𝑍𝐴 + 𝑍𝐵 2. Next, the voltage source being removed (i.e. voltage source is short circuited) and current through ZB is found. 𝐼 ′′ = Department of Electrical Engineering ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 𝑍𝐴 . 𝛽𝐼 𝑍𝐴 + 𝑍𝐵 Page 2 Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E. Electrical 3. The resultant current by using superposition theorem is 𝐼 = 𝐼 ′ + 𝐼 ′′ Procedure: 1. Connections are made as per the circuit diagram 2. The readings of voltmeter and ammeter are noted with one source at a time. 3. After connecting both sources, the voltmeter and ammeter readings are noted. 4. The procedure is repeated for different values of source voltage 5. Observed readings and calculated readings are compared to verify superposition theorem. Observation table: IRL1 Observed Values Calculated values IRL2 Observed Values Calculated Values With V1 With V2 Both V1 & V2 Calculations: Do the calculation on Blank ruled pages. Conclusion: ======================================================= Department of Electrical Engineering ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 Page 3