Child & Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders: Nursing Care
advertisement
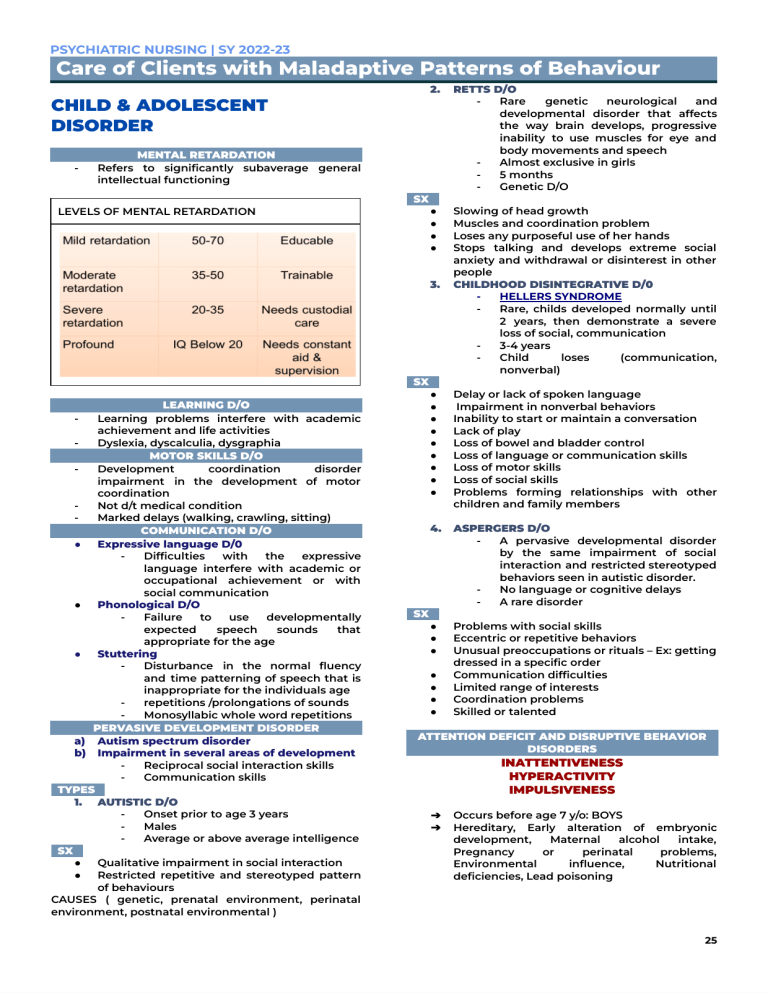
PSYCHIATRIC NURSING | SY 2022-23 Care of Clients with Maladaptive Patterns of Behaviour 2. CHILD & ADOLESCENT DISORDER - MENTAL RETARDATION Refers to significantly subaverage general intellectual functioning LEVELS OF MENTAL RETARDATION SX . ● ● ● ● 3. LEARNING D/O Learning problems interfere with academic achievement and life activities Dyslexia, dyscalculia, dysgraphia MOTOR SKILLS D/O Development coordination disorder impairment in the development of motor coordination Not d/t medical condition Marked delays (walking, crawling, sitting) COMMUNICATION D/O ● Expressive language D/0 Difficulties with the expressive language interfere with academic or occupational achievement or with social communication ● Phonological D/O Failure to use developmentally expected speech sounds that appropriate for the age ● Stuttering Disturbance in the normal fluency and time patterning of speech that is inappropriate for the individuals age repetitions /prolongations of sounds Monosyllabic whole word repetitions PERVASIVE DEVELOPMENT DISORDER a) Autism spectrum disorder b) Impairment in several areas of development Reciprocal social interaction skills Communication skills TYPES . 1. AUTISTIC D/O Onset prior to age 3 years Males Average or above average intelligence SX . ● Qualitative impairment in social interaction Restricted repetitive and stereotyped pattern ● of behaviours CAUSES ( genetic, prenatal environment, perinatal environment, postnatal environmental ) SX . ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● 4. SX . ● ● ● ● ● ● ● RETTS D/O Rare genetic neurological and developmental disorder that affects the way brain develops, progressive inability to use muscles for eye and body movements and speech Almost exclusive in girls 5 months Genetic D/O Slowing of head growth Muscles and coordination problem Loses any purposeful use of her hands Stops talking and develops extreme social anxiety and withdrawal or disinterest in other people CHILDHOOD DISINTEGRATIVE D/0 HELLERS SYNDROME Rare, childs developed normally until 2 years, then demonstrate a severe loss of social, communication 3-4 years Child loses (communication, nonverbal) Delay or lack of spoken language Impairment in nonverbal behaviors Inability to start or maintain a conversation Lack of play Loss of bowel and bladder control Loss of language or communication skills Loss of motor skills Loss of social skills Problems forming relationships with other children and family members ASPERGERS D/O A pervasive developmental disorder by the same impairment of social interaction and restricted stereotyped behaviors seen in autistic disorder. No language or cognitive delays A rare disorder Problems with social skills Eccentric or repetitive behaviors Unusual preoccupations or rituals – Ex: getting dressed in a specific order Communication difficulties Limited range of interests Coordination problems Skilled or talented ATTENTION DEFICIT AND DISRUPTIVE BEHAVIOR DISORDERS INATTENTIVENESS HYPERACTIVITY IMPULSIVENESS ➔ ➔ Occurs before age 7 y/o: BOYS Hereditary, Early alteration of embryonic development, Maternal alcohol intake, Pregnancy or perinatal problems, Environmental influence, Nutritional deficiencies, Lead poisoning 25 PSYCHIATRIC NURSING | SY 2022-23 Care of Clients with Maladaptive Patterns of Behaviour CAUSES . ● Genetic Factors ● Organic factors - brain damage ● Biochemical factors ● Psychosocial Factors child abuse a dysfunctional family parents who abuse drugs or alcohol Poverty Parental rejection - SX . ● ● ● ● CONDUCT D/O persistent antisocial behavior in children and adolescents that significantly impairs their ability to function in social, academic or occupational areas Aggression to people and animals Destruction of property Deceitfulness & Theft Serious violation of rules Types of Conduct Disorder a) b) TREATMENT . a. Drugs may include: ● Anticonvulsants ● Lithium ● Antipsychotics b. Psychotherapy c. Guidance and counselling Social skill training Role playing Modelling Shaping of behavior Childhood- onset type occurs when the signs of conduct disorder appear before age 10 Adolescent onset type occurs when the signs of conduct disorder appear during the teenage years CONDUCT DISORDER CAN BE CLASSIFIED AS: ❖ ❖ ❖ Mild - Minor harm to others - Example: lying, truancy, staying out late without permission Moderate Conduct problems increases Example: vandalism and theft Severe considerable harm to others Example: Forced sex, cruelty to animals, use of weapon, burglary and robbery Manzano, Audrey Alexis