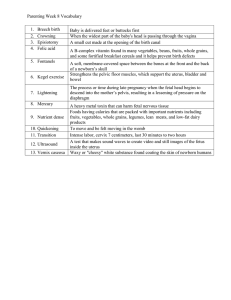
AdventHealth University NURS 330: Childbearing Family Key terms for the first day of clinical Labor and Delivery: Amniotomy - artificial rupture of the membranes. Abbreviation: AROM Attitude - relationship fetal body parts to one another Bloody show - mixture of cervical mucus and blood from ruptured capillaries in the cervix; often precedes labor and increases with cervical dilation Braxton Hicks contractions - irregular, mild uterine contractions that occur before true labor Crowning- appearance of the fetal scalp or presenting part at the vaginal opening Contraction: Muscle tightening of the uterus. The following terms are used to describe aspects of a contraction: Frequency - period from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction Intensity - strength of the uterine contraction Interval - period between the end of one to the beginning of the next uterine contraction. Dilatation/Dilation: How open the cervix is, measured from 1 – 10 cm. Measured by vaginal examination with sterile glove and sterile lubricant. Effacement: thinning of the cervix, communicated in “%”. As in “cervix 50% effaced”. Measured by vaginal examination at the same time as “dilatation” and “station”. Engagement - descent of the widest diameter of the fetal presenting part to at least zero station (level with the ischial spines in the maternal pelvis) Epidural: Regional anesthesia to decrease pain from childbirth. Injection of a “caine” drug into the epidural space in the spine. Important to monitor BP after insertion Episiotomy - incision of the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening. Not done as frequently these days. Fetal Heart Rate: Normal rate is 110 – 160. May also be referred to as “Fetal Heart Tones” Gravida- a pregnant woman; also refers to the total number of pregnancies including the one in progress if applicable. Primigravida refers to woman pregnant for the first time. Multigravida refers to a woman pregnant 2 or more times. 1 Lie - relationship of the long axis (spine) of the fetus to the long axis of the mother. Lightening - descent of the fetus toward the pelvic inlet before labor. Mother is able to breathe easier, but may feel increased perineal pressure Lochia - vaginal drainage after birth (see further description under Postpartum) Multipara -a woman who has given birth after two or more births of 20 weeks gestation. Molding - shaping of the fetal head during movement through the birth canal. Usually resolves within 24 hours after birth Nuchal cord - cord around the fetal neck Nullipara - a woman who has not completed a pregnancy to at least 20 weeks Para - A woman that has given birth after a pregnancy of at least 20 weeks. Also designates the number of pregnancies that end after 20 weeks. Twins( and other multiples) are considered one delivery or parity. Position - relationship of a fixed reference point on the fetus to the quadrants of the maternal pelvis. Presentation - fetal part that enters the pelvic inlet or the presenting part Newborn: Acrocyanosis: bluish coloration of newborn’s hands and feet Asphyxia: low (insufficient) blood oxygen and high blood and tissue carbon dioxide levels Bilirubin: unusable component of hemolyzed (broken down) erythrocytes. This may occur in newborns due to immature liver function and increased breakdown of fetal red blood cells after birth. Brown Fat (or brown adipose tissue): highly vascular fatty tissue in the newborn designed for newborn heat production. Provides more heat than other fat when stimulated by cold stress and release of adrenaline Candidiasis: yeast infection seen as white patches in the mouth of the newborn. Caput succedaneum: area of subcutaneous edema over the head of the newborn resulting from pressure during the birth process. This crosses suture lines, like a “cap”. Usually resolves within 12 – 24 hours after birth(Don’t confuse with Cephalohematoma!!) Cephalohematoma: swelling on the infant’s head resulting from bleeding between the periosteum and skull from pressure during the birth process; does not cross suture lines. Usually 2 doesn’t show up for 12 – 24 hours after birth and may last up to 6 weeks after birth(Don’t confuse with Caput Succedaneum!!) Circumcision: surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis (cultural, usually not necessary!) Colic: irritable crying for no obvious reason in a healthy newborn Colostrum: precedes true milk, contains antibodies to help immune system development. Cooing: vowel sounds made by the infant Crepitus: “grating” sensation during palpation. In infants, may be heard and felt over a broken bone such as the clavicle. Erythema toxicum: benign rash of unknown cause in newborns, with blotchy red areas that may have white or yellow papules or vesicles in the center. Although not proven, thought to be related to the infant skin reacting to the environment. Fontanel - space at the intersection of sutures connecting fetal or infant skull bones. The anterior fontanel is diamond shaped. The posterior fontanel is triangle shaped. Jaundice: yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclera. Result of build up of bilirubin. May be physiologic or pathologic. Kernicterus: permanent neurologic damage from bilirubin staining of brain cells Lanugo: fine, soft hair that covers the fetus. Most often seen on the back and shoulders. Meconium: the thick blackish-green first bowel movements of a newborn. Milia: small white cysts on the newborns face. Look like “whiteheads”. Do not “pinch”: they are plugged sebaceous ducts and will resolve in a few weeks. Mongolian spots: bluish, bruise-like marks on the back and/or buttocks of newborns, mostly those with darker skin tones. Neutral Thermal Environment: Surroundings in which the infant can maintain a stable temperature with minimal oxygen consumption and a low metabolic rate. Non-shivering Thermogenesis: production of heat by specialized fat – brown fat. Newborns are unable able to shiver at birth to produce heat Polydactyly: more than 10 digits on the hands or feet. Rugae: scrotal skin creases. Strabismus: “crossed” eyes. Normal finding in newborns due to weak eye muscles. 3 Subconjunctival hemorrhage: broken vessels in the sclera of newborn eyes, usually from pressure during the birth. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS): abrupt and unexplained death of an apparently healthy infant. Decreased incidence when infants are put to sleep on their backs Surfactant: combination of lipoproteins produced by the lungs of the mature fetus that reduces surface tension in lung alveoli to keep them open. Thermogenesis: heat production. Triage: determining whether there is a serious problem and need for treatment and follow-up. Vernix caseosa: the “cheesy” white substance present on the developing fetus’ skin. Usually just traces left on the skin of a term infant, may be present in large amounts with birth before 40 weeks. Postpartum: After pains: Cramping pain after childbirth caused by alternating relaxation and contraction of uterine muscles. May be exacerbated with breast feeding and for a multipara (woman who has given birth to more than 2 children) Atony: Absence or lack of usual muscle tone. Referring to uterus post-birth, the uterus should stay firm and contracted to prevent blood loss. Uterine atony is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage, which can lead to death. Decidua: name applied to the endometrium during pregnancy. All except the deepest layer is shed after childbirth. Diastasis recti: separation of the longitudinal muscles of the abdomen (rectus abdominis) during pregnancy Engorgement: swelling of the breasts resulting from increased blood flow, edema, and presence of milk. Episiotomy: surgical incision of the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening Gravida/Para: Gravida: number of times a woman has been pregnant. Para: Number of times a woman has given birth to a fetus over 20 weeks gestational age. Seen in this context: G1P0 (pregnant for the first time, has not given birth) or G6P3 (pregnant for the 6th time, has given birth 3 times to a fetus over 20 weeks. Involution: retrogressive changes that return the reproductive organs, particularly the uterus, to their nonpregnant size and condition. Takes about 10 days for the uterus to shrink in size and go below the symphysis pubis. 4 Lochia: vaginal discharge after birth Rubra: reddish or red-brown vaginal discharge that occurs immediately after childbirth; composed mostly of blood, lasts approximately 3 days post birth Serosa: pink or brown-tinged vaginal discharge present on days 4-14 post birth Alba: white, cream colored, or light-yellow vaginal discharge, composed of leukocytes and mucous. Present up to 6 weeks post birth Puerperium: period from the end of childbirth until involution of the reproductive organs is complete; approximately 6 weeks REEDA: acronym for redness ecchymosis, edema, discharge, and approximation; useful for assessing wound healing or the presence of inflammation or infection, as in a vaginal laceration or episiotomy Subinvolution: delayed return of the uterus to its nonpregnant size and consistency 5