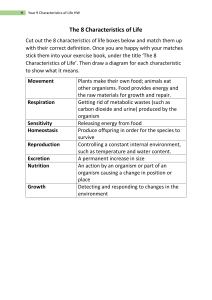
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS Dr Taat Htun Thu Movement • The ability of an organism, or part of it, to change position or place. • By the action of muscles in animals, and slow growth movements in plants • Movement in pant is non locomotion, related with to growth Respiration • Released energy from their food • The chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy for metabolism • Many organisms have gaseous exchange systems that supply their cells with from their environment. • Release energy, use in stay as alive Sensitivity (Response to stimuli) • Sensitive to change their environment • The ability to detect or sense stimuli in the internal or external environment and to make appropriate responses • There are two main types of stimulus – External stimulus (Pain and touch, Vision, Taste, Smell, Sound, Balance) • Internal stimulus (Blood Pressure, Homeostasis) Growth and development • Increase and size and complexity, using materials from their food • Every living organisms increase in size and cell numbers • As the numbers of cell increase, the complexity increases also of the organism Reproduction • Produce the offspring (the same kind) • the processes that make more of the same kind of organism Excretion • Removal from organisms of toxic materials, waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements Control their internal conditions • Maintain the study state inside the body. • The condition inside our body are know as its internal environment. • Our body have to keep this conditions are called Homeostasis. • In this conditions involve chemicals are called Hormone. • In this control also involved Nervous system. Nutrition • Taking of nutrients which are organic molecules and minerals and oils plants makes their own food (Autotrophic) require light, carbon dioxide, water and ions; 1.2 The biological classification system Classification - Putting things into the same groups Species - Classified into small groups - a group of organisms that reproduce with each other - Produce offspring - That offspring can also reproduce - Offspring are fertile The binomial naming system - scientific names always have two words - therefore called the binomial system - ‘Bi’ means two, and ‘nomial’ means to do with names - In the two-word name, the first name is genus, always written with a capital letter. - The second name was species, always written with small letters - When printed as Italic - When writing, underline 1.3 KEYS Dichotomous key - means branching (dividing) into two. - is a way of leading you through to the name of your organism - giving you two descriptions at a time and asking you to choose between them. - Each choice you make then leads you on to another pair of descriptions, until you end up with the name of your organism.