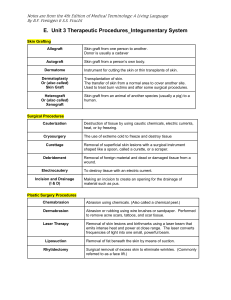
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY • If "itis" means inflammation then, bronchitis means inflammation of the bronchi • If "otomy" means "incision" or "cut into" then craniotomy means to cut into the skull or cranium • If "ectomy" means "surgical removal" then the surgical removal of a person's urinary bladder would be a cystectomy • An arthrotomy would involve an incision into a joint • Inflammation or "itis" of the skin is called dermatitis • Colitis is an inflammation of the colon • The surgical removal ("ectomy") of a person's "gall" "bladder" is known as a cholecystectomy • Bradycardia refers to a slow heart rate. • The area between ("inter") two ribs is called intercostal • "osis" means being in the "condition of": the condition of "blueness" (such as a blue tint to the skin) is refered to as cyanosis • Enterocolitis is an inflammation of the small intestine and the colon • If hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the "uterus", then Colectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the "colon". • If "megaly" means irregular enlargement, then an enlargement of a "liver" may be referred to as hepatomegaly • Cardiomegaly is an enlargement of the heart • A gastrectomy is the surgical removal of the stomach. • If hypo- is something that is "depleted or low", and -emia refers to something "in the blood", then the term for "low" "glucose or sugar" levels "in the blood" is hypoglycemia • Cystectomy refers to the surgical removal of the bladder. Creating a new temporary opening into the bladder with a surgical incision is referred to as a Cystotomy • If -lysis means "destruction of" then hemolysis is the destruction of blood cells • -penia indicates a "deficiency or low-level": "leukocytopenia" (also called leukopenia) literally refers to a condition of low white blood cells in the blood. • Vomiting blood is referred to as hematemesis • -scopy refers to an "examination of" something; an examination of the inside of the abdomen is a "laparoscopy". Following the same naming principle, the thin, lighted scope utilized to examine the inside of the abdomen is typically called a laparoscope • Inflammation of the stomach may be called gastritis • An inflamed kidney is "pyelonephritis". "pyelo" refers to the renal pelvis • if "ology" refers to "the study of" then the study of the nervous system may be refered to as neurology • An osteoma is a tumor of the bone. Using a root/combining form, create a word referring to a tumor originating from the cells of the bone marrow: myeloma • A flexible medical tube inserted in the nose and terminating in the stomach is refered to as a nasogastric tube. • The suffix "iasis" means "produced by". Cholelithiasis describes stones produced in the gallbladder. • The surgical removal of a breast is called mastectomy • Mammoplasty refers to the "plasty" or "reshaping" of the breast. Although the term angioplasty refers to the reshaping of a "vessel" (blood vessel) - in use, it often refers to the reshaping of an artery (typically widening a narrow carotid, coronary or peripheral artery to improve blood flow). • A surgically reconstructed urinary bladder to replace a diseased bladder is known as a neobladder (" neo" is the word root for new) • The oculomotor nerve controls most eye movements. • A lighted instrument used for examining the inner eye is called an ophthalmoscope • This word derives from the three word roots for "bone" "joint" and "inflammation": osteoarthritis • The prefix "dys" means abnormal, difficult, or painful. Using this prefix, difficult breathing may be refered to as dyspnea • The surgical removal of one lung lobe is a "lobectomy". The surgical removal of a whole lung (one side) is a pneumonectomy • "pathy" means "pertaining to disease". Cardiomyopathy refers to a "heart" "muscle" "disease" • Rhinopathy refers to disease of the nose; rhinitis is inflammation of the nose; rhinoplasty is the surgical reshaping of the nose. • The urethra is below the bladder, the two ureters are above and are similarly named. If a ureteroplasty is the reshaping or repair of a ureter, a urethroplasty is the reshaping or repair of a urethra. • "Vas/o" refers to "vessel", "ven/o" refers to "vein", and "angio" refers to "artery". If an angiogram specifically examines an artery, a venogram specifically examines a vein. • Vaso"active" drugs may cause blood vessels to tighten or relax, changing the size of their lumen. Vasoconstriction refers to the tightening of a blood vessel, Vasodilation refers to the relaxing of a blood vessel. • The word roots "pyro" and "pyo" are very simular and easily confused. Something that is "pyrogenic" is "fever" producing; something that is pyogenic is "pus" producing. • "Ven/o" and "phleb/o" both refer to "vein". Recall the suffix for "cut into". The act of "opening" a vein with a needle to draw a blood sample is referred to as venotomy • The suffix "cele" is a bulging or herniation. When the rectum herniates (usually toward the vaginal canal), it is called a rectocele • Within body cavities we need to differentiate between the cavity wall surface and the organ surfaces. The abdominal and pelvic cavities are lined with 2 kinds of peritoneum. The "parietal" ("belonging to walls") peritoneum lines the wall of the cavity. From the root "viscer/o", the visceral peritoneum lines most abdominal organs • There is a condition of low platelet count in which a person lacks the cells nessessary to clot adequately. It is composed of the root words for "clot" "cell" and the suffix "penia" (meaning deficient or low): thrombocytopenia (create the word) • If hypo"thermia" means below normal body temperature, and hyper"thermia" is above body temperature, a normal body temperature could be called Normothermia • "pyel/o" and "pylor/o" are close in sound but very different. pyel/o refers to "pelvis" it usually refers specifically to the renal pelvis / kidney while pylor/o refers to the "pylorus" lower portion of the stomach. • A tracheostomy involves creating a "new opening" in the portion of upper respiratory airway that runs through the neck. • "Splen/o" refers to the spleen; splenomegaly refers to an "enlarged" spleen. • "lymph/o" refers to lymph fluid, "lymphaden/o" refers to lymph nodes. "Disease of" the lymph nodes would be called lymphadenopathy • The word empyema refers to the collection of pus in a body cavity especially the pleural space. • The prefix "anti"means "against". An anti-infective agent is a drug used against an infection. Using this same prefix, an ___antiarrhythmic___ is a medication that works "against" cardiac arrhythmias. • The prefix "anti" should not be confused with "ante" which means "before" (in time or space). When a patient is isolated for infection control, it is beneficial to have a small enclosed chamber, called an ___antechamber___ in which you can wash, mask, gown and glove before entering the patient room • "phasia" and "phagia" are two similar looking and sounding combining forms. "phagia" refers to "eating" while "phasia" refers to "speech". A word meaning "difficult" speech or "impairment of language" is ___dysphasia___You should know how this word slightly differs in meaning and use from the words "aphasia" and "dysarthria". • It is helpful to be able to describe when a body limb is moving towards the midline of the body, or moving away from the midline of the body. Movement toward the midline of the body is: ___adduction___ • When the trachea descends to the lungs it divides into two branches or is said to ___bifurcate___ : a word created using the prefix for "two" and the latin word "furca" meaning "fork". • The dura mater is the outermost of the three layers of the meninges that surround the spinal cord. The ___epidural___ space is "on", or "upon" the dura mater - it is often used for delivering analgesia. • "systole" refers to contraction of the heart muscle. A similar looking word, ___asystole___is the absence of contractions in a heart. • When discussing intravascular volume, a patient may be hypovolemic, hypervolemic, or, if their volume is normal, ___euvolemic___ • "colectomy" is the surgical removal of all or part of the colon. A ___hemicolectomy___ is a procedure to remove one side or "half" of the colon and is usually proceeded by "left" or "right" • intercostal___ means in between the ribs • Laparoscopy, cystoscopy, and colonoscopy are all forms of ___Endoscopy___ (one word) which is the generic word for when a flexible lighted instrument is used to examine the inside of a hollow body cavity or organ • The procedure of inserting an artificial airway through the mouth and into the trachea is referred to as "intubation". When this "tube" or "airway" is removed, the procedure is called ___extubation___ • An "incision" is a surgical cut made into the skin or tissue. An ___excision___ refers to the surgical removal of tissue by cutting (cuttingaway, cutting-out) (similar to biopsy, resection) • When describing disease that impacts both ventricles of the heart at the same time, the word ___biventricular___is useful. • The prefix "de-" is commonly used to create a word for the "removal of" or "decrease" of something. For example the word ___demyelination___ is the loss of myelin from the nerve or nerves. •