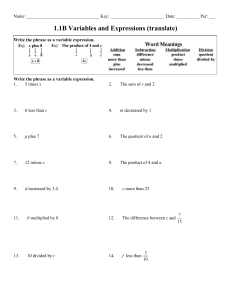
Mission Republic of the Philippines Vision The premier University in historic Cavite recognized for excellence in the development of globally competitive and morally upright individuals. CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY Silang Campus Biga I, Silang, Cavite A Detailed Lesson Plan for Grade 7 Algebraic Expression Cavite State University shall provide excellent, equitable, and relevant educational opportunities in the arts, sciences and technology through quality instruction and responsive research and development activities. It shall produce professional, skilled and morally upright individuals for global competitiveness. I. Objectives At the end of discussion, the students should be able to: A. translates English phrases to mathematical phrases and vice versa; B. relate the algebraic expression in real life situation; and C. evaluates algebraic expressions for given values of the variables. II. Subject Matter A. Topic: Algebraic Expression B. Materials: Cartolina and strips of paper for the lesson proper and application. C. Values Integrated: Relating the algebraic expression in real life situation. D. References: Mateo, MAT, R. R. & Mercado, PhD, E. T. (2014). Integrated Mathematics. Dasmariñas City, Philippines: Siam Rein Publishing House. Oronce, O. A. & Mendoza, M. O. (2011). e-Math (K to 12). Philippines: Rex Book Store Idrees, M. (2019b, June 12). Introduction to Algebraic Expressions and Polynomials. Retrieved November 10, 2019, from https://www.emathzone.com/tutorials/algebra/introduction-to-algebraic-expressionand-polynomials.html Evaluate expressions (Pre-Algebra, Introducing Algebra) – Mathplanet. (n.d.). Retrieved November 10, 2019, from https://www.mathplanet.com/education/prealgebra/introducing-algebra/evaluate-expressions Introduction to Algebra. (2017). Retrieved November 10, 2019, from https://www.mathisfun.com/algebra/introduction.html III. Learning Activities Teacher’s Activity A. Daily Routine Student’s Activity 1. Prayer Everyone, please stand for a prayer. Kiel, kindly lead the prayer. 2. Greetings Good afternoon, Grade 7! Good afternoon, Ma’am! 3. Classroom Management Before you sit, pick up all the pieces of trash under your chairs and arrange your chairs properly. 4. Checking of Attendance Miss secretary, is there any absent today? None, Ma’am. 5. Checking of Assignment Do you have assignment? None, Ma’am. 6. Review Let’s have a short recap to our previous topic. What did we tackle last meeting? Yes, Erra. Ma’am we discuss about problem solving involving conversion of units. Very good! What is the rule in converting metric? Yes, Isaac. To change from a larger unit to a smaller unit move the decimal point in the given quantity one place to the right for each smaller unit until the decimal unit is reached. Very good! How about converting smaller unit to larger unit? Yes, Mikaila. Move the decimal point in the given quantity one place to the left for each larger unit until the decimal unit is reached. Very good! In English system what we will do in order to eliminate the unit? Yes, Angel. The unit we need to introduce, must appear in the numerator and the unit we need to eliminate, must appear in the denominator. Very good! It seems that you all learn a lot to our previous topic. 7. Motivation Let's have a short activity. Are you all familiar with the game The Boat is Sinking? Yes, Ma’am Let's put a twist on it. All you need to do is to group yourselves into the number that I will flash but, before you’ll group yourselves, you needed to add the two numbers first. The sum will be the number you will group yourselves into. The three players who will reach the last round will be the winners. Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Any questions? None, Ma’am. Are you ready? Yes, Ma’am. The boat is sinking group yourselves into (the game will start) The boat is sinking group yourselves into The boat is sinking group yourselves into The boat is sinking group yourselves into The boat is sinking group yourselves into Did you enjoy the activity? Yes, Ma’am. B. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation of Lesson What do you think is the connection of the activity you have done earlier to our topic? Yes, Faith. In our activity, we solve letter and number which has an equivalent value. I think our topic for today is about algebra. Very good! Today we will talk about algebraic expression. Let’s define first what is algebraic expression? An algebraic expression is a combination of variables and constants involving at least one arithmetic operation. Examples: 3x2 – x – 2 7x4 – 3x3 + 9x-3 Give me an example of algebraic expression. Yes, Athena. 6x + 4 Very good! Give me another example. Yes, Issac. Very good! Give me another example. Yes, 5xy Roliven. Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Algebra is a means of computing using non numeric objects. 2x + 3y – 4z In here 2, 3 and – 4 are the constants. From does examples what is a constant? Yes, Kiel. It refers to the number in the expression. Very good! A constant is a symbol that assumes one specific value. Quantities whose values do not change are called quantities or simply, constant. Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. 2x + 3y – 4z In here x, y and z are the variables. From does examples what is a variable? Yes, Samantha. It refers to the alphabet or letter in the expression. Very good! A variable is a symbol that assumes many values. It is a letter used to represent one or more numbers in an expression, equation or inequality. A quantity whose value change is called a variable. Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. 2x + 3y – 4z This whole expression is a polynomial. From this example what is a polynomial? Yes, Ralph. Very good! A polynomial is an algebraic expression involving only non-negative integer power of one or more variables and containing no variable in the denominator. Examples: 7x + 3 x 5 It refers to the combination of variable and constant involving at least one arithmetic operation. 8x3 – 4xy + 16z Yes, Ma’am. Is everything clear? Translation of mathematical phrase to mathematical symbol. I have here a matching type. Match the column A in column B. Mathematical Phrase Column A Mathematical Symbol Column B 1. greater than increase by more than added to sum of a. – 1. c b. × 2. a c. + 3. b 2. less than decreased by smaller than fewer than difference d.3x 4. h e.÷ 5. d f.4x 6. e g. = 7. g 3. multiplied product of times h. 2x 4. double 5. triple 6. divided by ratio of quotient of 7. equals Very good! There are many ways to express addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division of algebraic expression. Examples: The sum of m and 8 m+8 The difference of 8 and m 8–m English Phrase 10 added to c 10 subtracted from c twice x x divided into 10 Is everything clear? Algebraic Translation c + 10 c – 10 2x 10 x Yes, Ma’am. Examples: 3+4 The sum of 3 and 4 or 3 plus 4 8–3 8 minus 3 or 8 less 3 Algebraic Translation n+5 7–n 20 ÷ 5 8(4) Is everything clear? English Phrase 5 more than n or n increased by 5 n less than 7 or 7 decreased by n The quotient of 20 and 5 8 times 4 Yes, Ma’am. Try it on board! 1. 5 more than t 2. 1 000 less f 3. 10 times c 4. The ratio of 7 to a t+5 1 000 – f 10c 7 a Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Any questions? None, Ma’am. I have here a puzzle For checking: Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Any questions? None, Ma’am. Try it on board! 1. 2x – 3 = 3 Checking: 2. 4x + 3 = 12 Checking: Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Any questions? None, Ma’am. Classification of Algebraic Expressions Exponent – a number at the upper right hand corner of the variables, constant, or expression indicates the number of time a constant, variable, or expression is used. Degree – the degree of a polynomial in one variable is a highest exponent of the viable in the term of the polynomial. If the term has more than one variable, the degree is the sum of the exponents of the variable. Term – either a single number, a letter, or a product of several numbers or letters. 1. Monomial – one term. 2. Binomial – two terms. 3. Trinomial – three terms. 4. Multinomial – more than three terms. Examples: 2x, 3y, 4z Examples: 3x + 4, 5x – 6, a + b Examples: 3x + 4y – 5, 4a – 3b + 8, 7m2 – 2m + 9 Examples: 5x + 3y – 2z, 3m3 + 2m2 – 6m + 2 –b Numerical coefficient – constant factor in a monomial Literal coefficient – the variable factor in a monomial. C. Application Board work Solve the following: 1. x + 2 = 3 2. y – 5 = 5 3. 2z = 10 4. 3a + 1 = 10 5. 25b = 50 x=1 y = 10 z=5 a=3 b=2 Is everything clear? Yes, Ma’am. Any questions? None, Ma’am. D. Generalization Let’s sum up our lesson today. What is a symbol that assumes one specific value? Yes, Isaac. constant Very good! What is a symbol that assumes many values? Yes, Mikaila. variable Very good! What is an algebraic expression involving only non-negative integer power of one or more variables and containing no variable in the denominator? Yes, Zylo. polynomial Very good! And what are the types of polynomial? Yes, Eduardo. Monomial, binomial, trinomial, and multinomial. Very good! What is a variable, a constant or a combination of variables and constants involving at least one arithmetic operation? Yes, Angel. algebraic expression Very good! It seems that you all learn a lot to our topic for today. IV. Evaluation Get ¼ sheet of pad paper. Complete the table. Ex. 2m2 1. 3a 2. 4abc 3. 2x3 4. 11xy 5. 2x3 + 1 constant 2 variable m Ex. 2m2 1. 3a 2. 4abc 3. 2x3 4. 11xy 5. 2x3 + 1 Who got 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 V. Assignment For your assignment, have an advance study on addition and subtraction of polynomials answer the following in your notebook Goodbye, Ma’am! 1. How to combine polynomials? 2. What format can be used in adding and subtracting polynomials? So that’s all for today. Goodbye, Grade 7! constant 2 3 4 2 11 2&1 variable m a abc x xy x Prepared by: MAUREEN S. TORINO BSE 4 - Mathematics Checked by: DOTHY C. GUMAMELA, LPT Cooperating Teacher Reviewed by: JANE A. MANARPIIS, M.A. Ed. BSE Coordinator Recommended by: CHRISTEL M. BELARO, LPT Officer-in-Charge SELSHS Approved by: ROSELYN A. YMANA, Ph. D. Teacher Education Department, Chairperson