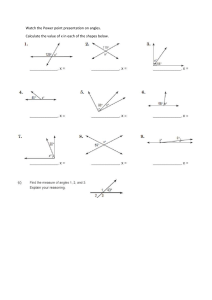
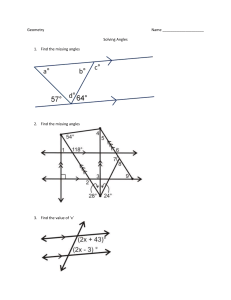
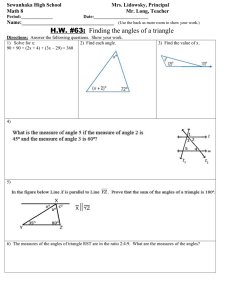
Congruence and Similarity Symbol for showing congruence ≅ Symbol for showing similarity ~ Two angles and one side = A.S.A (or) A.A.S Two sides and one angles = S.A.S Three sides = S.S.S One right angle included = R.H.L (or) R.H.S Two similar angles = A.A Three similar sides = S.S.S Two similar sides and one angles = S.A.S Pythagoras Theorem a(square) + b(square) = c(square) Angles in Two-Dimensional figures = line .----. = line segment . = ray supplementary = two angles add up to 180 degree complementary = two angles add up to 90 degree adjacent angles on a line = all angles add up to 180 degree vertically opposite angles = four angles add up to 360 degree three types of matching angles = corresponding, alternate, angles between parallel lines Geometric Measurement Polyhedron = many faces, prism and pyramid non-Polyhedron = cylinder, cone, sphere (or) hemisphere equations area of square = s (square) area of rectangle = l x b area of triangle = ½ bh area of circle = 𝜋 r(square) circumference of circle = 2 𝜋 r surface area of square based pyramid = area of square base + 4(area of triangle) surface area of cone = 𝝅 r(square) + 𝝅 r s surface area of cylinder = 2 𝝅 r(square) + 2 𝝅 r h surface area of sphere = 4 𝝅 r(square) surface area of hemisphere or hollow hemisphere = 2 𝝅 r(square) surface area of solid hemisphere = 3 𝝅 r (square) volume of prism = base are x height volume of pyramid = 1/3 bh volume of hemisphere = 2/3 𝝅 r(cube) volume of sphere = 4/3 𝝅 r(cube) Linear Graphs linear equation straight line origin = (0,0) general equation y = mx + c Coordinate Geometry midpoint of a line segment (x1 + x2 /2, y1 + y2 /2) distance formula (length) = square root of (x2 – x1)the whole square + (y2 – y1)the whole square Probability probability = number of favorable outcomes /numbers of possible outcomes Data and Graphs dot diagram Mode peak value or most common value (the most frequent data) Cluster a place with lots of data surrounding Outliers or extreme value the uncommon data (too high or too low) Spread of the data range of the data stem and leaf diagram must include key must be ascending order Important factors Mode = most common value Median = middle number Mean = average Range = difference between the start and the end (not included in average)