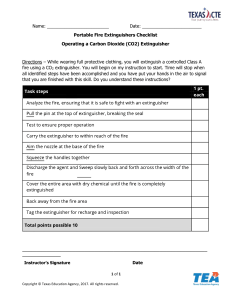
BASIC FIRE FIGHTING TRAINING Presented and Prepared By: Farrukh Ahmed Objectives • Understand the combustion process and different fire classes • Understand fire extinguisher types, operating procedures • Understand basic firefighting concepts: –R.A.C.E. –P.A.S.S. Consequences of Fire •Loss of life •Loss of friends or family •Injury or disability •Loss of home, workplace, income, job •Loss of irreplaceable belongings •Financial (uninsured losses and premiums) The Fire Triangle Three things must be present at the same time to produce fire: 1. Enough OXYGEN to sustain combustion 2. Enough HEAT to reach ignition temperature 3. Some FUEL or combustible material Together, they produce the CHEMICAL REACTION that is fire Take away any of these things and the fire will be extinguished The Combustion Process • Three components • Need all three components to start a fire • Fire extinguishers remove one or more of the components. Sources of Ignition • • • • • Smoking Electrical equipment Heaters Process machinery Contractors tools and equipment • Torching Fuels • • • • • • • Paper and boxes etc. Packaging (polystyrene beads etc) Plastics Solvents Soft furnishings (Mattresses, cushions) Furniture Waste materials (rubbish, old pallets) Fuel Classifications • Fires are classified according to the type of fuel that is burning. • If you use the wrong type of fire extinguisher on the wrong class of fire, you might make matters worse. • Its very important to understand the four different fire (fuel) classifications… Oklahoma State University Environmental Health & Safety Dept. Fire Classes A Trash Wood Paper • • • • B Liquids Grease wood paper cloth etc. C Electrical Equipment • • • COMBUSTIBLE computers fax machine other energized electrical equip. D METALS • • • • gasoline oil grease other solvents • • • • • magnesium sodium potassium titanium other flammable metals Fire Classes (cont.) CLASS K FIRES • Recently recognized. • Fires involving combustible oils, lards and fats in commercial cooking. K Cooking Media Basic Fire Prevention • Be mindful of Fire Safety • Don’t block fire exits, call points or extinguishers, know your exits • No smoking policy • Take care with any hot process, follow manufacturers instructions • Maintain any machinery • Observe good security • Don’t block Fire Doors On Hearing the Alarm Observe any instructions in your building evacuation plan • • This may include providing assistance to other persons and evacuating area by area • But Generally Walk quickly but don’t run, closing doors behind you Leave the building immediately by the nearest exit Do not delay your exit to collect your belongings Do not use lifts Attend the Fire Assembly Point and report to the Fire Warden or Responsible Person • Do not return until told to do so • • • • • Do Not Fight a Fire if •It is bigger than a waste paper bin •One extinguisher is not enough •Smoke is affecting your breathing •You cannot see the way out •Gas cylinders or chemicals are involved •Your efforts are not reducing the size of the fire •There is any risk to yourself If You Discover a Fire • Raise the alarm • Fight the fire if you are competent and you consider it safe to do so (generally only to facilitate escape) • Evacuate as per normal fire procedure • Inform the Fire Warden or Responsible Person Fire Emergency Response R Rescue A Alarm C Contain E Extinguish Fire Extinguisher Anatomy DISCHARGE LEVER DISCHARGE LOCKING PIN AND SEAL PRESSURE GAUGE (not found on CO2 extinguishers) CARRYING HANDLE DISCHARGE HOSE DATA PLATE BODY DISCHARGE NOZZLE DISCHARGE ORIFICE Class A - Combustible material such as paper and wood Class B - Fires involving flammable liquids such as gasoline, paint, diesel fuel or solvents Class C - Fires started in electrical equipment by arching or overheating Class D - Fires involving combustible metal powders, flakes or shavings Most fire extinguishers will have a pictograph label telling you which types of fire the extinguisher is designed to fight. For example, a simple water extinguisher might have a label like this… …which means it should only be used on Class A fires. Fire Extinguisher Types A Trash Wood Paper A Trash Wood Paper 1. PRESSURIZED WATER • Class “A” fires only • 2.5 gal. water (up to 1 minute discharge time) B Liquids Grease B Liquids Grease • Has pressure gauge to allow visual capacity check • 30-40 ft. maximum effective range C Electrical Equipment C Electrical Equipment • Can be started and stopped as necessary • Extinguishes by cooling burning material below the ignition point. 1.PRESSURIZED WATER (contd.) Large silver fire extinguishers that stand about 2 feet tall and weigh about 25 pounds when full. APW stands for “AirPressurized Water.” Filled with ordinary tap water and pressurized air, they are essentially large squirt guns. 1. PRESSURIZED WATER (contd.) APW’s extinguish fire by taking away the “heat” element of the Fire Triangle. 1. PRESSURIZED WATER (contd.) APW’s are designed for Class A fires only: Wood, paper, cloth. Using water on a flammable liquid fire could cause the fire to spread. Using water on an electrical fire increases the risk of electrocution. If you have no choice but to use an APW on an electrical fire, make sure the electrical equipment is un-plugged or de-energized. 1.PRESSURIZED WATER (contd.) APWs will be found in older buildings, particularly in public hallways, as well as in Residence Halls. They will also be found in computer laboratories. It is important to remember, however, that computer equipment must be disconnected from its electrical source before using a water extinguisher on it. A Trash Wood Paper A Trash Wood Paper 2. CARBON DIOXIDE (CO2) • Class “B” or “C” fires • 2.5-100 lb. of CO2 (8-30 seconds discharge time) B Liquids Grease B Liquids Grease • Has NO pressure gauge--capacity verified by weight • 3-8 ft. maximum effective range • Extinguishes by smothering burning materials C Electrical Equipment C Electrical Equipment • Effectiveness decreases as temperature of burning material increases. 2. CARBON DIOXIDE (CO2) (Contd..) Carbon dioxide is a non-flammable gas that takes away the oxygen element of the fire triangle. Without oxygen, there is no fire. CO2 is very cold as it comes out of the extinguisher, so it cools the fuel as well. 2. CARBON DIOXIDE (CO2) (Contd..) A CO2 may be ineffective in extinguishing a Class A fire because it may not be able to displace enough oxygen to successfully put the fire out. Class A materials may also smolder and re-ignite. 3. MULTIPURPOSE DRY CHEMICAL A Trash Wood Paper A Trash Wood Paper B Liquids Grease B Liquids Grease C Electrical Equipment C Electrical Equipment • Class “A”, “B”, or “C” fires • 2.5-20 lb. dry chemical (ammonium phosphate) 8-25 seconds discharge time) • Has pressure gauge to allow visual capacity check • 5-20 ft. maximum effective range • Extinguishes by smothering burning materials. 3. MULTIPURPOSE DRY CHEMICAL (contd..) Dry chemical extinguishers put out fire by coating the fuel with a thin layer of dust. This separates the fuel from the oxygen in the air. The powder also works to interrupt the chemical reaction of fire. These extinguishers are very effective at putting out fire. 3. MULTIPURPOSE DRY CHEMICAL (contd..) Dry chemical extinguishers come in a variety of types… You may see them labeled: • DC (for “Dry Chemical”) • ABC (can be used on Class A, B, or C fires) • BC (designed for use on Class B and C fires) Halon • Best for computers / electronics • • • • • Weight-for-weight TWICE as effective as C02 No residue, easy clean-up VERY SHORT range, 3 to 6 ft. Like C02, Discharges QUICKLY! Like C02, Disperses QUICKLY! – Continue after flames are extinguished 3. MULTIPURPOSE DRY CHEMICAL (contd..) It is extremely important to identify which types of dry chemical extinguishers are located in your area! An “ABC” extinguisher will have a label like this, indicating it may be used on Class A, B and C fires. You don’t want to mistakenly use a “BC” extinguisher on a Class A fire thinking that it was an “ABC” extinguisher. Fire Extinguisher Summary EXTINGUISHER TYPE PRESSURIZED WATER CARBON DIOXIDE MULTIPURPOSE DRY CHEMICAL WORKS BY COOLING SMOTHERING SMOTHERING EFFECTIVE AGAINST How to Use an Extinguisher Pull Aim Squeeze Sweep •Pull the pin this will allow you •to discharge the extinguisher •Get the hose or nozzle ready for •use •Aim at the base of the fire to •hit the fuel…if you aim at the •flames the extinguishing agent •will pass through and do no •good How to Use an Extinguisher Pull Aim Squeeze Sweep •Squeeze the top handle, this •depresses a button that releases •the pressurised extinguishing •agent Sweep from side-to-side until the fire is completely out Remember: Start using the extinguisher from a safe distance away, say 2-3m, and then slowly move forward. Once the fire is out, keep an eye on the area in case it reignites. P Pull the pin A Aim low at the base of flames S Squeeze the handle S Sweep side to side Labeling: • Easily seen • Easily located in an area Inspections: • Monthly – Can be done in house by qualified/knowledgeable/trained person or by qualified 3rd party. • Annually – Qualified 3rd party • Hydrostatic – Done Periodically, per manufacture specification (~6 years), by qualified 3rd party. (A qualified 3rd party vendor can provide all these services including recharging when necessary to meet your needs.) Accessibility: • • • • Easily retrieved No obstruction or reaching over anything. 3 foot clearance around the extinguisher. Nothing stored in front of it, PERIOD. • Keep these guidelines in consideration when storing extinguishers in or on vehicles. – – – – Locations and Signs Readily accessible 75 feet—Class A 50 feet—Class B 50–75 feet—Class C – 75 feet—Class D – Highly visible sign Use a portable extinguisher ONLY if the: • Building is being evacuated (Fire alarm has been pulled) • Fire Department has been called • Fire is NOT spreading (small and contained) • EXIT IS CLEAR (fight fire with your back to an exit ) • Proper extinguisher is at hand, and... – You have been trained and know how to use it! – You use “Buddy System” - have someone back you up! • Get assistance BEFORE trying to fight a fire! UNTRAINED PEOPLE Cannot use a fire extinguisher safely because they are: • UNABLE to evaluate a fire • UNAWARE of DANGER due to... • LACKING JUDGEMENT regarding: – Safe and correct use of, and – Limitations of portable extinguishers WHY UNTRAINED PEOPLE Can’t use a fire extinguisher safely (continued): INEXPERIENCED • Don’t know about the proper type of extinguisher • Don’t know how to make a “Fight or Flight” analysis • Unfamiliar with the “P.A.S.S. method” Fire Blanket • Any colour body or label but they are usually red or white • For use on any type of fire but best on small contained class B (flammable liquids, may include small cooking pans) fires and people on fire • Can be used on microwaves • Extinguishes by smothering Fire Signs Maintenance and Inspection • Detection and Alarm systems should be tested weekly and inspected by a competent person periodically • Fire extinguishers and other fire fighting equipment should be checked at a frequency determined by risk (but at least monthly) for location, condition and state of charge and serviced by a competent person annually • Any Fire fighting device must be replaced, serviced or checked by a competent person after any use And Finally… • Most extinguishers are heavy and constructed from metal….. • They make excellent battering rams to break a window or un-jam a door • But seriously the prime consideration is your safety and the only priority is to get everybody out and leave fire fighting to the professionals Summary • Combustion Process (Fire Triangle) • Class A, B, C, D, K fires • Types of portable fire extinguishers: – Operating procedures – Capabilities and limitations • Basic firefighting concepts: R.A.C.E. P.A.S.S. To uses, you’ve got to PASS: Pull the pin Aim at base of fire Squeeze the handle Sweep from side to side Fire Classification & Extinguisher Types Extinguishers are classified by the type of fire they can put out. Some extinguishers are Combination types that can be used on several different types of fires. Class A - Combustible material such as paper and wood Never Fight a Fire If: •You don’t know what is burning •Fire is spreading rapidly •You don’t have adequate equipment •You might endanger yourself or others •Your instincts tell you not to. Class B - Fires involving flammable liquids such as gasoline, paint, diesel fuel or solvents Class C - Fires started in electrical equipment by arching or overheating Class D - Fires involving combustible metal powders, flakes or shavings Fuel Fire Triangle Ignition Source Air Always position yourself with an exit or means of escape at your back before you attempt to use an extinguisher to put out a fire. Fire extinguishers are limited supply and can be emptied in a few minutes. Quiz Question 1 Fire extinguisher marked with an A is used on: A) oil fires B) Electrical fires C) paper material fires D) none of the above Quiz Question 2 Fire extinguishers marked with a B can be used on: A) Paper, trash B) Oil or Grease C) Electrical D) Non of the above Quiz Question 3 Fire extinguisher marked ABC can be used on: A) Wood, Paper B) Electrical C) Liquids and grease D) All of the above Quiz Question 4 Fire Extinguishers marked with D are used for A) Combustible chemicals B) Magnesium C) Potassium D) other flammable metals E) all of the above Quiz Question 5 What does PASS mean? A. Pass, Aim, Squash, Surround B. Pull, Align, Span, Surround C. Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep