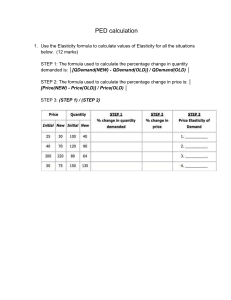
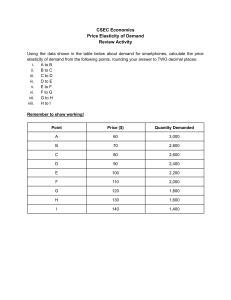
PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND Types of Price Elasticity of Demand Price elasticity of demand is the degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price of a good. Demand is said to be unitary elastic if a change in price of a good leads to a proportionate change in the quantity demanded of the good. When demand is unitary elastic, absolute elasticity is equal to 1. This type of demand is drawn as a line at a 45-degree angle to the horizontal axis as shown in the diagram below: Demand is price elastic if a change in price of a good leads to a more than proportionate change in the quantity demanded of the good. When demand is price elastic, the absolute value of elasticity is more than 1). This type of demand is drawn as a line with a gentle slope as shown in the diagram below: Demand is price inelastic if a change in price of a good leads to a less than proportionate change in the quantity demanded of the good. When demand is price inelastic, the absolute value of elasticity is less than 1). This type of demand is drawn as a line with a steep slope as shown in the diagram below: There are other two special cases of price elasticity of demand: Perfectly elastic demand: Demand is perfectly elastic when its elasticity is equal to infinity. This happens when consumers will demand any quantity at a single price. This type of demand is drawn parallel to the quantity demanded axis as shown in the diagram below: Perfectly inelastic demand: Demand is perfectly inelastic when its elasticity is equal to zero. This happens when no matter the change in price, quantity demanded remains unchanged. This type of demand is drawn parallel to the price axis as shown in the diagram below: