Intermolecular Attractions: Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

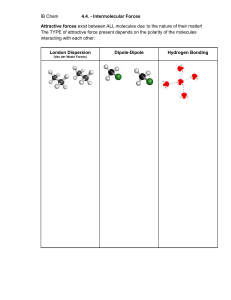
Course: Chemistry Chapter/lesson: Chapter 8: Intermolecular Attractions Lesson Objectives: • Describe the types of attractions between molecules. • Explain how intermolecular attractions between molecules influence the bulk properties of a material. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 Standards: HS-PS1-3: Plan and conduct an investigation to gather evidence to compare the structure of substances at the bulk scale to infer the strength of electrical forces between particles. HS-PS1-A-3: The structure and interactions of matter at the bulk scale are determined by electrical forces within and between atoms. HS-PS3-5: Develop and use a model of two objects interacting through electric or magnetic fields to illustrate the forces between objects and the changes in energy of the objects due to the interaction. Bell-Work/ Teacher Demo: 1. Why did the hand sanitizer dry so much faster than the water? 2. What do you notice about the drops of water and the isopropyl alcohol on the bench? 1 Forces of Attraction There are 2 types of forces: INTRAmolecular and INTERmolecular forces of attraction. Forces of Attraction INTRAmolecular Ionic Bond Covalent Bond INTERmolecular Metallic Bond London Dispersion Diploe-Dipole Hydrogen Bond INTRAmolecular forces (bonds) hold atoms together. INTERmolecular forces hold molecules together. Which forces are stronger? Intramolecular attractions are stronger than intermolecular bonds. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 2 Attractions between Molecules Among other things, these attractions are responsible for determining whether a molecular compound is a gas, a liquid, or a solid at a given temperature. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 3 Attractions between Molecules Van der Waals Forces The two weakest attractions between molecules are collectively called van der Waals forces, named after the Dutch chemist Johannes van der Waals. Van der Waals forces consist of dipole interactions and dispersion forces. Van der Waals Forces Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 4 In groups of 3-4 Choose one of the 3 intermolecular bonds You will need to produce a PowerPoints or poster Points to include • Explain how the bond is formed • Include images • Examples Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 5 IM Forces effects on Macroscopic Properties Bulk properties such as melting point, boiling point and volatility depend on intermolecular attractions. Strong IM forces, such as hydrogen bonding and dipole interactions, hold the molecules together more tightly than weaker dispersion forces. Volatility is a measure of how easily a liquid evaporates. Volatile liquids have a greater number of molecules in the gas phase above the liquid. The stronger the IM force, the lower the volatility because the molecules are held more strongly in the liquid phase, preventing them from going into the gas phase. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 6 IM Forces effects on Macroscopic Properties Melting Point and Boiling Point: Molecular substances tend to melt and boil at lower temperatures than ionic or metallic compounds because IM attractions are weaker than ionic and metallic bonds. The stronger the IM forces, the higher the melting and boiling points because it takes more energy to separate the molecules. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 7 Like dissolves like A simple way to predict which compounds will dissolve in other compounds. Polar compounds dissolve polar compounds, non-polar compounds dissolve nonpolar compounds, but polar and non-polar will not dissolve each other. Lesson Objectives: 5/2/2023 8 Exit Ticket • Please complete the intermolecular forces quiz. Formative link is on GC. • Teacher’s link: https://app.formative.com/assign /YZK3CX 5/2/2023 Lesson Objectives: 9