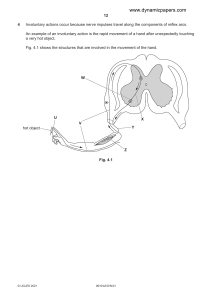
Cambridge IGCSE™ * 1 2 6 0 5 8 1 3 5 8 * BIOLOGY 0610/42 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 2021 1 hour 15 minutes You must answer on the question paper. No additional materials are needed. INSTRUCTIONS ● Answer all questions. ● Use a black or dark blue pen. You may use an HB pencil for any diagrams or graphs. ● Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes at the top of the page. ● Write your answer to each question in the space provided. ● Do not use an erasable pen or correction fluid. ● Do not write on any bar codes. ● You may use a calculator. ● You should show all your working and use appropriate units. INFORMATION ● The total mark for this paper is 80. ● The number of marks for each question or part question is shown in brackets [ ]. This document has 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. DC (KN/FC) 202969/5 © UCLES 2021 [Turn over 2 1 (a) Complete the sentence about the nervous system. and The brain and spinal cord form the ............................................... nervous system and the Ǘ nerves coming into and out of the spinal cord are part of the ............................................... nervous system. per [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 shows part of a human eye and three neurones that conduct electrical impulses between the eye and the brain. These neurones are involved in the pupil reflex. K J A H B C G onto F E D 焄 not to scale Fig. 1.1 (i) State the type of neurone identified as A in Fig. 1.1. Jenny neuron ..................................................................................................................................... [1] motor 说不出话 © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 3 (ii) Table 1.1 shows the names of some parts of the eye, their functions and the letters in Fig. 1.1 that identify the parts of the eye. Complete Table 1.1. Table 1.1 part of the eye suspensory ligament function Connects the ciliary letter in Fig. 1.1 muscles G wit in contracts in response to a bright light refracting cornea tǘ (c) (i) Ī contains a high density of cones for colour vision [4] The eye can adjust how light is refracted through it in order to focus on a near object. State one process that uses energy when focusing on a near object. muscle corny ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (ii) Mitochondria require oxygen to release energy. Oxygen is transported to cells in the eye by red blood cells. haemoglobin State the name of the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (iii) hemoglobin Explain how oxygen in the capillaries reaches the cells in the eye. diffuses diffusion隐The oxygen By ........................................................................................................................................... through the single cell cell wall of coping ........................................................................................................................................... to the eels in the due the eye concentatimgradient.LT 我说你别急 ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... molecules ..................................................................................................................................... [2] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 4 (d) Eyelashes and eyelids are mechanical barriers that help to prevent particles and pathogens entering the eye. (i) Give two other mechanical barriers that defend the body against pathogens. nosed 1 ........................................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................................ [2] (ii) State the name of the white blood cells that digest pathogens. ..................................................................................................................................... [1] sky phagoc .gg (iii) Conjunctivitis can be caused by pathogens and affects the tissues lining the eyelids and covering the sclera. People with conjunctivitis that is caused by a pathogen can develop active immunity. Explain why the shape of specific parts of a pathogen is important in the development of active immunity. ........................................................................................................................................... pathogen'The antigens on the pathogens enable ........................................................................................................................................... the lymphocytes to recognise the Shut type unique ........................................................................................................................................... coma me Pathogen and produce the A antibodies ........................................................................................................................................... antibodies t bind with them so that the mat........................................................................................................................................... can slow down and be killed by phagocytes pipe antigens able Memory cells produced recognise ..................................................................................................................................... [3] and produce the antibodies faster ........................................................................................................................................... are to (e) Most insects and some crustaceans have compound eyes. State the name of the group that contains insects and crustaceans. inverti ............................................................................................................................................. [1] arthropods © UCLES 2021 [Total: 17] 0610/42/M/J/21 5 2 The classification of giant pandas, Ailuropoda melanoleuca, is debated by many scientists. Fig. 2.1 shows a giant panda eating bamboo plants. Fig. 2.1 Fig. 2.2 shows a red panda, Ailurus fulgens, and a polar bear, Ursus maritimus. o red panda eating bamboo plants polar bear eating fish Fig. 2.2 (a) State one dietary component that is more likely to be found in bamboo plants than in fish. plant ............................................................................................................................................. [1] (b) (i) State two features, visible in Fig. 2.1 and Fig. 2.2, that identify the three animals as all belonging to the same vertebrate group. the 型品品望 弘⼀ 1 ........................................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................................ [2] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 6 (ii) DNA can also be used to classify species. Molecular biologists compared the DNA base sequences of eight species from the same vertebrate group. They used the differences to draw a classification diagram. Fig. 2.3 shows the classification diagram for these eight species. The shorter the horizontal distance from two species to the branching point that they share, the more similar their DNA sequences are and the more closely the two species are related. The scale on Fig. 2.3 shows the time at which the molecular biologists estimate that each branching point occurred. red panda ferret o giant panda polar bear wolf tiger human mouse 100 80 60 40 million years ago Fig. 2.3 © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 20 0 7 Morphology can also be used to classify species. Some scientists think that morphology suggests that the giant panda is more closely related to the red panda than it is to the polar bear. Discuss the evidence for and against the giant panda being more closely related to habitats the red panda than it is to the polar bear. Use the information in Fig. 2.1, Fig. 2.2 and Fig. 2.3 in your answer. similar position ........................................................................................................................................... Dearsimilar For i D Giant pandais more close grey red panda acceding morphbgy ........................................................................................................................................... Giant panda and red panda both is to ........................................................................................................................................... to plant D Giant eat ........................................................................................................................................... Against ........................................................................................................................................... hhafplmgbearha mnec.be DNA ........................................................................................................................................... sequence Giant Panda and par bears ........................................................................................................................................... size is cbs ........................................................................................................................................... 成 shrterkanchdisanstuithp.la ........................................................................................................................................... bear ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [5] (iii) State one other type of evidence that is used to classify species. apparel ..................................................................................................................................... [1] [Total: 9] anatomy ability © UCLES 2021 to produce 0610/42/M/J/21 fertile offsprings [Turn over 8 3 (a) Fig. 3.1 shows some of the events that occur in the menstrual cycle. A i follicle is fully developed B gamete is released into the oviduct C lining of the uterus is removed from the body D lining of the uterus reaches a maximum thickness E lining of the uterus gets thicker (i) Fig. 3.1 Put the events shown in Fig. 3.1 into the correct sequence. One has been done for you. E (ii) Ait B c [1] State the name of the hormone that stimulates event A to occur. n FSH them 的 release ..................................................................................................................................... [1] not (iii) Event C means that menstruating females lose blood regularly. Two females of the same age have different dietary needs because one has started menstruating and the other has not started menstruating. Suggest why the dietary needs of the two females are different. needs ........................................................................................................................................... who men has started The one stung ........................................................................................................................................... a make bbodbss.int her body up ........................................................................................................................................... She need more Irons in her dietary may ........................................................................................................................................... need u hid in es send for transport of ..................................................................................................................................... [2] oxygen © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 9 (b) During pregnancy menstruation does not occur. Fig. 3.2 shows some of the organs of a pregnant woman, viewed from the side. fetus P V Q U T R S Fig. 3.2 Describe what happens between ovulation and the formation of a fetus. Use the letters in Fig. 3.2 to support your answer. at Q theovary then ................................................................................................................................................... ovulation news It moves to dig shapbr the P and ................................................................................................................................................... oviduct fuses with sperm fdnule_r.yusatfwhichtlhespemB.com ing fan ................................................................................................................................................... and R cervix.The formed ads.vagina ................................................................................................................................................... the tigre ................................................................................................................................................... meantime uterus continues to move to int The embryo eventually ................................................................................................................................................... and umbilical the uterus wall T Phil ................................................................................................................................................... and U is formed to provide neon and ................................................................................................................................................... wastes exchange for the fetus via diffusion ................................................................................................................................................... differencing implants into ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................. [6] [Total: 10] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 10 4 (a) Climate change is one reason why a plant species could become endangered. (i) State other reasons why a plant species could become endangered. monoculture of crops ........................................................................................................................................... deforestation ........................................................................................................................................... natural disasters ........................................................................................................................................... 醼 plant doses ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [3] (ii) Describe how human actions are causing climate change. ssim.hr Esteem emission ........................................................................................................................................... Human increase for foie an farming of animals example and soon.Also ........................................................................................................................................... like increase the ........................................................................................................................................... cows of emissimduett amount ........................................................................................................................................... dige.nu inside it BothCo2 ........................................................................................................................................... the CHzanegcggns.es ........................................................................................................................................... cause climate change which taps heat reactions ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [4] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 11 (b) Seed banks are used to conserve endangered plant species. Fig. 4.1 shows some of the steps involved in managing a seed bank. seeds are collected from many populations of each species seeds are checked using X-rays seeds are stored at low temperatures in the seed bank variationpollination genetic cross a small sample of seeds is germinated ensure chae of more chaaesofsuaesshngermnatm io Fig. 4.1 increases (i) Explain why seeds from one species are collected from many populations to store in a seed bank. ensure the average 尴 required quality and our ........................................................................................................................................... the seeds different populations ........................................................................................................................................... are The kind A species ........................................................................................................................................... the same growth environment requirements as ........................................................................................................................................... same easier grow ueaghave.fr ........................................................................................................................................... makes it to a same result species Seed bank is able to endangered ........................................................................................................................................... conserve plant species ..................................................................................................................................... [3] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 12 (ii) Seeds are X-rayed before they are stored to check that they contain an embryo. State one possible consequence of using ionising radiation on seeds. mu Ǘ ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (iii) Seeds stored at low temperatures have very low respiration rates. Explain why. certain enzyme requires ........................................................................................................................................... range to reach activation energy to let ........................................................................................................................................... t take place low temperatures the reaction doesnh ........................................................................................................................................... a respiration's in gslei.tk ........................................................................................................................................... neat to tak place and let the enzyme each t One purpose of seed banks is to reintroduce plant species into their natural environment. optimum engine ..................................................................................................................................... [2] (c) A survey was done to find out why some reintroduction programmes are not successful. Fig. 4.2 shows the results of the survey. 40 35 30 percentage of species that were not successfully reintroduced 25 20 15 10 5 0 reason unknown wrong habitat changing seeds did seedlings too few habitat not too young individuals germinate reasons why reintroductions failed Fig. 4.2 © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 wrong season 13 (i) Some of the seeds in the reintroduction programmes did not germinate. State the conditions that are necessary for seeds to germinate. 跮 Oxygen Suit water ........................................................................................................................................... a 吣 m ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [3] (ii) Some reintroduction programmes failed because the seedlings were too young. Young seedlings only have a few small roots. Explain why it would be important to reintroduce plants with many large roots. absorb sufficient ........................................................................................................................................... nutrients mineral and water from the soil ........................................................................................................................................... Minerals like IN P k Mg containing ........................................................................................................................................... substones are essential A growth allow them Large ........................................................................................................................................... to roots and fruit phot synthesis for development Water is ........................................................................................................................................... essential reactions take place like respiration ........................................................................................................................................... Small have limited ability of ........................................................................................................................................... absorbing roots reintroducing plants with ........................................................................................................................................... nutrients so enough B ..................................................................................................................................... [4] 0 rots i (iii) many large 呻 The low number of individuals also caused some reintroduction programmes to fail. State the name of the phase in a population growth curve where the number of individuals is very low. 㘜 ..................................................................................................................................... [1] © UCLES 2021 [Total: 21] 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 14 5 Fig. 5.1 shows some of the stages in the reproduction of the bacterium Escherichia coli. loop of DNA original bacterial cell bacterial cell expands to a critical length and a copy of DNA is synthesised daughter cells are formed daughter cells grow Fig. 5.1 (a) Complete the sentences about the cells in Fig. 5.1. The DNA is in the form of a double ............................................... . The DNA is copied so that the number of loops of DNA after cell division is ............................................... in each 嚡 identical daughter cell. The daughter cells are genetically ............................................... to the original cell. [3] (b) Students used a microscope and time-lapse photography to observe E. coli cells reproducing. They used the series of photographs to identify which cells were dividing. They measured the lengths of the dividing cells and put their data into two groups: • cell lengths immediately before cell division • cell lengths immediately after cell division. Fig. 5.2 shows their results. © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 15 key: 100 immediately after division immediately before division 90 80 70 60 number of cells 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1 2 ⼝ 3 5 4 6 cell length / μm 7 8 9 10 Fig. 5.2 (i) Yg Use the information in Fig. 5.2 to state the most frequent cell length of the E. coli cells immediately after cell division. Give your answer in millimetres. 我真 你 95 Nm o (ii) 095mm ......................................................... mm [2] Some students concluded that the cells must be at least 6 µm in length before cell division can occur. Describe the evidence against the students’ conclusion. Use the information in Fig. 5.2 to support your answer. There cells that are below Gum ........................................................................................................................................... are cell length ltecellisio somecelbae.be ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... then 3mm after ........................................................................................................................................... chim o ..................................................................................................................................... [2] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 16 (c) Bacteria are useful in genetic engineering because they contain plasmids. (i) A restriction Describe how a plasmid is cut so that a new gene can be inserted into the plasmid. A endonuclease ........................................................................................................................................... cut to make to By using ........................................................................................................................................... end at the plasmid and filth ..................................................................................................................................... [2] (ii) List two reasons, other than the presence of plasmids, that make bacteria and single-celled fungi useful to biotechnology industries. usingen died They 2 ........................................................................................................................................ They all share the San DNA [2] 1 ........................................................................................................................................ © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 qdfg [Total: 11] 17 6 (a) Some students set up the apparatus shown in Fig. 6.1 to compare transpiration in two sets of leaves. Set A was kept in a transparent bag and set B was left in the open air. All other conditions were kept constant. The mass of the leaves in each set was measured at the start of the investigation and after five hours. string line paper clip clamp stand transparent bag set A set B Fig. 6.1 (i) Predict the results for this investigation. Explain the reason for your prediction. be heavier would prediction ........................................................................................................................... set A ........................................................................................................................................... 点赞idhmuyneae explanation ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................... © UCLES 2021 ........................................................................................................................................... [3] 0610/42/M/J/21 [Turn over 18 (ii) Explain how transpiration occurred in the leaves shown in Fig. 6.1. and water man gas ........................................................................................................................................... diffuses out through the sonata down The ........................................................................................................................................... becomes the concentrating ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [3] (iii) The students needed two additional pieces of apparatus to take measurements so that they could calculate the rate of transpiration from their results. State the two additional pieces of apparatus the students needed to take the measurements. timer 1 ........................................................................................................................................ balance.lvscale 2 ........................................................................................................................................ [2] (b) Fig. 6.2 shows the positions of the different tissues in part of a dicotyledonous leaf. P 汽 Fig. 6.2 © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 19 Identify the tissues described in Table 6.1 by: • drawing label lines with the corresponding letter on Fig. 6.2 and • stating the name of each tissue in Table 6.1. The label, line and name of the tissue for letter P has been completed for you on Fig. 6.2 and in Table 6.1. Table 6.1 letter description P a protective transparent layer that allows light to reach the inner tissues Q conducts water from the stem R contains many interconnected air spaces name of the tissue upper epidermis xyleml spmgmesopgl ph palisade.me S transports sucrose and amino acids T traps the most light energy to synthesise carbohydrates sphgk [4] [Total: 12] © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21 20 BLANK PAGE Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced online in the Cambridge Assessment International Education Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download at www.cambridgeinternational.org after the live examination series. Cambridge Assessment International Education is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group. Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of the University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which itself is a department of the University of Cambridge. © UCLES 2021 0610/42/M/J/21