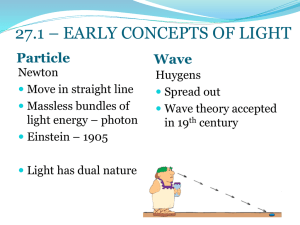
DETAILED LESSON PLAN I. OBJECTIVE At the end of 30 minutes, the students should be able to: 1. State and explain Huygens Principle. II. SUBJECT MATTER (LEARNING TASK) 1. Topic: Physical Optics: The Wave Nature of light. 2. Reference: Encyclopedia Britanica, ScienceDirect Topics. 3. Materials: Laptop, Visual aids and Mobile Phone. III. PROCEDURE (DEVELOPMENTAL ACTIVITY) Teacher’s Activity 1. Pre Activity 1. Preparation Student’s Activity (Amen!) Let’s stand up and let us pray! Good morning ma’am! Good morning class! May you now take your seat. Please say present when I call your name. 2. Review (The students will say present when their name is called) What is our last topic yesterday? (The student will answer: our last topic is all about Diffraction and Polarization) But before we start to our new lesson lets freshen up first by recalling our last topic. Okay, so what is Diffraction and Polarization? (The student will answer: Diffraction and Polarization are the bending of waves around obstacles, corners, or openings.) 3. Motivation Now, I have here three (3) images at the screen. What are you going to do is to simply identify each image and explain why? PICTURE 1 PICTURE 2 PICTURE 3 So, for picture number one (1), as I call your name please stand up and identify the picture and the same for picture number two (2) and three (3). Ok, very good! Since I’ve discussed yesterday the things about diffraction and polarization. Now, we will be discussing about Physical Optics: The Wave Nature of light especially the Huygens Principle. 4. Unlocking of Terms But before we go deeper to our main goal this (Three students will stand up and day, let’s define first these terms: identify the pictures.) Huygens Principle- states that every point on a wave front may be considered as a source of secondary waves. Wave front- is an imaginary surface representing corresponding point of a wave that vibrate in unison. Diffraction- is the spreading of waves from as they pass through or around obstacle. Refraction- is the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another 5. Activity Proper So, do you want some fun? But before that I will give you some important information about Huygens Principle, especially the person behind this principle Christian Huygens. So, Christiaan Huygens, also spelled Christian Huygens, (born April 14, 1629, The Hague- died July 8, 1695, The Hague). Dutch mathematician, astronomer, and physicist, who founded the wave theory, discovered the true shape of the rings of the Saturn, and made an original contribution to the science of dynamics- the study of the action of forces of bodies. So, lets go back to the principle called Huygens Principle. Huygens Principle, also called Huygens Fresnel Principle, a statement that all points of a wave front of sound in a transmitting medium of light in a vacuum or transparent medium may be regarded a new source of wavelets that expand in every direction at a rate depending on their velocity. (Students will read in the definition of terms together.) Huygens Principle and Diffraction When light passes through an aperture, every point on the light wave within the aperture can be viewed as a source creating a circular wave that propagates outward from the aperture. The aperture thus creates a new wave source that propagates in the form of a circular wave front. The center of the wave front has greater intensity while the edges have a lesser intensity. This explains the observed diffraction pattern and why a perfect image of the aperture on a screen is not created. A daily life example of this phenomenon is common. If someone in another room calls toward you, the sound seems to be coming from the doorway. Advantages and Disadvantages of Huygens Principle Advantages: 1. Huygens concept proved the reflection and refraction of light. 2. The concepts like diffraction of light, as well as interference of light, were proved by Huygens. Disadvantage: 1. Concepts like emission of light, absorption of light and polarization of light were not explained by Huygens principle. 2. Huygens principle failed to explain the photoelectric effect. 3. A serious drawback is that the theory proposes an all-pervading medium required to propagate light called luminiferous ether. This was proved to be false in the 20th century. Okay, now let’s have some fun! This is an individual activity. Instruction: I have here a picture and what are you going to do, is to name every part of the diagram. C. Post Activity 1. Analysis I am glad that you’ll already know how to identify each part of the diagram as an example of diffraction that we tackled earlier! I hope you all enjoy having this kind of activity as part of our lesson for this day. Okay, so everyone, please pass your paper in front for I will check it who got the perfect score! Anyone? who can go to front and name each part of the diagram. Okay! Very good! 2. Abstraction So, Huygens Principle is also called as what? What the advantages of Huygens Principle? What are the disadvantages of Huygens principle? 3. Application Why it is really important to study Huygens principle and its importance to our daily lives? Now, what are the contributions of Huygens principle to us? Ok, very good! So, did you know how to identify the parts of diffraction? Are you sure? Any questions or clarification? (The students will stand up and pass their works to me.) (one student will go to the front and name each part.) (The students will answer: it is also called as Huygens Fresnel Principle.) (The student will enumerate the two (2) advantages of the principle.) (The students will enumerate the three (3) disadvantages of the principle.) (One student will stand up and answer the question according to his/her understanding.) (One student will stand up and answer the question according to his/her understanding.) (Yes sir!) (Yes sir!) (No sir!) IV. EVALUATION Get 1 whole sheet of yellow pad paper and answer the following questions! TEST I: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is Huygens Principle? 1. an imaginary surface representing corresponding point of a wave that vibrate in unison. 2. states that every point on a wave front may be considered as a source of secondary waves. 2. 3. 4. 5. 3. the spreading of waves from as they pass through or around obstacle. 4. the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another. What is a wave front? 1. the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another. 2. states that every point on a wave front may be considered as a source of secondary waves. 3. an imaginary surface representing corresponding point of a wave that vibrate in unison. 4. the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another. What is Diffraction? 1. the bending of light as it passes from one transparent substance into another 2. states that every point on a wave front may be considered as a source of secondary waves. 3. an imaginary surface representing corresponding point of a wave that vibrate in unison. 4. the spreading of waves from as they pass through or around obstacle. Which is best describe as an advantage of Huygens principle? 1. Concepts like emission of light, absorption of light and polarization of light were not explained by Huygens principle. 2. Huygens principle failed to explain the photoelectric effect. 3. A serious drawback is that the theory proposes an all-pervading medium required to propagate light called luminiferous ether. This was proved to be false in the 20th century. 4. Huygens concept proved the reflection and refraction of light. Huygens Principle also called as? 1. Huygens Fresnel Principle 2. Huygens freshnel Principle 3. The Principle of Huygens 4. Fresnel Huygens Principle TEST II: Explanation 1. Why is Huygens Principle is correct? 2. How is Huygens Principle is derived? 3. What are the main drawbacks of Huygens Principle? V. ASSIGNMENT Why is Huygens Principle is important? elaborate your answer. VI. Remarks M.L. : I. D. : Prepared by: JESTER L. OLAM