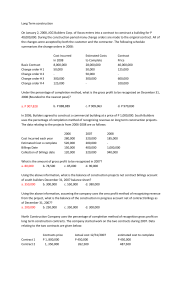
REGULAR INCOME TAXATION The Regular Income Tax Model Gross Income – inclusions Less: Allowable deductions Taxable Income P xxxx xxxx xxxx Gross Income consists of the major topics 1. Exclusions of gross income – list of income exempt to regular income tax 2. Inclusions in gross income – list of income subject to regular income tax 3. Special topics – covers income that are either exclusion or inclusion depending on certain circumstances, such as: a. Fringe benefits b. Dealings in properties ALLOWABLE DEDUCTIONS Are expenses of the conduct of business or exercise of profession. They are commonly known as business expenses. ❖ EXCLUSIONS FROM GROSS INCOME The term “exclusions” refer to items that are not included in the determination of gross income either because: • They represent return of capital or are not income, gain or profit; • They are subject to another kind of internal revenue tax; or • They are income, gain or profit that are expressly exempt from income tax under the constitution, tax treaty, tax code, or a general or special law. Note: Exclusions from gross income are not included in the amount of reportable gross income in the income tax return. The amount of deductions is initially included in the amount of gross income but is separately presented as deduction against gross income in the income tax return. ITEMS THAT ARE NOT INCLUDED: 1. Proceeds of life insurance – paid to the heirs or beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. BUT if such amounts are held by the insurer under an agreement to pay interest thereon, the interest payments are included in gross income. 2. Return of insurance premium – amount received by the insured, as a return of premiums paid by him, either during the term or at the maturity of the term mentioned in the contract or upon surrender of the contract. BUT the excess over premiums paid (whether or not in the current year) is included in the gross income. 3. Gift, bequest or devise – value of the property received is excluded BUT the income from such property is included in gross income. 4. Compensation for personal injuries or sickness – amounts received, through accident or health insurance or under Workmen’s Compensation Acts, plus the amount of damages received, whether by suit or agreement, on account of such injuries or sickness. 5. Income exempt under Treaty – income of any kind, to the extent required by any treaty obligation binding upon the government of the Philippines. 6. Retirement benefits, pension, gratuities, etc. a. Those received under R.A. 7641 – The Mandatory Retirement Law (for private firms without retirement trust fund) b. Those received by employees of private employers in accordance with a reasonable private benefit plan; c. Those received as a result of involuntary separation – causes beyond the control of the employee d. Social security benefits, retirement gratuities, pensions, etc. from foreign government agencies and other institutions, private or public benefits due to residents who are US veterans e. SSS benefits f. GSIS benefits Retirement benefits received under R.A. No. 7641 and those received by officials and employees of private firm. Any amount received by an official or employee as a consequence of separation Retirement benefits pursuant to RA 4917 (Private Retirement Benefit Plan) 1. Retiring employee must not be less than 50 years old. 2. Must have been in the service for at least 10 years of the same employer. 3. Exemption must be availed only once. 4. The private benefit plan must be approved by the BIR. (Reasonable private pension plan.) Retirement benefits under RA 7641 (In the Absence of Retirement Plan) 1. The retiring employee is 60 years old. (The compulsory retirement age of an employee under the Mandatory Retirement is 65 years old.) 2. He must have served the company for at least 5 years in said establishment. Any amount received by an official or employee or by his heirs from the employer as a consequence of separation of such official or employee from the service of the employer because of death, sickness, or physical disability or for any cause beyond the Social security benefits, retirement gratuities, pensions and other similar benefits received from foreign government agencies and other institutions, private or public Social Security System (SSS) Benefits Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) Benefits United States Veterans Administration Benefits control of the said official or employee is not included in the gross income The provisions of any existing law to the contrary notwithstanding, social security benefits, retirement gratuities, pensions and other similar benefits received from foreign government agencies and other institutions, private or public, received by resident or nonresident citizen of the Philippines or aliens who come to reside permanently in the Philippines are not included in the gross income Benefits received from or enjoyed under the Social Security System are not included in the gross income Benefits received from the GSIS including retirement gratuity received by government officials and employees are not included in the gross income Payment of benefits due or to become due under United States Veterans Administration are not included in the gross income 7. Miscellaneous Items a. Passive income derived from investments in the Philippines in loans, stocks, bonds, or other domestic securities, or from interest on deposits in banks in the Philippines by: • Foreign governments • Financing institutions owned, controlled, or enjoying refinancing from foreign governments • International or regional financial institutions established by foreign government b. Income derived from any public utility or from the exercise of any essential governmental function by the Philippine Government or political subdivision thereof c. Prizes and awards made primarily in recognition of religious, charitable, scientific, educational, artistic, literary, or civic achievement but only if: • The recipient was selected without any action on his part to enter the contest or proceeding; and • The recipient is not required to render substantial future services as a condition to receiving the prize or award. d. All prizes and awards granted to athletes in local and international sports competitions and tournaments whether held in the Philippines or abroad and sanctioned by their national sports associations e. 13th Month Pay and other benefits of public and private entities – BUT total exclusion under this item not to exceed P90,000. f. f. GSIS, SSS, Medicare, PAG-IBIG contributions, and union dues of individuals (RMC 27-2011) Contributions to SSS, GSIS, PHIC and HDMF in excess of mandatory contributions are not exempt from withholding tax on compensation. 1. Only the mandatory or compulsory contributions of employees to SSS, GSIS, PHIC and HDMF are exempt from income tax and consequently, from the withholding tax on compensation. 2.The voluntary contributions in excess of what the law requires as mandatory contributions are taxable gross income of the employee, hence, subject to income tax and withholding tax on compensation. The exemption from withholding tax on compensation referred to in Section 2.78.1(B)(12) of Revenue Regulations (RR) No. 2-98 shall apply only to mandatory/compulsory GSIS, SSS, Medicare and Pag-ibig contributions. It does not include voluntary contributions. g. Gains from the sale or exchange or retirement of bonds, debentures or other certificate of indebtedness with a maturity of more than five (5) years. h. Gains realized by the investor upon redemption of shares of stock in a mutual fund company as defined in Section 22 (BB). ❖ INCLUSIONS IN GROSS INCOME GROSS INCOME Except when otherwise provided in this Title, means all income derived from whatever source, including (but not limited to) the following items: (1) Compensation for services in whatever form paid, including, but not limited to fees, salaries, wages, commissions, and similar items. (2) Gross income derived from the conduct of trade or business or the exercise of a profession; (3) Gains derived from dealings in property; (4) Interests; (5) Rents; (6) Royalties; (7) Dividends; (8) Annuities; (9) Prizes and winnings; (10) Pensions; and (11) Partner's distributive share from the net income of the general professional partnership. 1. Compensation for personal services Gross compensation income means all remuneration for services performed by an employee to his employer whether paid in cash or in kind, unless specifically excluded under the Tax Code (e.g. salaries, wages, emoluments, honoraria, bonuses, allowances, director’s fee) All kinds of compensation for services rendered constitute gross income. They include: a. Salaries, wages and fees b. Commission paid to salesman c. Compensation for services on the basis of a percentage of profits d. Commission on insurance premiums e. Tips f. Pensions or retiring allowances paid by private pensions or by the government (except pension exempt from tax) and g. Marriage fees, baptismal offering sum paid for saying masses for the dead, and other contributions received by a clergyman, evangelist, or religious worker for services rendered Forms of compensation a. Payment made in cash- taxable amount is the full amount received b. Service paid for with something other than money - taxable amount is the fair market value (FMV) of the consideration received c. Services rendered at a stipulated price- In the absence of evidence to the contrary, the stipulated price shall be presumed to be the fair market value (FMV) 2. Gross income derived from the conduct of trade or business or the exercise of a profession Gross Sales/receipts Less: sales returns and allowances/sales discount Net Sales/receipts Less: Cost of sales/services Gross income from operation Add: Other income: Other Incidental income Gross Income xxx (xxx) xxx (xxx) xxx xxx xxx 3. Gains derived from dealings in property Sale of Capital Assets Other than Real Property and Shares of Stock that are subject to a special CGT rate. The net capital gain realized from the sale of assets classified as capital assets shall be subject to ordinary income tax. Sale of 3 types of property which may give rise to taxable events: Ordinary asset – 100% of the gain or loss shall be recognized in the ITR Capital asset – subject to final taxes (capital gains tax) Other capital asset - holding period of the asset shall be taken into consideration if the seller is an individual, and only the net capital gain shall be included in the ITR. HOLDING PERIOD RULE: If the capital asset is held by an individual taxpayer for a period of: • Not more than one year (short-term holding period)- 100% of the capital gain or loss is recognized • More than one year (long-term holding period) – 50% of the capital gain or loss is recognized For corporate taxpayers: Regardless of the length of the holding period, 100% of the capital gain or capital loss is recognized. THE HOLDING PERIOD RULE DOES NOT APPLY TO CORPORATIONS. 4. Interest Income This particularly refers to interest income other than passive interest income subject to final tax. A taxable interest income must have been actually paid out of an agreement to pay interest. It cannot be imputed. Interest income, as a rule, is taxable included in the ITR Exclude: a. Interest income from bank deposits or deposit substitutes in the Philippines subject to FT (passive income); b. Interest income which are exempt from tax: • Interest income from long-term deposits or investment in the form of savings, trust funds, deposit substitutes, investment management accounts; • Interest income earned from passive investments of foreign governments, financing institutions owned by foreign governments, and international financial institutions established by foreign governments. 5. Rent Income Rent income arises from leasing properties of any kind. It is a passive income but is not subject to final tax under the NIRC; hence, it is subject to regular income tax. Aside from the periodic receipts of such, the following should be considered. 1. Obligations of the lessor that are assumed by the lessee are additional rental income to the lessor. 2. Leasehold improvements made by the lessee on the leased property are recognized by the lessor as income using the spread-out method or outright method. 3. On advance rentals 6. Royalties Royalties earned from sources within the Philippines are generally subject to final income tax except when they are active by nature. Active royalty income and royalties earned from sources outside the Philippines are subject to regular income tax. 7. Dividends These pertain to dividends declared by foreign corporations. It should be recalled that dividends declared by domestic corporations are generally subject to 10% final tax if the recipient is an individual taxpayer and exempt if the recipient is a domestic or a resident foreign corporation. Cash, property, and script dividends from foreign corporations are items of gross income subject to regular income tax. 8. Annuities 9. Prizes and winnings a. Prizes and winnings from foreign sources received by individuals and corporations b. Prizes and winnings from Philippine sources received by corporations c. Prizes from Philippine sources received by individuals amounting to P10,000 or less. 10. Pensions These pertain to pensions and retirement benefits that fail to meet the exclusion criteria and hence subject to regular tax. 11. Partner's distributive share from the net income of the general professional partnership.