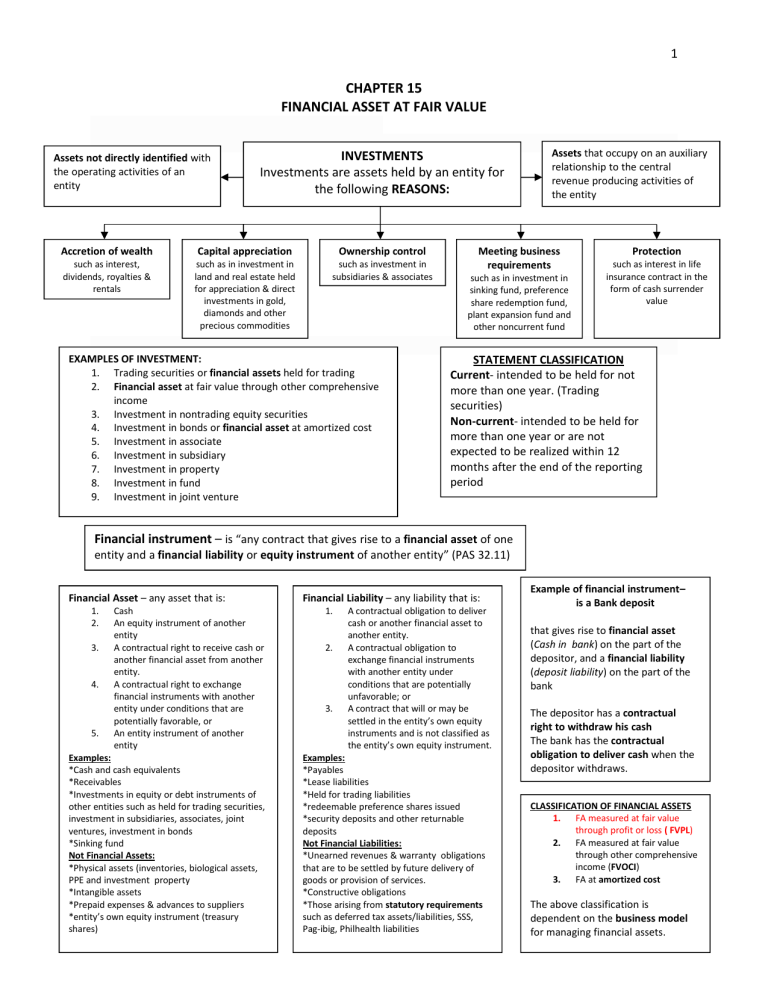
1 CHAPTER 15 FINANCIAL ASSET AT FAIR VALUE Assets not directly identified with the operating activities of an entity Accretion of wealth such as interest, dividends, royalties & rentals INVESTMENTS Investments are assets held by an entity for the following REASONS: Capital appreciation such as in investment in land and real estate held for appreciation & direct investments in gold, diamonds and other precious commodities Ownership control such as investment in subsidiaries & associates EXAMPLES OF INVESTMENT: 1. Trading securities or financial assets held for trading 2. Financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income 3. Investment in nontrading equity securities 4. Investment in bonds or financial asset at amortized cost 5. Investment in associate 6. Investment in subsidiary 7. Investment in property 8. Investment in fund 9. Investment in joint venture Assets that occupy on an auxiliary relationship to the central revenue producing activities of the entity Meeting business requirements such as in investment in sinking fund, preference share redemption fund, plant expansion fund and other noncurrent fund Protection such as interest in life insurance contract in the form of cash surrender value STATEMENT CLASSIFICATION Current- intended to be held for not more than one year. (Trading securities) Non-current- intended to be held for more than one year or are not expected to be realized within 12 months after the end of the reporting period Financial instrument – is “any contract that gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity” (PAS 32.11) Financial Asset – any asset that is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cash An equity instrument of another entity A contractual right to receive cash or another financial asset from another entity. A contractual right to exchange financial instruments with another entity under conditions that are potentially favorable, or An entity instrument of another entity Examples: *Cash and cash equivalents *Receivables *Investments in equity or debt instruments of other entities such as held for trading securities, investment in subsidiaries, associates, joint ventures, investment in bonds *Sinking fund Not Financial Assets: *Physical assets (inventories, biological assets, PPE and investment property *Intangible assets *Prepaid expenses & advances to suppliers *entity’s own equity instrument (treasury shares) Financial Liability – any liability that is: 1. 2. 3. A contractual obligation to deliver cash or another financial asset to another entity. A contractual obligation to exchange financial instruments with another entity under conditions that are potentially unfavorable; or A contract that will or may be settled in the entity’s own equity instruments and is not classified as the entity’s own equity instrument. Examples: *Payables *Lease liabilities *Held for trading liabilities *redeemable preference shares issued *security deposits and other returnable deposits Not Financial Liabilities: *Unearned revenues & warranty obligations that are to be settled by future delivery of goods or provision of services. *Constructive obligations *Those arising from statutory requirements such as deferred tax assets/liabilities, SSS, Pag-ibig, Philhealth liabilities Example of financial instrument– is a Bank deposit that gives rise to financial asset (Cash in bank) on the part of the depositor, and a financial liability (deposit liability) on the part of the bank The depositor has a contractual right to withdraw his cash The bank has the contractual obligation to deliver cash when the depositor withdraws. CLASSIFICATION OF FINANCIAL ASSETS 1. FA measured at fair value through profit or loss ( FVPL) 2. FA measured at fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI) 3. FA at amortized cost The above classification is dependent on the business model 1 for managing financial assets.




