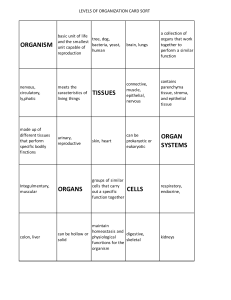
Cells, tissues, and organs are essential components of living organisms. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. It is surrounded by a cell membrane, which acts as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of materials in and out of the cell. Inside the cell, there are various organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and cytoskeleton. Each organelle has a specific function, such as DNA storage and replication, energy production, protein synthesis, detoxification, and cell division. Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissue covers and lines body surfaces and cavities, such as the skin, digestive tract, and lungs. Connective tissue supports and connects organs and tissues, such as bone, cartilage, and blood vessels. Muscle tissue enables movement and contraction, such as skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Nervous tissue transmits and processes information, such as neurons and glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. Organs are collections of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain. Each organ has a specific structure and function, and is composed of different types of tissues. For example, the heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body. It is composed of muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue. In summary, cells are the basic units of life, tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function, and organs are collections of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. All three are essential components of living organisms and work together to maintain homeostasis and carry out vital functions.