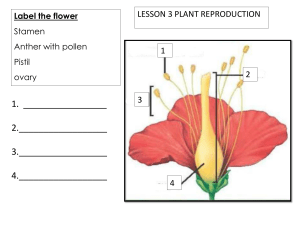
LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL SAMPLE PAPER MARKING SCHEME This marking scheme is the work of practicing teachers – and is a suggested solution to the paper. 1. 4(5) (a) Ear (b) Liver (c) Stoma (Stomata) (d) Ligaments (e) Omnivore 2. 5(4) Rods (Bacillus) Spheres (Cocci) Binary fission Spores (Endospores) Disease causing 3. 5(4) Cell membrane Lipid Vacuole Sap Mutation Variation Organ Liver Gamete Haploid 4. 13 April / May / June There is plenty of food/ it is warmer Lack of food / predation / temperature / decrease Any two 3 3(3) 3 3+2 5. (a) (b) Vitamin: A or D or K 3 Source: liver/ milk/ green vegetables 3 Disease: Night blindness or rickets (osteomalacia) or reduced clotting of blood 4 Minerals: Calcium and Iron Calcium – for strong bones and teeth or blood clotting OR Any one Iron – for red blood cells or to make haemoglobin 6. 2(3) 4 5(4) Six Two Three 7. (a) (b) 1. Reproduction 2. Growth / Repair (i) A biological/ organic/ protein catalyst 3 (ii) Substrate 3 Catalase or amylase (must match substrate) 3 Hydrogen peroxide or starch (must match enzyme used) 3 Diagram of set up Labels: water bath(s)/ test tubes/ solutions/ 6,3,0 3(1) Water baths/ at different temperatures/ thermostat 3 Volumes of foam/ per minute/ disappearance of blue colour/ per minute 3 8. (a) (b) (i) Named ecosystem (ii) Matching three plants % frequency or % cover. Named plant Position quadrat / at random / number of times / count plants / estimate cover / result / number per area / % frequency / % cover Any four 3 3(1) 3 4(3) Results presented in words or a diagram or a graph or a table Source of error: Lack of randomness/ insufficient quadrats/ species identification/ carelessness/ human error/ unsuitable equipment. 9. (a) The growth of a seed/ sprouting/ re growth of the embryo plant Moisture (water) / warmth ( correct temperature) / oxygen (b) Seed type: mustard/ cress/ radish/ peas Diagram: 4 dishes/ tubes. A- minus water/ B minus oxygen/ C with every thing/ D – minus correct temperature. Labels to match diagrams. ( title may be considered a label) Set up apparatus as in sketch / placed A, B and C in incubator at 20 °C / place D in fridge / for 2-3 days A, B, D – no germination C – germination 3 3(1) 3 6,3,0 3 3(3) 3 3 10. (a) (b) (c) 11. (a) (i) 72 beats per minute ( allow 5 either side) 3 (ii) Decrease: sleep / rest / cold / drugs Any one Increase: exercise / excitement / drugs Any one 3 3 (i) A- ventricle, B- bicuspid valve, C- atrium, D – aorta, E- pulmonary artery, F – vena cava (ii) The lungs 3 (iii) To prevent backflow (of blood)/ from ventricle to atrium 3 (iv) Coronary ( cardiac) 3 (i) Plasma 3 (ii) Glucose / amino acids / vitamins / urea / hormones Any two 2(3) (iii) To transport substances / act as a medium Any one 3 (iv) RBC- transport oxygen Any one WBC- defence against disease / produce antibodies / engulf bacteria Any one 3 (v) ABO and Rhesus systems (i) Examining DNA / for a pattern or band / to compare (ii) Forensic / paternity case s/ medical or examples 6(3) 3 2(3) 3 2(3) (b) Gametes X X (c) X XX XX Y XY XY Gametes: X and X or Y Genotypes: XX and XY ( 50% chance of either) 3(4) 2(6) (i) Change / producing new organisms / example 6+3 (ii) organisms have variations / that are inherited / beneficial / will reproduce / struggle for existence / pass on these variation s/ ‘survival / of fittest’ / origin of species Any four Fossils / comparative anatomy / embryos / DNA changes / horse / bones Any two 4(3) (iii) 2(3) 12. (a) (b) (c) (i) A group of similar cells (ii) Xylem and Phloem 2(3) (i) A, B and C correctly marked on the diagram 3(3) (ii) Absorption of water (and minerals) / anchorage / food storage / asexual reproduction 3(3) (iii) Radicle 3 (iv) At the tip 3 (i) A seed leaf / embryonic leaf 3 (ii) Daffodil / onion / any correct 3 (iii) Daisy / dandelion / buttercup / any correct 3 3 (iv) Distribution of veins in leaf Leaf shape Distribution of vascular bundles in stem Monocotyledon Dicotyledon parallel Netted / reticulate Strap broad No definite pattern Definite pattern 6(3) 13. (a) (b) (i) 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy 2(3) (ii) Mitochondria 3 (i) To show that it is the mouse that releases the carbon dioxide 3 (ii) Lime water in 2 proves that any carbon dioxide in the incoming air has been removed. Lime water in 3 proves that it is the mouse that releases the CO2 To act as a comparison/ a standard against which to compare. The same set up but with no mouse ( organism) No. Photosynthesis by the plant would use up the CO2 that the plant produces in respiration (iii) (iv) (c) 3 3 6 3 3 3 (i) To remove the oxygen 6 (ii) To keep the system anaerobic/ to stop oxygen getting in 6 (iii) No. The control would be the set up without the yeast. It is the yeast that is respiring. 3 Baking / brewing 2(3) (iv) 6 14. 14. 14. 14. Any two of (a), (b), (c) (a) (b) (c) (30, 30) (i) Nitrogen Cycle (ii) Any named herbivore and carnivore related to an Irish ecosystem (iii) Proteins / nucleic acids / enzymes 6 (iv) Denitrification / death and decay / decomposition 3 (v) Nitrogen fixation 3 (vi) Bacteria / Rhizobia 3 (vii) To prevent washing excess nitrates into rivers and streams /causing pollution 3 (i) The sun 3 (ii) Photosynthesis 3 (iii) Chlorophyll 3 (iv) (v) Name of ecosystem A – ( plant), B ( herbivore), C ( carnivore) B. Because the energy decreases / is lost as you move up through a food chain (vi) Food web (must include A, B, C above) (i) Addition of harmful substance to the environment/ undesirable change Any Example: release of toxic gases from manufacturing. One Control: legislation / filters 1. Bad odours / disease / unsightly / production of toxic chemicals / run off 2. Waste management: safe disposal of waste / reduce / reuse / recycle / example of waste / how managed / role of micro-organisms (ii) (iii) 6 2(3) 3 3(3) 3 3 3 6 3 3 3 3 (iv) Protection / preservation / wise management of the environment 6 (v) Conservation practice: net mesh size in fishing industry to allow young fish escape to breed 6 15. 15. Any two of (a), (b), (c) (a) (30, 30) (i) A – cortex, B- medulla ( pyramid), C – pelvis, D – ureter (ii) Bladder 3 (iii) In the cortex. ( A)/ nephron/ glomerulus/ Bowman’s capsule 3 (iv) Glucose/ amino acids/ vitamins/ red blood cells/ white blood cells 4(3) 2(3) Any two 15. (b) (v) Put on a dialysis ( kidney) machine 3 (vi) Lungs / skin / liver Any one 3 (i) Fungi 3 (ii) A- hypha ( stolon), B – rhizoid, C – sporangium (iii) Anchorage / absorption Any one Asexual reproduction / production of spores / storage of spores Any one Name: Mushrooms/ TrufflesBenefit: for food/ fungi of decay – to decompose and recycle nutrients Name: Destroying Angel/ Death Cap – Harm: Is a poisonous fungus (iv) (v) (vi) 15. (c) (i) 3(3) A – petal, B – anther, C – sepal, D – carpel 3 3 3 3 3 3 4(3) (ii) C – protection / photosynthesis (iii) The anther / stamen 3 (iv) The carpel / ovary / ovule 3 (v) The ovary / ovary wall 3 (vi) By insects / animals. The nectar is a ‘reward’ for the insect visiting the flower and at the same time transfers pollen 3 Any one 3 3