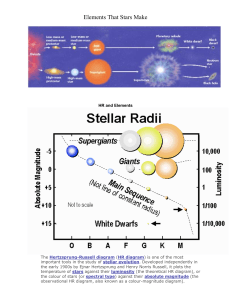
CONSTELLATIONS MODULE 3 -Summary Report- WHAT IS A STAR? Are the stars same in size? Are the stars same in color? Are the stars equally bright? When we look at the sky, we see thousands of stars. In reality, there are approximately 400 billion stars in our galaxy, and there are about 170 billion of galaxies. THE SUN Sun is only about 150 million kilometers away, and it takes only 8 minutes and 20 seconds for sunlight to reach our world. It’s diameter is about 1.4 million kilometers, 100 times of the earth. But yet it is only a medium-size star. Many other stars are much, much bigger. CHARACTERISTICS OF STARS • Color and Temperature • Brightness and Magnitude of Stars • Sizes of Stars • Distance of Stars • Composition of Stars SHORT REVIEW Which star is the hottest? RED BLUE Which star is very similar to our sun? YELLOW ORANGE Which is the coolest star? BLUE YELLOW TEMPERATURE AND COLOR Let’s play a game, our class is divided into two groups. In three minutes I want you to identify the following color of each star based on their temperature. STAR COLOR TEMPERATURE Sun 5,700 Vega 9,900 Alnilam 27,000 Sirius 10,000 Proxima Centuari 2,300 Epsilon Iridani 4,600 ANSWER COLOR AND TEMPERATURE Stars emit colors of many different wavelengths, but the wavelength of light where a star's emission is concentrated is related to the star's temperature - the hotter the star, the more blue it is; the cooler the star, the more red it is. • Star color ranges from red to blue. The color of star indicates its surface temperature. • The coolest star is about 2800 ℃ at the surface. These star appear red. The temperature of the hottest star is about 28 000℃ or higher. These star appear blue. BRIGHTNESS AND MAGNITUDE WHICH STAR IS BIGGER? SIRIUS AND RIGEL ACTUAL SIZE DISTANCE The star’s brightness as seen from Earth is its apparent brightness. Apparent brightness depends on how far a star is from the Earth. On Figure 1 Sirius appears bigger than Rigel, is actually very small compared to Ringel. It appears larger only because it is closer to us. ACTUAL BRIGHTNESS Astronomers consider the star’s absolute brightness when comparing stars. A star’s absolute brightness is the brightness the star would have if all stars were the same standard distance from earth. SIZES OF STARS • Stars varies in size, from huge to supergiants to tiny neutrons stars. • Astronomers group stars into five types: • Neutron stars, white dwarfs, medium-sized stars, giants and supergiants. • Neutron stars are the smallest, it has a diameter of about 16 km. • White dwarf is about 7300 km., slightly greater than that of earth. • Medium-sized star is about one-tenth the diameter of the sun. • Giant star is 10 to 100 times that or the sun. • Supergiant stars is up to 1000 times the diameter of the sun. DISTANCE OF STARS • Scientist use parallax to determine how far away a star is from Earth. A parallax is an apparent change in the position of an object caused by a change in the position of the observer. • The closer a star is to Earth, the greater its apparent change of position. Very distant stars seem not to shift position at all. • Scientist express distances between stars in light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year at a speed of 300 000 km per second (kps). A light year is about 9.5 trillion km or 9 500 000 000 000 km. • The closest star is Proxima Centauri, 4.2 light years from Earth. Other stars are hundred of light years away. COMPOSITION OF STARS Using spectroscope, astronomers have found that almost all stars have the same general chemical make up. The most element in stars is hydrogen, the lightest element that make 60% to 80% of the total mass of a star. The second element is Helium, make up about 96% to 99% of stars mass. Other elements are oxygen ,neon ,carbon , and nitrogen. STARS Stars is composed mostly of two lightest elements Hydrogen Helium CONSTELLATION When you look at the sky, what do you see? Do you see images of animals ,objects, or people? CONSTELLATIONS Observers in ancient times also imagined group of stars that form pictures of animals, objects, and people. These imaginary groups of stars are called constellations. CONSTELLATIONS Many constellations have names that can be traced back early Babylonians and Greek civilizations, but nearly all cultures have different names for the constellations. For example, Greeks called the large constellation Orion, which means hunter and is prominent in the night sky all over the world during winter. Early Filipinos visualized the same group of stars as Balik, a trap used in hunting wild pigs. Christian Filipinos named the three stars (Orion’s belt) Tatlong Maria or Tres Marias. ORION LYRA PISCES GEMINI ARIES APPARENT MOVEMENT OF THE STARS THROUGH THE NIGHT By observing the Sun’s movement and position in the sky, we can tell what time of the day it is. When it seems to rise in the east, it is morning. When it is above us, it is noon. When it seems to move towards the west, it is afternoon. At night, stars are used to tell the time. Just like the sun, stars also seem to move from east to west. THE POLARIS Polaris, commonly known as the North Star, is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor (Little Dipper). It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star. Because it lies nearly in a direct line with the axis of Earth’s rotation “above” the north Pole, Polaris stands almost motionless in the sky, and all the stars of the Northern sky appear to rotate it. STAR TRAIL Star trail is a type of photograph that utilizes long-exposure times to capture the apparent motion of stars in the night sky due to the rotation of the Earth. POLARIS In Metro Manila, when you face North Polaris, which is 11.3° from the horizon is seen at around 15° due to atmospheric refraction. In some parts of the country (i.e Southern Philippines), it would be difficult to locate Polaris since starlights near the horizon are washed out by lights lit by men, or obstructed by man-made or topographical structures or trees. HOW TO LOCATE POLARIS? To locate the Polaris, face North and locate the Big Dipper. Two stars (Merak and Dubhe) in the Big Dipper are called pointer stars because they seem to point to Polaris. DIFFERENT STAR PATTERNS THROUGHOUT THE YEAR MARCH NIGHT SKY 9 P.M. JUNE NIGHT SKY 9P.M. SEPTEMBER NIGHT SKY 9P.M. DECEMBER NIGHT SKY 9 P.M. STARS APPEAR TO MOVE IN THE NIGHT SKY The rotation of the earth on its axis causes the apparent nightly movement of the stars across the sky, the revolution is responsible for the fact that we can see different parts of the sky at different parts of the year. An observer from Earth will be able to see the stars that are on the night side. The stars on the same side as the sun cannot be seen because sunlight overpowers all the starlights. During summer in the Philippines, the constellations of Orion and Taurus are not visible at night. They will be visible again as the cold season begins. During this time, Scorpio will not be seen in the night sky. The Earth revolves around its orbit, the stars that were concealed by the bright light of the Sun in the previous months will appear in the night sky. HOW EARLY PEOPLE USED THE CONSTELLATIONS? USES OF CONSTELLATIONS While constellations were associated with religion, they also have practical uses. Before calendars, people had no way of determining when to sow or harvest except by looking at these patterns in the sky. Ancient people developed a way to remember the patterns by giving them names and stories. USES OF CONSTELLATIONS For example, in the northern hemisphere, the constellation Orion indicates the coming of cold season. The constellations made easier for them to recognize patterns in the sky. For example, Gemini is seen in the Philippines during the months of April and May. Farmers interpreted the appearance of Gemini as the end of planting season and it signified rich harvest. STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS USED BY MATIGSALUG MANOBO OF BUKIDNON OTHER USES Another use of constellation is navigation. The polaris used in navigation because it does not change its position at any time of the night year. Also, one can figure out his/her latitude just by looking at how high Polaris appears in the night sky. This allowed sailors to find their way as they sail across the seas. LETS TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE QUESTION AND ANSWER PORTION How do stars appear to move in the night sky? What is the closest star to Earth? Why do stars have colors? What are the imaginary group of stars? This constellation is prominent during winter It is commonly known as North Star What is the brightest star? It is a type of photograph that capture the apparent motion of stars in the night due to the rotation of the Earth. Give 10 constellations The Sun is also know as? What is the name of our galaxy? What is the largest constellation?