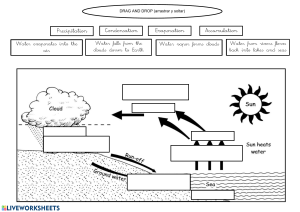
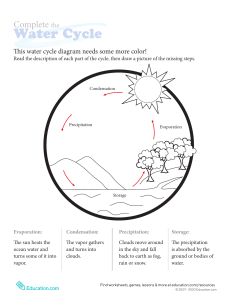
A Detailed Lesson Plan In Science 8 I. Objectives At the end of the lesson, the students would be able to: a. identify the processes involved in the water cycle; b. appreciate the importance of water cycle in daily living; and c. illustrate the process of water cycle. II. Subject-Matter a. Topic: Water Cycle b. Materials: PowerPoint presentation, video presentation, illustration, visual aids, and chalkboard c. Reference: Learning Module; Science 8, Quarter 4 - Module 7, Biogeochemical Cycles p.5 d. Duration: 1hour III. Procedure A. Preparatory Activities/ Daily Routine 1. Prayer Everyone please stand. Kindly lead the prayer, Jamyr. In the name of the Father, …. Amen. 2. Greetings Good morning, 8-Molave! Good morning, Ma’am. 3. Classroom Management Before you take your seats, kindly pick up the pieces of paper around you and arrange your chairs properly. Always observe the safety protocols such as wearing of your masks properly. 4. Checking of Attendance Ms. Secretary, are there any absentees for today? Very Good! You’re all present. (The students will pick up the pieces of paper and will arrange their chair properly.) No one is absent for today, Ma’am. Because of that, give yourselves a round of applause. As your incentive for your perfect attendance, I will give you +5 points for your activity later. 5. Checking of Assignment Last meeting, I gave you an assignment, pass it forward and I will be the one to check it. (The students will pass their assignments) B. Review Before we discuss today's lesson, let us first review what you have learned last meeting. Can anyone in the class tell me what is our topic yesterday? (The students will raise their hands) Yes, Maenard. We discussed about “Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Cycle. Very good. Thank you, Maenard! So, what can you say about oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle? (The students will raise their hands) Yes, Neri. Carbon and oxygen are two elements that are essential to life. Since they are circulating between the soil, air and water, living matter goes always with cycle. Very good, Neri! How does the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle occur in nature? (The students will raise their hands) Yes, Alexandra. Oxygen comes mainly from green plants as a product of photosynthesis. It will be used by the animals during the process of respiration to produce carbon dioxide gas. Very good! Thank you, Alexandra. And what will happen to the carbon dioxide after? (The students will raise their hands) Yes, Charlene. These carbon dioxide gases from the atmosphere will be used by plants to manufacture its own food. It will be absorbed by plants during respiration process. Then, the cycle will repeat again. Very good! Thank you, Charlene. B. Motivation I prepare a short game for you, class. But first, I will group you into 5. (The teacher will group the students into 5.) (The students will go to their designated groups and will form a circle.) Direction: I will give each group a shuffled jigsaw puzzle. You have to solve it within 5 minutes. The first group to finish will win. Are you ready class? Timer starts now! …5,4,3,2,1 Stop! Now, tell me what can you see in the puzzle. Yes, ma’am! (The students will start to play) … Very Good! You all did a great job! Because of that, let’s do the Hooray clap! (The students will do the Hooray clap) (Each group will now present their work. Each group should answer: drying of clothes under the sun; watering plant; glass of water with ice; dry ice and rain) Please assign one member to hold the puzzle and go back to your designated area quietly. Those words that you’ve answered a while ago were all included to our lesson today. C. Presentation The teacher will challenge the students to think about these questions: Where does the rain come from? Where do clouds come from? These elements are part of something called the water cycle. (The teacher will show a picture of a globe and will explain the following in the class.) 75% of the Earth’s surface is filled with water and 25% of the Earth is covered with land. Therefore, water covers a wider area of the Earth surface than land. Motive question: Do you think the amount of water on Earth decreases since its existence? Who says no, and who says yes? The students will raise their hands (Answer may vary) The amount of water in the Earth does not change. It remains the same. Why? Today, we will find out. (The teacher will present an illustration of water cycle.) Can anyone in the class tell what is your idea about the illustration? Yes, Vincent. Ma’am, it is a kind of cycle. Very good, Vincent! And what cycle do you think it is? Yes, Myca. It is a water cycle, ma’am. That’s great, Myca! This is a water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle. It describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water cycle is like a big circle that does not really have starting point. Today, you will learn the different processes of water cycle. (The teacher will start to explain each process of water cycle by showing illustrations of things included in the cycle.) Okay class, what is this? (The teacher will show an illustration of the Sun) Yes, Zaida. Ma’am, that is the Sun. Okay, you’re right. And what can you say about the sun? Yes, Wendy. The Sun gives the Earth sunlight and it can heat up the water. Very Good, Wendy! As the sun shines over water, it will heat up and may cause the surface to evaporate. And what happens in evaporation? Yes, Phim. Very Good, Phim! The liquid turns to gas. The water vapor rises up to the atmosphere. And using those puzzles, will you please tell me what do you think is an example of evaporation process and why? (The group with an image of “drying of clothes under the sun” will raise their hand to answer) Ma’am, drying of clothes under the sun is an example of evaporation because the water on the clothes dries or evaporates. Yes, very good! You’re right. Drying of clothes under the sun is an example of evaporation. (Will you please go in front and post it on the board.) Thank you! Let’s move on to our next process. Transpiration is similar to evaporation as the liquid turns into gas. But this only takes place on plants. The escape of water through leaf pores adds water vapor to the atmosphere. And which among the remaining groups has this example? Very good! As you can see, when you pour water on the plants, it will absorb by their roots, and it goes to their leaves. The water in their leaves will now evaporates. (Please come in front and post it on the board.) Thank you. In special cases in mountains where snow and ice mixed with high humidity of air may cause the snow and ice to sublimate. (The group with “watering plant” puzzle will raise their hand) And what do we mean by sublimate? Yes, Rhian. Solid phase turns to water vapor, without passing to liquid. Very Good, Rhian! And with the two remaining groups, which of you holds the example of sublimation? (The group holding the puzzle of dry ice will raise their hand) Very good! Dry ice is an example of sublimation because when it gets exposed in the air, it will directly change its phase from solid-state to gaseous state which is visible as fog. (Please come here in front and post it on the board.) When water vapor reaches the cooling point at higher altitude, that makes them to condense and forms clouds. And what happens in condensation? The vapor turns to water. Yes, Marcus. Very good, Marcus! And which group has the example of condensation? And where did it occur? Very good! (The group holding the wet glass will raise their hand) Ma’am, the condensation happens when the water droplets appeared outside the glass. The condensation happened in the glass because the warm air outside the glass hits the surface of the glass’s colder surface, turning gas into liquid. (Please come in the front and post it on the board.) And when the water formed in clouds become heavy, it will fall back on Earth in the form of precipitation. What do we mean by precipitation? Please read, Marco. Thank you, Marco. And it happens when clouds can no longer hold water. The water will then fall to the Earth because of the gravity. Which group has the example of precipitation? Very good! (Please come here in front and post it on the board.) Thank you! Precipitation has different forms: Rain or the liquid state, freezing rain is like a rain but becomes frozen when it hits the ground while snow is the frozen form of precipitation like sleet and hail. The process will also form snow or hail when the temperature gets colder. Fell down water from clouds in the form of precipitation goes directly to mountains, on the ground as run-off water, some go down deeply Precipitation is the water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow or hail. (The group with the rain puzzle will raise their hands) into the soil (transpiration) some go to the lakes, seas, ocean, and the cycle repeats again. None ma’am. And those are the processes of water cycle. Are there any questions? 5. Generalization Water cycle is the continuous movement of water in different surface of the Earth. If so, then let us see what have you learned from our discussion a while ago. We’re going to have an activity. And I will call it “Express with Emoji” Directions: Each of you will hold two kinds of emoji that can be seen on facebook. (The teacher will give each students two emoji, care and sad emoji.) Just raise the care emoji if the statement is correct and sad emoji if it is not. Let’s begin! • The water cycle has different processes. Those are evaporation, transpiration, condensation and cooperation. Why do you say it is wrong? Okay! Very good! You’re right! . (The students will raise the sad emoji.) It should be precipitation and not cooperation. (The students will raise the care emoji.) (The students will raise the care emoji.) • Water cycle has no starting point. It is a continuous process and it is very important to all living organisms. • Water circulates around the environmentthe oceans, land, air and living organisms. • When sun energy warms the Earth’s surface, water condenses from the oceans, rivers, lakes and land. (What should it be?) Very good! • The escape of water through leaf process (transpiration) adds water vapor to the atmosphere. Okay, Very good! Most of you got the right answers! Because of that let’s do the Hooray clap! Is there any question, class? Is everything clear? Let’s have now another activity. (The students will raise the sad emoji.) Ma’am, it should be evaporating not condenses. (The students will raise the care emoji.) (The students will do the hooray clap.) None, ma’am. Yes, ma’am. E. Application: The teacher will flash an instruction on the screen. BREAKING THE CODE Direction: Crack the code to find the answer to the questions below. • It is the process by which water molecules gather from evaporated gas into stored water in clouds, or precipitation into collecting bodies of water. CODE: 3 15 14 4 5 14 19 1 20 9 15 14 • It is the process of collected water in the clouds returning to the Earth’s surface in rain, sleet, snow. CODE: 16 18 5 33 I 16 9 20 1 20 9 15 14 • It is the process that allows solid water in the form of ice to escape as gas without turning into liquid water. CODE: 19 21 2 12 9 13 1 20 9 15 14 • The process that allows water released from the process of photosynthesis in plants to be released into the environment. CODE: 20 18 1 14 19 16 9 18 1 20 9 15 14 • It describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth CODE: 23 1 20 5 18 3 25 3 12 5 • Evaluation Direction: Illustrate the water cycle diagram. (The paper that students will use was provided by the teacher.) • Assignment Direction: In a short bond paper, create a poster showing the ways on how we can conserve water. Name: ___________________________________ Date: _____________ Grade&Section: ____________________________ Score: ____________ BREAKING THE CODE Direction: Crack the code to find the answer to the questions below. • It is the process by which water molecules gather from evaporated gas into stored water in clouds, or precipitation into collecting bodies of water. CODE: 3 15 14 4 5 14 19 1 20 9 15 14 • It is the process of collected water in the clouds returning to the Earth’s surface in rain, sleet, snow. CODE: 16 18 5 33 I 16 9 20 1 20 9 15 14 • It is the process that allows solid water in the form of ice to escape as gas without turning into liquid water. CODE: 19 21 2 12 9 13 1 20 9 15 14 • The process that allows water released from the process of photosynthesis in plants to be released into the environment. CODE: 20 18 1 14 19 16 9 18 1 20 9 15 14 • It describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth CODE: 23 1 20 5 18 3 25 3 12 5