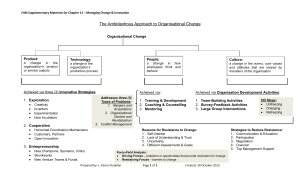
Conclusion and course review Topic 12 Dr Hugh Bainbridge LEARNING OUTLINE 1. The big picture Post MGMT1001. How does MGMT1001 connect to the rest of your degree? I.e., where to from here? MGMT1001: How does it add to your employability? Course feedback and suggestions 2. Review of remaining course assessment How is the exam structured? What’s on the exam? 3. Exam preparation Tips and tricks for improving the efficiency of your revision Tips for increasing your exam performance International Business Human Resource Management Management Major in International Business Why study International Business? – You are interested in the global business environment in general and the operations of multinational enterprises in particular – Careers: Asset Management Trainee, Business Analyst, Cross-Cultural Advisor, Export and Import Officer, Global Product coordinator, International Marketing Officer Major in International Business Compulsory International Business courses MGMT1101 Global Business Environment MGMT2101 International Business and Multinational Operations MGMT2102 Managing Across Cultures MGMT3101 International Business Strategy MGMT3102 Asia-Pacific Business Elective courses MGMT2002 Managing Business Communication MGMT2010 Innovation & Entrepreneurship MGMT2105 East Asian Business Enterprise MGMT2106 Comparative Management Systems MGMT2725 Career Management MGMT2726 Business Ethics and Sustainability MGMT3003 Global Entrepreneurship MGMT3702 International Human Resource Management MGMT3721 Negotiation Skills Major in Human Resource Management Why study Human Resource Management? – You are interested in the people side of business – It is accredited by the Australian Human Resource Institute (AHRI) – Careers: Employment relations Consultant, Human Resource Coordinator, Recruitment Officer, Staff Development Officer and Training Coordinator Potentially interested in HRM? Australian Human Resource Institute – https://www.ahri.com.au/ – https://www.ahri.com.au/become-amember/student-membership SHRM, Academy of HR Development – https://www.shrm.org/ – http://www.ahrd.org/ Major in Human Resource Management Compulsory Human Resource Management courses MGMT1001 Managing Organisations and People MGMT1002 Managing Organisational Behaviour MGMT2705 Industrial Relations MGMT2718 Human Resource Management MGMT3701 Legal Aspects of Employment Elective courses MGMT2200 Thinking Skills MGMT2704 Social Organisation of Work MGMT2724 Health and Safety at Work MGMT2725 Career Management MGMT2726 Bus. Ethics and Sustainability MGMT3702 International HRM MGMT3721 Negotiation Skills MGMT3724 Strategic Human Resource Management MGMT3728 Managing Pay and Performance MGMT3729 Managing Workplace Training Major in Management Why study Management? – You are interested in the effective combination of people and resources in needed in all organisations, – Learning about the interrelationship between people, power & resources, – Leading or managing an organisation, OR – Being your own boss – Careers: General Manager, or more focused e.g., Client Service Manager, Business Analyst, Corporate Planning Officer… a variety of management positions Interested in Management? Australian Institute of Management – http://www.aim.com.au/ UNSW Student societies – MSOC - http://www.unswmsoc.com/ – 180 degrees - http://180dc.org/branch/unsw/ – AIESEC - http://180dc.org/branch/unsw/ Looking for the perfect opportunity to network and gain valuable insight into the start up world of business? Firms attending include Austern, Generation Entrepreneur, Conexie, Village, and more... • Date: Wednesday, 18 October 2017 • Time: 6pm-8pm • Location: Engineering Design Lab, Level 5, Ainsworth Building • Register now to secure your spot! https://goo.gl/forms/Wi14tLMyDEwbxQQ53 Major in Management Compulsory courses MGMT1001 Managing Organisations & People MGMT1002 Managing Organisational Behaviour MGMT2001 Managing Innovation & Organisational Change MGMT2002 Managing Business Communication MGMT3101 International Business Strategy Elective courses MGMT2010 Innovation & Entrepreneurship MGMT2102 Managing Across Cultures MGMT2106 Comparative Management Systems MGMT2200 Thinking Skills MGMT2718 Human Resource Management MGMT2725 Career Management MGMT2726 Business Ethics and Sustainability MGMT3003 Global Entrepreneurship MGMT3702 International Human Resource Management MGMT3721 Negotiation Skills MGMT3728 Managing Pay and Performance MGMT3729 Managing Workplace Training MGMT 1002: Managing organisational behaviour Overview – Introduction to Organisational Behaviour What drives behaviour at work? – – – Personality and individual differences Work Attitudes Workplace Motivation Managing yourself & others – – – – – – – – Leadership Job Design Stress Turnover Power and Conflict Organisational Culture Organisational Change Review Exam structure Students are expected to sit the exam on the prescribed day and should not make travel arrangements, work functions or other plans on this day. Exam schedule – https://my.unsw.edu.au/ – Check location – Time What to bring – UNSW student ID – Blue or black ink pens – 2B pencils and erasers Time allowed – Two (2) hours and 10 minutes reading time This exam is worth 35% of the total assessment for the course. There are 2 Parts to the exam paper – students must attempt each Part. Part A consists of 30 Multiple Choice questions. Your responses must be filled in on the multiple choice answer sheet. Answer Part B using the exam books. Note, each Part is a different number of marks Part A: 15 marks Suggested time: 30 minutes Part B: 20 marks Suggested time: 90 minutes The following materials are provided by the Enrolment and Examinations Section: – Answer sheet for part A (multiple choice questions), – Exam book(s) for writing part B. Answers for the multiple choice questions must be written in pencil on the answer sheet. Answers for part B must be written black or blue ink. Ensure that you have written your name and other details on the multiple choice answer sheet as well as every exam booklet used. Candidates cannot retain a copy of the exam paper. Exam instructions for Part A Part A is Multi-choice questions (filled out on answer sheet that is provided in the exam) Bring along 2B pencils and erasers! Allow approximately 30 minutes to do Part A Sample questions and answers will be uploaded on the course website Revising for Part A MGMT 1001: Course structure Topics Topic 1: Introduction to organisations and management Topic 2: Foundations of management theory Topic 3: Communication Topic 4: Attitudes, perception, and personality Topic 5: Groups and teams Topic 6: Decision making Topic 7: Leadership Topic 8: Human resource management Topic 9: Strategy Topic 10: International business Topic 11: Social responsibility and ethics Topic 12: Course review and exam preparation L E A R N I N G R E V I E W (Topic 9) The importance of strategic management Definition and importance of strategic management The strategic management process 6 steps of the strategic management process External and internal analyses Resources, capabilities, and core competencies Elements of the organisation’s specific and general environment. Types of organisational strategies Corporate, business and functional-level strategies Role of competitive advantage in business-level strategies Porter’s five forces model Generic competitive strategies Evaluation of strategy and the strategic management process Contrast the action of manager according to the omnipotent and symbolic views. Explain the parameters of managerial discretion. L E A R N I N G R E V I E W (Topic 10) 1. How do managers think about international business? Opportunities and threats of the global economy Ethnocentric, polycentric, and geocentric attitudes. 2. How do businesses expand globally? 3 stages organisations go through as they go global. Exporting, importing, licensing, and franchising. Global strategic alliances, joint ventures, and foreign subsidiaries. MNCs, TNCs, and borderless organisations. 3. What are the rules governing the global trading environment? Explain why countries become part of regional trading alliances. WTO, ASEAN, EU, NAFTA and other regional trade alliances. 4. How do firms choose between investment destinations? The global legal-political environment affects managers. Hofstede’s five dimensions, 9 GLOBE dimensions for assessing cultures. Adjustment challenges faced by global managers. L E A R N I N G R E V I E W (Topic 11) 1. What is social responsibility? What distinguishes the classical and socioeconomic views of social responsibility? What role do stakeholders play in the four stages of social responsibility? Why should or shouldn’t an organisation act in a socially responsible way? What is the difference between social obligation, social responsiveness, and social responsibility What relationship is there between social involvement and economic performance? 2. Managerial ethics What different views of ethics exist? What are the levels of moral development? What four variables that affect ethical and unethical behavior What are the six determinants of issue intensity? What is a code of ethics and how can the effectiveness of one be improved? How can organisations improve the ethical behavior of their employees? Revising for Part A HRM Review Questions 1-3 – 1. Explain how an organisation’s human resources can be a significant source of competitive advantage. – 2. Identify the nine activities in the HRM process necessary for staffing the organisation and sustaining high employee performance. – 3. Discuss the environmental factors that most directly affect the HRM process. Review Question Chapter 7 Yes 1 2 No Unsure 3 4 5 6 … … … … Chapter 11 1 2 … 12 13 Part B Part B contains questions that require a written response. (use the exam booklets provided) – Complete the 4 Short Answer Questions in the same booklet (or two booklets if you run out of space) – Start each Short Answer Question on a new page. Reminder! Don’t forget to fill out the front of each booklet with your name, student ID, subject, etc. Part B: Short Answer Questions You will answer 4 short answer questions – Question B1, B2, B3, B4 – Each question is worth 5 marks – You must answer all four questions Suggested structure: – Introduction (1-2 sentence) – Body (several themes) – Conclusion (1-2 sentence) You do not need to provide references specifically i.e. you don’t need pages, dates, journal name, but do need to relate to theories and cite authors where applicable. You will present an argument—your point of view (use first person) Writing a response to an exam question Plan your answer – Make sure you cover the basic information – Then move into analysis of the issues relating to the question Answer the obvious question and then think about how you can add to it – That is, integrate the various areas that were covered this session Answer the question that is asked – Read it three times before you start to plan – Avoid “canned” essays Marks vs time allocated to short answer question Marks High Low 0 10 20 30 Minutes spent on question 25 30 In summary… Plan your time – T-40 mins: Arrive at exam venue – T-10 mins to exam start (i.e., reading time) – Think about the major themes that each short answer question should address and the themes that would be useful additions to these. – 0 to 5 mins: Write down the major themes in bullet point form only next to the exam questions. Write your name and student ID on the multi-choice cover sheet AND the exam booklets – 5 to 35 mins: Complete the 30 multi-choice questions – 35 to 115 mins: Complete the 4 short answer questions – 115 to 120 mins: Finalise any remaining questions