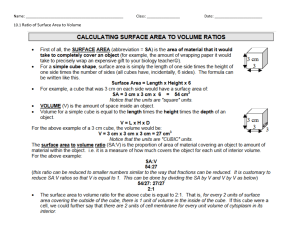
Statistics How To Statistics for the rest of us! GPS / GNSS Frequency Standards Ultra low Phase Noise / Allan Deviation. Phase Noise -120 dBc @ 1 Hz OPEN ptsyst.com HOME TABLES PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS CALCULATORS MATRICES EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN CALCULUS BASED STATISTICS THE PRACTICALLY CHEATING STATISTICS HANDBOOK How to use a frequency distribution table fo… How to use a f… Probability of … 5C3 or 5 choo… How to Ads by Stop seeing this ad Why this ad? GPS / GNSS Frequency Standards Ultra low Phase Noise / Allan Deviation. Phase Noise -120 dBc @ 1 Hz ptsyst.com Class Width: Simple Definition OPEN Find an article Share on Search A frequency distribution table showing a class width of 7 for IQ scores (e.g. 125-118 = 7) Class width refers to the difference between the upper and lower boundaries of any class (category). Depending on the author, it’s also sometimes used more speci cally to mean: The difference between the upper limits of two consecutive (neighboring) classes, or The difference between the lower limits of two consecutive classes. Note that these are different than the difference between the upper and lower limits of a class. Calculating Class Width in a Frequency Distribution Table Watch the video or read on below: Feel like "cheating" at Statistics? Check out the gradeincreasing book that's recommended reading at top universities! Class Width for a Frequency Distribution Table Statisticshowto.com 5,728 likes Like Page Share NEED HELP NOW with a homework problem? CLICK HERE! In a frequency distribution table, classes must all be the same width. This makes it relatively easy to calculate the class width, as you’re only dealing with a single width (as opposed to varying ones). To nd the width: 1. Calculate the range of the entire data set by subtracting the lowest point from the highest, 2. Divide it by the number of classes. 3. Round this number up (usually, to the nearest whole number). Example of Calculating Class Width Suppose you are analyzing data from a nal exam given at the end of a statistics course. The number of classes you divide them into is somewhat arbitrary, but there are a few things to keep in mind: Make few enough categories so that you have more than one item in each category. Choose a number that is easy to manipulate; usually, something between ve and twenty is a good idea. For example, if you are analyzing a relatively small class of 25 students, you might decide to create a frequency table with ve classes. Example: Find a reasonable class with for the following set of student scores: 52, 82, 86, 83, 56, 98, 71, 91, 75, 88, 69, 78, 64, 74, 81, 83, 77, 90, 85, 64, 79, 71, 64, and 83. 1. Find the range by subtracting the lowest point from the highest: the difference between the highest and lowest score: 98 – 52 = 46. 2. Divide it by the number of classes: 46/5, = 9.2. 3. Round this number up: 9.2≅ 10. References Gleaton, James U. Lecture Handout: Organizing and Summarizing Data. Retrieved from http://www.unf.edu/~jgleaton/LectureTransCh2.doc on August 27, 2018. Gonick, L. (1993). The Cartoon Guide to Statistics. HarperPerennial. Jones, James. Statistics: Frequency Distributions & Graphs. Retrieved from https://people.richland.edu/james/lecture/m170/ch02-def.html on August 27, 2018. Levine, D. (2014). Even You Can Learn Statistics and Analytics: An Easy to Understand Guide to Statistics and Analytics 3rd Edition. Pearson FT Press CITE THIS AS: Stephanie Glen. "Class Width: Simple De nition" From StatisticsHowTo.com: Elementary Statistics for the rest of us! https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/descriptive-statistics/frequencydistribution-table/class-width/ -----------------------------------------------------------------------------Need help with a homework or test question? With Chegg Study, you can get step-by-step solutions to your questions from an expert in the eld. Your rst 30 minutes with a Chegg tutor is free! Probability and Statistics Topic Indexes Basic Statistics. Bayesian Statistics and Probability Descriptive Statistics: Charts, Graphs and Plots. Probability. Binomial Theorem. De nitions for Common Statistics Terms. Critical Values. Hypothesis Testing. Normal Distributions. T-Distributions. Central Limit Theorem. Con dence Intervals. Chebyshev's Theorem. Sampling and Finding Sample Sizes. Chi Square. Comments? Need to post a correction? Please post a comment on our Facebook page. Online Tables (z-table, chi-square, t-dist etc.). Regression Analysis / Linear Regression. Non Normal Distributions. © 2021 Statistics How To | About Us | Privacy Policy | Terms Of Use