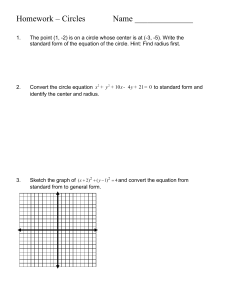
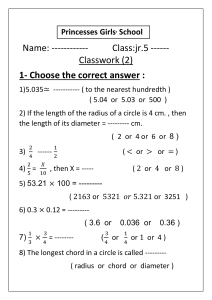
School Teacher BALETE INTEGRATED SCHOOL AIRAJOYCE N. CUATERNO (T-1) Grade 7 SEMI-DETAILED Teaching FEBRUARY 1, 2019; 1:00-2:00 LESSON PLAN Date and PM Time Grade 7 Level Learning Mathematics 7 Area Quarter THIRD (Week 7) I. Objectives A. Content Standard The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of geometry of shapes and sizes, and geometric relationships. The learner is able to create models of plane figures and formulate B. Performance and accurately authentic problems involving sides and angles of a Standard polygon. The learner illustrates a circle and terms related to it: radius, diameter C. Learning chord, center, arc, chord, central angle, and inscribed angle. (M7GECompetency IIIg-1) II. Content Circles III. Learning Resources Mathematics 7, Teacher’s Guide pp. 286-289 1. References Mathematics 7, Learner’s Material pp. 233-236 Mathematics Curriculum Guide p. 84 2. Other Learning Chalkboard, Books, ruler, compass, protractor, laptop and projector Resources IV. Procedures Say: “We will have a puzzle game. I will divide you into three groups. The first group will be the column to my right, the second group will be the column to my left and the third group will be A. Drill the last two rows at the back.” “What you are going to do is to complete the puzzle and then post it on the board. The first group to finish the game will be the winner.” B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson Play “Circle Song | Circle Shapes | I'm A Circle | Circles | Educational Songs | Jack Hartmann“ using a projector. Have the students do the activity: C. Presenting Examples/instance s of new lesson Activity: Draw a point somewhere in the middle of a sheet of paper. Now, using a ruler, mark 20 other points that are 5 cm from the first point. Compare your work with that of your seatmates. Ask: “What shape do you recognize?” D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills Show a picture of a circle, discuss the definition, and show the illustration and how it is named. 1 Answer the following questions: 1. Why do all radii (plural of radius) of a circle have the same length? 2. Which of the following figures are circles? a. b. c. 3. Your grandfather told you that when he was young, he and his playmates buried some old coins under the ground, thinking that that these coins will be valuable after several years. He also remembered that these coins were buried exactly 4 kilometers from Tree A (see map) and 5 kilometers from Tree B. Where could the coins possibly be located? E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 Discuss the terms related to circles (diameter chord, center, arc, chord, central angle, and inscribed angle). Let the students try to illustrate every term on the board based on the given definition. Let the pupils answer the following: F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment) 1. Determine whether each statement is true or false. a. Two radii always have the same length. b. Two chords always have the same length. c. All chords are diameters. d. All diameters are chords. e. All chords intersect at one point. f. A radius is not a chord. g. All diameters intersect at one point. 2. On circle O, a. Name each radius. b. Name each diameter. c. Name each chord. d. Name each central angle. 2 e. Name the arcs subtended by the central angles in (d) Ask: “What is a circle? What are the terms related to it?” G. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson H. Evaluating Learning A circle is the set of all points that are the same distance from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the center of the circle. A segment drawn from any point on the circle to the center is called a radius. A chord is a segment that connects any two points of a circle. A diameter is a chord that passes through the center of a circle. It is the longest chord of a circle and it is twice the length of a circle’s radius. A central angle is an angle whose vertex is on the circle’s center, and whose sides intersect the circle at two points. An arc is a portion of a circle determined by a central angle. Using a compass, draw a circle whose radius is 5 cm. Then draw the following objects. Write “impossible” if the object cannot be drawn. a. One chord measuring 2 cm. b. One chord measuring 10 cm. c. One chord measuring 12 cm. d. Three radii measuring 5 cm. e. One central angle measuring 90o. f. One central angle measuring 135o. g. One arc subtended by an angle that measures 35o. h. Three adjacent central angles, each measuring 100. V. Remarks VI. Reflection A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter 3 which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? 4