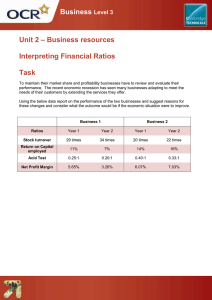
S trategic B usiness Analysis Phase 2 Group 2 Chayl Barola Diana Mae Gonzales Jayra Nica Napuli Mark Arthur Mantilla Genesel Mercado Jenith Tejada SLIDESMANIA.COM Agenda Revisit Financial Ratios 1 SLIDESMANIA.COM Investment Performance Measures 2 Key Performance Indicator Balanced Score Card 3 4 Gap Analysis 5 2 Industry • • SLIDESMANIA.COM An industry is a group of companies that are related based on their primary business activities. Because of this relatedness to each other, competition exist. Wellknown Rivalry SLIDESMANIA.COM FINANCIAL RATIOS • F inancial ratios are created with the use of numerical values taken from financial statements to gain meaningful information about a company. The numbers found on a company’s financial statements – balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement – are used to perform quantitative analysis and assess a company’s liquidity, leverage, growth, margins, profitability, rates of return, valuation, and more. SLIDESMANIA.COM Main Purpose of Financial Ratios 1. 2. SLIDESMANIA.COM T rack C ompany P erformance Make C omparative judgements regarding company performance Different Financial Ratios LIQUIDITY RATIOS Liquidity ratios -are financial ratios that measure a company’s ability to repay both short- and long-term obligations. Common liquidity ratios include the following: The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term liabilities with current assets: Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities, if high it means enough cash The acid-test ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term liabilities with quick assets: Acid-test ratio = Current assets – Inventories / Current liabilities, if high it means faster cash conversion cycle SLIDESMANIA.COM LIQUIDITY RATIOS The cash ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term liabilities with cash and cash equivalents: Cash ratio = Cash and Cash equivalents / Current Liabilities, if high it means greater amount of cash on hand while lower short-term liablity The operating cash flow ratio is a measure of the number of times a company can pay off current liabilities with the cash generated in a given period: Operating cash flow ratio = Operating cash flow / Current liabilities, if high, it means higher cash generated than what is normally needed to pay short-term liabilities. SLIDESMANIA.COM LEVERAGE RATIOS Leverage ratios- measure the amount of capital that comes from debt. In other words, leverage financial ratios are used to evaluate a company’s debt levels. Common leverage ratios include the following: The debt ratio measures the relative amount of a company’s assets that are provided from debt: Debt ratio = Total liabilities / Total assets, the higher the more risky The debt to equity ratio calculates the weight of total debt and financial liabilities against shareholders’ equity: Debt to equity ratio = Total liabilities / Shareholder’s equity, the higher the more risky SLIDESMANIA.COM LEVERAGE RATIOS The interest coverage ratio shows how easily a company can pay its interest expenses: Interest coverage ratio = Operating income / Interest expenses, the higher the healthier its finance The debt service coverage ratio reveals how easily a company can pay its debt obligations: Debt service coverage ratio = Operating income / Total debt service, means the higher the more reliable to settle debt by operating income SLIDESMANIA.COM LEVERAGE RATIOS Efficiency ratios, also known as activity financial ratios, are used to measure how well a company is utilizing its assets and resources. Common efficiency ratios include: The asset turnover ratio measures a company’s ability to generate sales from assets: Asset turnover ratio = Net sales / Average total assets, if higher, company is better performing The inventory turnover ratio measures how many times a company’s inventory is sold and replaced over a given period: Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / Average inventory, SLIDESMANIA.COM higher level indicates timely dispose of inventory LEVERAGE RATIOS The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how many times a company can turn receivables into cash over a given period: Receivables turnover ratio = Net credit sales / Average accounts receivable, the higher means the more efficient the company exercised its collections The days sales in inventory ratio measures the average number of days that a company holds on to inventory before selling it to customers. Days sales in inventory ratio = 365 days / Inventory turnover ratio, the higher the more inefficient the company is disposing its inventory SLIDESMANIA.COM PROFITABILITY RATIOS Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate income relative to revenue, balance sheet assets, operating costs, and equity. Common profitability financial ratios include the following: The gross margin ratio compares the gross profit of a company to its net sales to show how much profit a company makes after paying its cost of goods sold: Gross margin ratio = Gross profit / Net sales, higher means efficiency The operating margin ratio compares the operating income of a company to its net sales to determine operating efficiency: Operating margin ratio = Operating income / Net sales, if high it SLIDESMANIA.COM means higher revenue in each peso PROFITABILITY RATIOS The return on assets ratio measures how efficiently a company is using its assets to generate profit: Return on assets ratio = Net income / Total assets, if high it means more productive to generate revenue out of its balance sheet The return on equity ratio measures how efficiently a company is using its equity to generate profit: Return on equity ratio = Net income / Shareholder’s equity, if high it means more productive to generate revenue out of its existing assets SLIDESMANIA.COM MARKET VALUE RATIOS Market value ratios are used to evaluate the share price of a company’s stock. Common market value ratios include the following: The book value per share ratio calculates the per-share value of a company based on the equity available to shareholders: Book value per share ratio = (Shareholder’s equity – Preferred equity) / Total common shares outstanding, the higher, the more healthier to the company The dividend yield ratio measures the amount of dividends attributed to shareholders relative to the market value per share: Dividend yield ratio = Dividend per share / Share price, if high, the more preferable to shareholders for they can be distributed by bigger amount of share SLIDESMANIA.COM MARKET VALUE RATIOS The earnings per share ratio measures the amount of net income earned for each share outstanding: Earnings per share ratio = Net earnings / Total shares outstanding, higher means more earnings gained every share The price-earnings ratio compares a company’s share price to its earnings per share: Price-earnings ratio = Share price / Earnings per share, the higher, the more difficult to sell a company’s stock SLIDESMANIA.COM Investment P erformance Measure - helps select good investment as it provides ongoing information about how our investment is doing. SLIDESMANIA.COM Methods: SLIDESMANIA.COM 1. P ayback P eriod Method – the amount of time an investment takes to recover the full cost. 2. Average Annual Rate of Return – the average annual amount of cash flow generated over the life of an investment. 3. Net P resent Value – an investment criterion that consists of discounting future cash flows 4. Internal Rate of Return – allows you to evaluate an investment by expressing as a percentage P ayback P eriod Method shorter paybacks mean more attractive investment Disadvantage: cash generated from the project after the agreed maximum payback is not taken into account. Sometimes used as preliminary evaluation and then supplemented with other methods due to its limitations. SLIDESMANIA.COM Average Annual Rate of Return The higher the value of the average rate of return, the greater the return on the investment. Disadvantage: it does not take considerations of the potential effect of compounding asset earnings over many years. SLIDESMANIA.COM Return on Capital Employed - measures how efficiently a company is using its capital to generate profits SLIDESMANIA.COM E xample of Return on C apital E mployed SLIDESMANIA.COM SLIDESMANIA.COM Investment P erformance Measures 4 Methods of E valuating P rofitability of Investment 1. P ayback P ayment (P B P )Method 2. Average Annual Rate of Return (AARR) 3. Net P resent V alue (NP V) 4. Internal Rate of Return (IRR) SLIDESMANIA.COM Net P resent Value - an investment criterion consists of discounting future cash flows - bring the expected cash flows to the present, discounting them at a given rate - express a measure of a project’s profitability in absolute terms SLIDESMANIA.COM T he NP V is calculated according to the following formula Where: IO is the original investment; F1, are the cash flows in each period; n, is the number of periods; and k the discount rate SLIDESMANIA.COM Indication: 1. NP V > 0, updating the cashflows will generate profits 2. NPV=0, investment will not generate profits or losses 3. NPV< 0, investment project will generate losses SLIDESMANIA.COM How to C ompute NP V? E xample: An investor made an investment of $500 in property and gets back $570 the next year. If the rate of return is 10% . C alculate the net present value. Solution: Given: IO= $500 NPV= - $500+ $570/1+.10 k= 10% = - $500 + $570/1.1 F1= $570 = - $500 + $518.18 n= 1 NPV = $18.18 SLIDESMANIA.COM Internal Rate of Return - a discount rate that makes the NPV of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis - tool to evaluate an investment - expressed as a percentage - is the discount rate in the NPV formula SLIDESMANIA.COM T o calculate, we take the NP V to z ero: Indication: 1. Higher IRR- more desirable investment 2. Compare IRR with an opportunity cost (R) IRR> R - investment makes economic sense SLIDESMANIA.COM E xample: Suppose an Investor has the opportunity to invest in a new company. At the same time, a financial entity offer you a financial product with 4% interest. In order to make the decision to invest in the new company, it will have to calculate its IRR. Once the calculation is made, the IRR obtained amounts to 6.8% Would the investor prefer to accept the offer of a financial product with 40% interest? Or would the investor choose to invest in the new company? SLIDESMANIA.COM T he main difference between the 2 methods is the RE S UL T . NP V vs. IRR SLIDESMANIA.COM 1. NP V - gives result in absolute (net terms), in monetary units E x. E uros - indicates the value of the investment at present time. 2. IRR- gives us a relative measure, expressed as a percentage - indicate the rate at which the initial investment will be recovered. Return on Investment - generally defined as the ratio of net profit over the total cost of an investment - measures how effective your investments into your business are at generating income. - is a way to measure whether a business decision is paying off - help understand what’s working and not working in business so you can make changes - ROI is not static SLIDESMANIA.COM H ow do you calculate ROI? ROI- usually represented as a ratio or percentage - obtained by dividing the gain or net benefits earned from the investment by the cost of the investment. SLIDESMANIA.COM Example: If you spend 1,000 dollars per month to payper click (PPC) advertising and generate 2,000 dollars revenues directly for the campaign. ROI= = = SLIDESMANIA.COM Net profit earned Cost of investment 1000 1000 1 Multiply by 100 to find the percentage. 1(100) = 100% ;Thus, for every dollar you spend on PPC adds, you earn a dollar in return. ROI and TIME Example 2: If you’re making $3,000 per month, but working 60 hours per week on your business. (240 hrs a month) • ROI= $3,000/240 hrs. = $12.5 Thus, for every hour you’re working, you’re only earning $12.5 SLIDESMANIA.COM Knowing your returns on the investment of your time, you can make changes to your business model that allows you to earn greater revenue in less time. SLIDESMANIA.COM KPI K ey P erformance Indicator SLIDESMANIA.COM K ey P erformance Indicator KPI- is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an individual or a company is achieving its key objectives.These indicators are commonly used in every business or organization to measure the overall business performance over time. SLIDESMANIA.COM E xamples of K P Is: Sales KPIs 1.Number of New Contracts Signed Per Period 2. Dollar Value for New Contracts Signed Per Period 3. Number of Engaged Qualified Leads in Sales Funnel 4. Hours of Resources Spent on Sales Follow Up 5.Average Time for Conversion 6.Net Sales-Dollar or Percentage Growth SLIDESMANIA.COM F inancial K P Is 7. G rowth in Revenue 8.Net P rofit Margin 9.G ross P rofit Margin 10.Operational C ash F low 11. C urrent Accounts Receivables 12.Inventory T urnover SLIDESMANIA.COM C ustomer K P Is 13.Number of C ustomers Retained 14. P ercentage of Market S hare 15. Net P romotor S core 16. Average T icket/S upport Resolution T ime SLIDESMANIA.COM There is a saying that says “WHAT GETS MEASURED, GETS DONE” -ANONYMOUS SLIDESMANIA.COM S MART states that clear, attainable, strategic goals are the most effective way to create concrete milestones and metrics. S MART goals are the individual steps of a well-considered strategy to achieving larger objectives. SLIDESMANIA.COM SLIDESMANIA.COM T he B alanced S corecard ROBERT KAPLAN AND DAVID NORTON SLIDESMANIA.COM B AL ANC E D S C ORE C ARD T he balance scorecard is a strategic planning framework that companies use to: 1. assign priority to their products, projects, and services; 2. communicate about their targets or goals; and 3. plan their routine activities. SLIDESMANIA.COM Financial Perspective Customer Perspective Vision and Strategy T he B alanced S corecard anchored with 4 P erspectives. SLIDESMANIA.COM Organization Capacity Perspective Internal Process Perspective F inancial P erspective - it reflects the measurement on organization’s success financially - key indicators: return on investment, gross margin, net profit and such. - S teps taken: introducing new products & services and cutting down on the costs of doing business SLIDESMANIA.COM C ustomer P erspective - looking the organiz ation from the viewpoint of the customers. It monitors how the entity is providing value to its customers. - sample indicators: customer satisfaction and customer retention - strategies to focus: improving product quality, enhancing the customer shopping experience and such. SLIDESMANIA.COM Internal P rocess P erspective - views organiz ational performance through efficiency of business process - Indicators can be ordering time, preparation time, or machine set-up time - company formulate strategies that lead to the creation of new and improved ways of meeting the needs of customers. SLIDESMANIA.COM B usiness C apacity P erspective - views organiz ational performance through human capital. - personnel are required to demonstrate high performance in leadership, the entity’s culture,application of knowledge, and skill sets. SLIDESMANIA.COM - organiz ation should use the latest technology to automate activities and ensure a smooth flow of activities. Financial Perspective Customer Perspective Vision and Strategy Organization Capacity Perspective Internal Process Perspective Balanced Scorecard Template SLIDESMANIA.COM How do you spot what’s missing in your business strategy? SLIDESMANIA.COM Gap Analysis • Is the Process of comparing your actual business performance with your desired performance to see what’s missing. • It is a project management tool to help you identify from point A to point B. SLIDESMANIA.COM Benefits of using Gap Analysis • Brainstorming Strategies • Identify weak points • Measure actual resources SLIDESMANIA.COM SLIDESMANIA.COM T hank you! SLIDESMANIA.COM SLIDESMANIA.COM And tables to compare data. SLIDESMANIA.COM 1P 2P 3P D OG S 150,000 160,000 350,000 C AT S 99,000 150,000 255,000 E L E P HANT S 25,000 125,000 99,000 Here goes your map title. D ouble click on the desired country and change fill color Y ou can use maps to show your offices or markets. Or as charts, highlighting the countries and adding your data. SLIDESMANIA.COM Y ou can create your own infographics, using shapes and icons. SLIDESMANIA.COM Title B Title D L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Title A Title C L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Title F L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Title E L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Or you can copy / paste an infographic from our infographics templates. Add your timeline here. 20 00 20 05 20 1 0 20 1 5 20 20 T IT L E A T IT L E B T IT L E C T IT L E D T IT L E E L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. SLIDESMANIA.COM L orem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. SLIDESMANIA.COM It is also useful to show the evolution of historical events. 2019 Or the history of your topic. 2018 Y ou can use this slide to show milestones 2017 2016 Or use this timeline. J ust add your text and the related years. Add your title here. If you are presenting a website, an internet product or an app, you can use this laptop mockup to showcase it. J ust replace the screenshot with your own. SLIDESMANIA.COM Add your title here. If you are presenting a website, an internet product or an app, you can use this smartphone mockup to showcase it. J ust replace the screenshot with your own. SLIDESMANIA.COM SLIDESMANIA.COM